Report Overview
Global Energy Bar Market Highlights
Energy Bar Market Size:
Global Energy Bar Market, at a 6.13% CAGR, is anticipated to reach USD 6.894 billion in 2030 from USD 5.119 billion in 2025.
The global energy bar market represents a high-growth category within the wider functional food and snacking ecosystem, primarily catalyzed by a confluence of evolving consumer lifestyles and advanced nutritional science. This market has transitioned beyond its initial niche focus on endurance athletes to become a mainstream solution for on-the-go nutrition, meal replacement, and health-conscious snacking. The central challenge for the industry remains the delicate balance between delivering immediate convenience, maintaining nutritional integrity, and mitigating escalating ingredient costs, particularly in a globally interconnected commodity market. Analyzing the market through the inverted pyramid model reveals that core structural shifts—specifically, the demand for clean labels and the impact of geopolitical trade policies on supply chain stability—are the most critical forces reshaping the competitive and financial landscape.
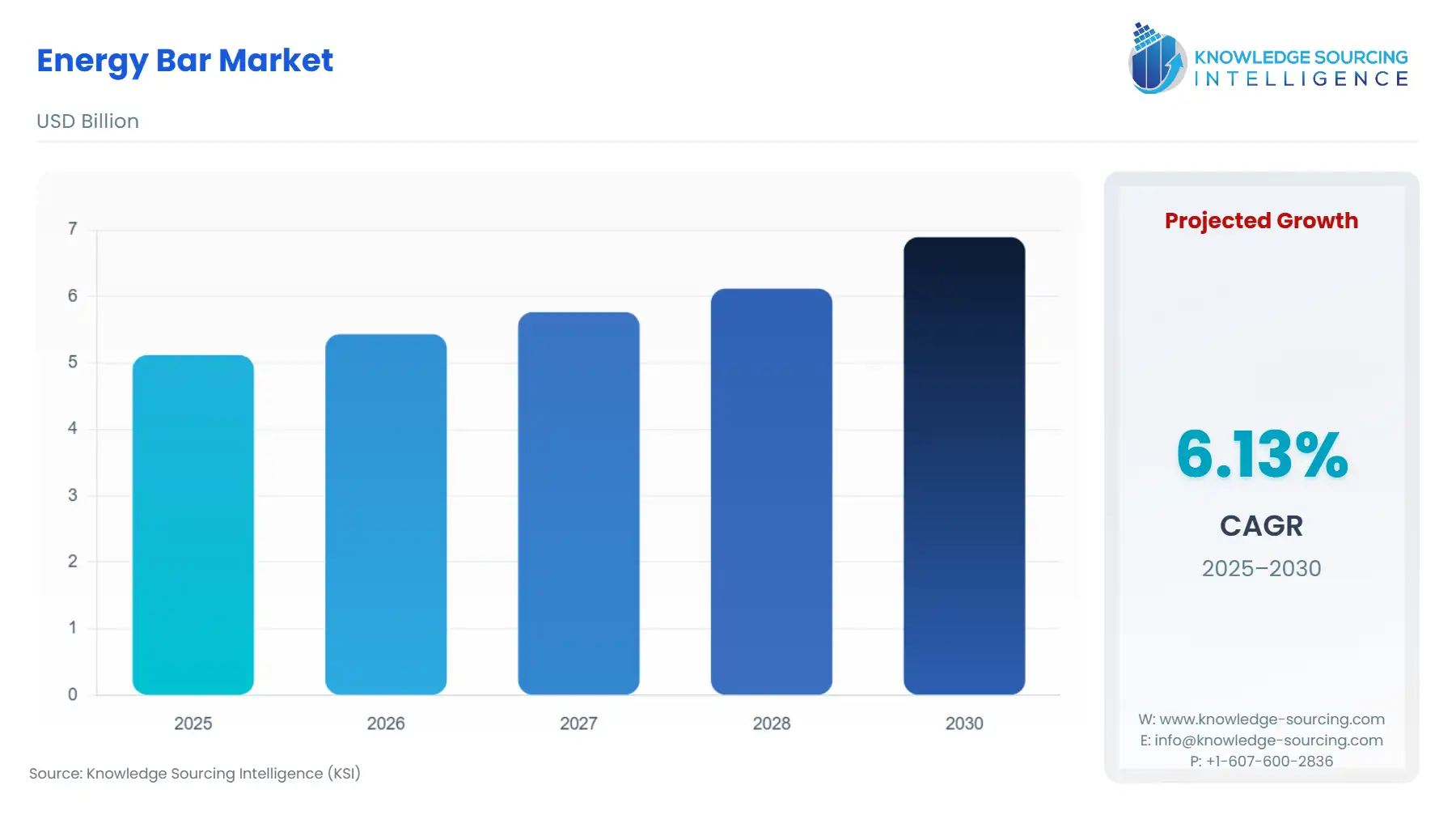
Global Energy Bar Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
The primary factors propelling market expansion are rooted in global sociological shifts and technological advancements in food science. The escalating demand for readily available, nutrient-dense meal alternatives, fueled by increasingly hectic consumer schedules and urbanization, directly increases the purchase frequency of energy bars, particularly among General Consumers. Concurrently, the growing global participation in fitness and wellness activities, ranging from marathon running to high-intensity interval training, creates an amplified need for specialized post-workout recovery and pre-activity fuel, directly driving demand for protein-fortified bars within the Athletes & Nutritionists segment. Furthermore, the sustained trend towards plant-based and vegan diets expands the total addressable market by forcing manufacturers to develop new lines based on pea, rice, and soy protein, thereby broadening product accessibility to a massive demographic of flexitarian and plant-forward consumers.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge facing the market is the sustained consumer aversion to products perceived as having excessive sugar content, which threatens the traditional carbohydrate-heavy formulation that initially defined the 'energy bar' category. This perception necessitates costly reformulation, particularly the replacement of sugar with high-intensity or natural, but often more expensive, sweeteners, which compresses manufacturer margins and creates a hurdle for mass-market pricing. Conversely, a substantial opportunity exists in leveraging functional ingredients beyond simple macronutrient balancing. The strategic inclusion of verifiable superfoods, adaptogens, probiotics, and fiber to address specific health concerns, such as gut health or stress management, allows premium positioning and directly unlocks demand from sophisticated, health-focused consumers willing to pay a premium for evidence-backed functional benefits.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The energy bar is a physical product directly dependent on global agricultural commodity markets. Key raw materials, including cocoa, whey protein isolate, and various nuts and seeds (such as almonds and peanuts), form the cost backbone of the product. Pricing dynamics are inherently volatile, influenced by weather-related yield fluctuations and, critically, by trade policy. The imposition of U.S. tariffs in 2025 on various imported food and agricultural products has demonstrably increased the cost of imported fruits and nuts by over 2400% in certain categories between April and July of 2025 compared to 2024, directly elevating input costs for U.S.-based manufacturers who rely on global sourcing. Although the U.S. granted tariff relief on select agricultural products in November 2025, the underlying volatility, coupled with retaliatory tariffs from countries like China on US tree nuts, peanut butter, and dried fruits, sustains a high-cost environment globally. This tariff impact forces manufacturers to either absorb the cost, leading to margin erosion, or pass it on to the consumer, which can negatively affect mass-market demand elasticity.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The energy bar supply chain is inherently complex and globalized, characterized by high-volume, low-margin agricultural sourcing integrated with specialized, high-cost manufacturing and packaging. The primary production hubs for key raw materials are geographically diverse: nuts and seeds are sourced heavily from the U.S. (California almonds), South America, and China; cocoa is primarily from West Africa; and functional proteins are produced in North America and Europe. The logistical complexity arises from managing the shelf-life constraints of natural ingredients and maintaining temperature-controlled transport for ingredients like chocolate coatings, especially across continents. This global dependence creates acute vulnerabilities to geopolitical instability, trade restrictions, and weather-related disruptions in key growing regions, demanding robust risk mitigation strategies such as dual sourcing and strategic commodity hedging to ensure consistent supply and product integrity.
Energy Bar Market Government Regulations:
Regulatory landscapes for energy bars are fragmented globally, primarily focusing on nutritional labeling and health claims. These regulations directly influence product formulation and consumer demand.
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
United States |
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Nutrition Facts Labeling Rule |
Mandates the presentation of calories, serving size, and nutrients. This regulation creates a direct headwind for products with high sugar or saturated fat, as clearer labeling allows the consumer to substitute towards bars that meet lower thresholds, thus decreasing demand for poorly formulated products. |
|
European Union |
European Commission Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 (Food Information to Consumers) |
Enforces mandatory allergen declarations, country of origin labeling, and the basis for health and nutrition claims. This increases the complexity of cross-border trade and formulation transparency, which, while raising compliance costs, increases consumer trust and demand for transparently labeled bars. |
|
United Kingdom |
Calorie Labelling (Out of Home Sector) (England) Regulations 2022 |
Mandates calorie counts on menus and packaging for large businesses. Though primarily targeting food service, this regulation's transparency ethos permeates packaged goods, increasing consumer scrutiny of bar calorie density and favoring lower-calorie, smaller-format products. |
|
Chile |
Law on Food Composition and Advertising (2016) |
Implements mandatory black octagonal warning labels for foods exceeding specific limits for calories, saturated fat, sugars, and sodium. This policy has been shown to cause a persistent 40% decrease in demand for labeled products which consumers previously believed were healthy, driving a sharp substitution effect toward unlabeled, reformulated bars. |
Energy Bar Market Segment Analysis:
- By Application: Athletes & Nutritionists Analysis
The Athletes & Nutritionists segment represents the premium, high-growth, and highly discerning end of the market, exhibiting demand inelasticity toward price when efficacy is proven. This group's demand is fundamentally driven by four non-negotiable criteria: macronutrient precision, functional efficacy, ingredient transparency, and certified compliance. The increasing sophistication of performance science compels athletes to seek out bars that function as precise nutritional tools, demanding high concentrations of quality protein (typically over 20 grams) for muscle protein synthesis, complex carbohydrates for glycogen replenishment, and low net sugar to avoid insulin spikes. This segment's demand is further amplified by the growth in "certified safe" sports nutrition, requiring third-party verification, such as from Informed-Sport, to ensure the absence of banned substances. This need for verification and precision inherently directs demand toward specialty brands and isolates mass-market players who cannot invest in complex supply chain validation protocols. Consequently, new product development focusing on bio-available whey and plant proteins, such as hydrolyzed pea protein, directly accelerates demand within this niche, positioning these bars as essential components of a calculated training regimen, rather than merely convenience snacks.
- By Ingredients: Nuts & Seeds Analysis
The Nuts & Seeds ingredient segment forms the core structural matrix and nutritional foundation for a vast majority of energy bars, acting as a crucial demand driver through the dual lens of texture and perceived health benefits. Consumer demand for clean label products favors the inherent "whole food" appeal of ingredients like almonds, cashews, peanuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds, viewing them as superior to synthetic fillers or highly processed cereal grains. This ingredient profile allows manufacturers to leverage consumer desire for healthy fats (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated) and dietary fiber, which provides sustained satiety—a key functional benefit that accelerates demand as consumers seek bars for meal replacement. Furthermore, nuts and seeds are foundational to both the protein-focused and the plant-based bar categories, making the segment critical for market innovation and diversification. However, this centrality exposes the segment to significant commodity price volatility and geopolitical trade constraints. The documented tariff increases on nuts and fruits, for instance, directly raise the production cost of the most popular bars, presenting a constant trade-off between maintaining premium ingredient quality and achieving a scalable retail price point.
Energy Bar Market Geographical Analysis:
- US Market Analysis
The US market represents the global nexus of energy bar innovation, characterized by a highly engaged and segmented consumer base. Local demand is critically driven by a dominant fitness culture, a widespread acceptance of functional foods, and the pervasive need for convenience stemming from demanding work schedules. The domestic market exhibits a strong bifurcation in demand: a premium segment aggressively seeks out high-protein, low-sugar, and certified-organic bars, compelling significant brand investment in clean-label sourcing and transparency. Conversely, the mass-market segment drives volume through convenience stores and supermarkets, where pricing and promotional activity dictate purchasing behavior. The impact of the FDA's enhanced nutritional labeling rules creates an inherent demand preference for bars with better 'headline' nutritionals (e.g., lower sugar count on the principal display panel), forcing a reformulation imperative across the industry.
- Brazil Market Analysis
The Brazilian market is defined by rapid urbanization and the emerging middle-class population that is increasingly adopting Western-style convenience consumption patterns. Demand for energy bars is accelerating, predominantly in metropolitan areas, fueled by a rising interest in physical aesthetics and a growing gym culture. Unlike mature markets, the Brazilian consumer places a high value on basic protein content and satiety, initially favoring conventional, value-driven brands over the premium, niche organic segment. Local factors impacting demand include high price sensitivity due to currency volatility and import logistics, making localized sourcing and domestic production a key competitive differentiator for multinational players seeking to expand their market footprint beyond the established South American snacking categories.
- Germany Market Analysis
The German market exhibits highly discerning, quality-driven demand, heavily influenced by strict domestic and EU food standards. Consumers prioritize locally sourced, certified-organic, and non-GMO ingredients, driving a strong preference for the Organic bar segment. Demand is primarily generated by active outdoor enthusiasts and health-conscious consumers who view energy bars as a precise nutritional complement to a balanced diet, rather than a mere snack replacement. The rigorous EU food information regulations, particularly concerning health claims and ingredient provenance, cultivate a high trust environment, which, in turn, boosts demand for brands that offer extensive supply chain transparency and verifiable ethical sourcing, creating a significant barrier to entry for brands that cannot meet these stringent local expectations.
- South Africa Market Analysis
The South African energy bar market is in an emergent growth phase, heavily concentrated in urban economic hubs like Johannesburg and Cape Town. Demand is primarily catalyzed by a rapidly growing health and wellness movement and the influence of international fitness trends, particularly among younger, aspirational consumers. The market exhibits a clear skew toward protein bars, reflecting a high local demand for performance nutrition. Key local constraints impacting demand include significant income inequality, which necessitates a strong price-to-value proposition for volume sales, and challenges in retail distribution infrastructure in less-urbanized areas, which limits the accessibility of niche, imported, or premium brands to a broader consumer base.
- Australia Market Analysis
The Australian market is characterized by a strong outdoor and sports culture, which drives sustained, high-volume demand for performance-focused bars. Local demand is highly receptive to innovation, particularly in the realm of functional ingredients and plant-based offerings, aligning with a prevalent national health-conscious mindset. A critical local factor is the consumer's high awareness and adoption of sustainable practices, which directly translates into a preference for energy bars utilizing compostable or low-impact packaging materials. This preference mandates a strategic investment in sustainable packaging technology for manufacturers, creating a market advantage for companies that can demonstrably reduce their environmental footprint while maintaining product quality and shelf-stability.
Energy Bar Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The global energy bar market is characterized by intense, multi-tiered competition, comprising large multinational food conglomerates with deep distribution networks alongside agile, niche, and highly specialized sports nutrition brands. Competition centers on three primary axes: superior ingredient sourcing to meet the clean label imperative, continuous product innovation in functional nutrition, and mastering direct-to-consumer (D2C) and e-commerce distribution to bypass traditional retail gatekeepers. The multinational presence ensures high market saturation and competitive pricing in the conventional segment, while the smaller players drive the market's premiumization trend through specialized and high-quality organic or niche health formulations.
Energy Bar Market Company Profiles
- Mars Incorporated
Mars Incorporated, primarily through its acquisition and subsequent portfolio integration, occupies a strong strategic position by leveraging globally recognized confectionery brands and translating them into the protein and energy bar format. This strategy, evidenced by recent collaborations, is built on the power of flavor, nostalgia, and brand familiarity to capture mass-market consumers who are transitioning from traditional snacking to performance-focused options. Mars's competitive advantage lies in its unparalleled global distribution network and deep supply chain expertise, allowing it to achieve significant economies of scale. Their key products in this space often feature protein-enhanced versions of iconic chocolate and caramel bars, providing a familiar taste profile while delivering the required macronutrient uplift, thereby attracting consumers on a foundational, enjoyment-led demand basis.
- Mondel?z International
Mondel?z International holds a powerful position, particularly in the premium health and wellness segment, significantly enhanced by its major strategic acquisitions. Their portfolio, notably featuring the CLIF Bar brand, addresses the sophisticated consumer who demands whole-food ingredients and a strong narrative of sustainability and authenticity. Mondel?z International's competitive strategy centers on integrating these high-growth niche brands into its broader global snacking ecosystem, utilizing its financial power for massive scale-up while retaining the acquired brand's core ethos and customer loyalty. Their strategic positioning emphasizes a focus on "snacking right," which directly captures the demand for nutritious, convenient meal replacements. The company also invests heavily in digital and AI-powered marketing capabilities, a move announced in 2024, to optimize consumer experiences and stay ahead of rapidly changing consumer tastes.
- General Mills Inc
General Mills Inc. maintains a significant market presence, particularly in the cereals and wholesome snacking categories, which serves as a foundational platform for their energy bar offerings. The company's key strategic positioning lies in bridging the gap between mainstream grocery shopping and the specialized nutrition aisle, leveraging existing brand equity and extensive supermarket/hypermarket distribution dominance. General Mills drives demand through continuous, accessible innovation, often adapting existing, recognizable cereal brands into the energy bar format. This approach appeals to a broader, family-oriented consumer base, focusing on fiber content and whole grains in their formulations. Their competitive advantage is rooted in supply chain efficiency and established retail relationships, which allow them to offer competitively priced bars with wide availability, ensuring a dominant volume presence in the conventional segment of the market.
Energy Bar Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 5.119 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 6.894 billion |
| Growth Rate | 6.13% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Type, Ingredients, Distribution Channel, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Energy Bar Market Segmentation:
- ENERGY BAR MARKET BY TYPE
- Organic
- Conventional
- ENERGY BAR MARKET BY INGREDIENTS
- Cereals & Grains
- Nuts & Seeds
- Dry Fruits
- Others
- ENERGY BAR MARKET BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS
- Online
- Offline
- Supermarket/ Hypermarket
- Convenience Stores
- ENERGY BAR MARKET BY APPLICATION
- Athelets & Nutritionnis
- General Consumers
- Others
- ENERGY BAR MARKET BY GEOGRAPHY
- North America
- USA
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Spain
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Thailand
- Taiwan
- Others
- North America