Report Overview
Global Microbial Identification Market Highlights
Microbial Identification Market Size:
The Microbial Identification Market is expected to grow from US$4.411 billion in 2025 to US$6.564 billion in 2030, at a CAGR of 8.28%.
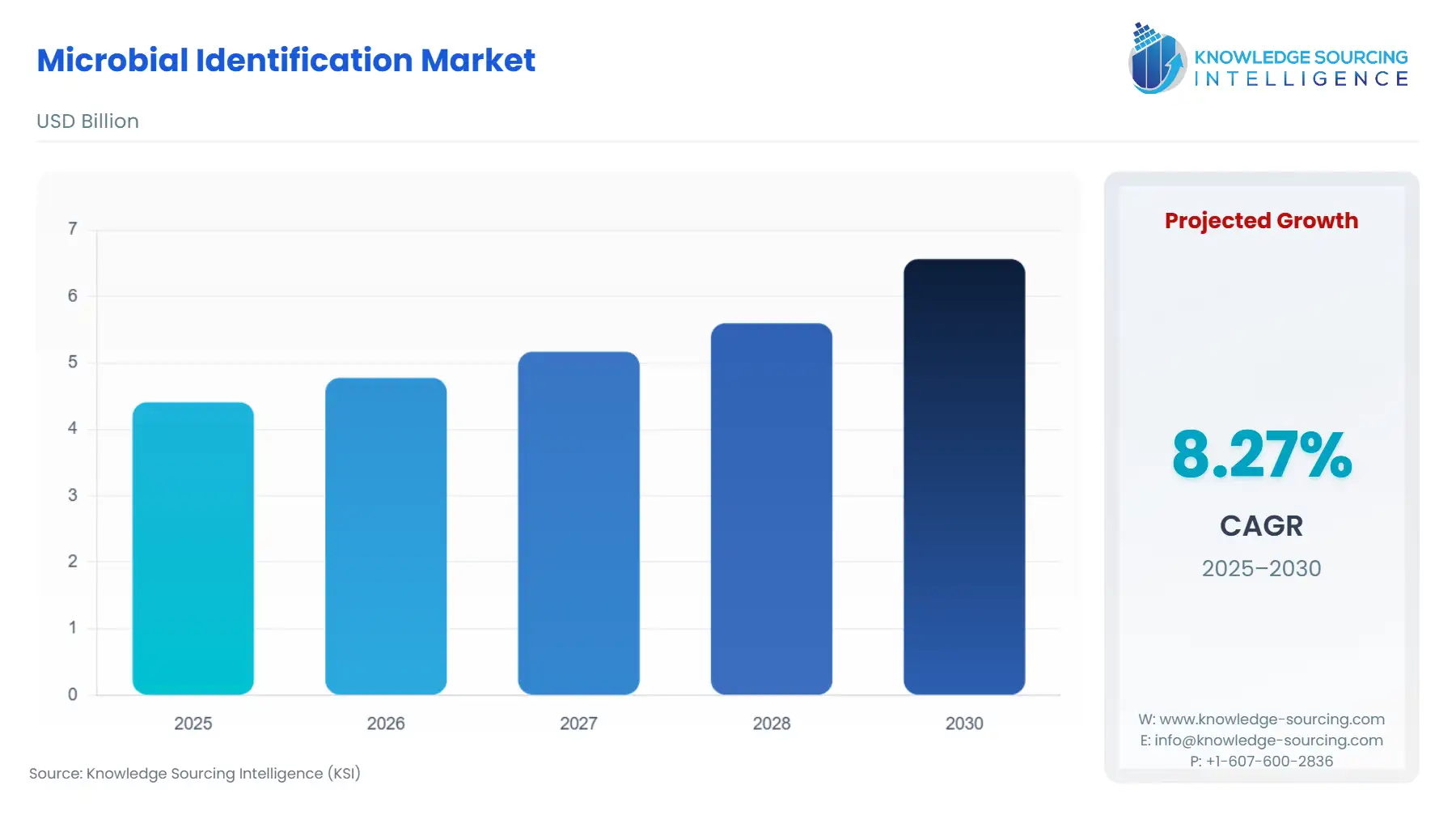
Global Microbial Identification Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Three verifiable forces elevate demand. Clinical and public-health systems require faster pathogen identification and antimicrobial-resistance tracking, pushing laboratories to procure NGS-based targeted panels and MALDI-TOF instruments that reduce diagnostic turnaround. Pharmaceutical manufacturers face stringent expectations for validated rapid microbiological methods, prompting procurement of fully documented instrument platforms, assay kits, and vendor-supported validation services. Consolidation among commercial laboratory networks, enabled by acquisitions such as Eurofins’ expansion of US microbiology capacity in 2024, increases throughput and drives recurring procurement of consumables, automated colony-handling systems, and workflow-integrated software.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The tariff landscape in the United States has a moderate but notable influence on the global microbial identification market, primarily through its impact on laboratory equipment, molecular diagnostic consumables, and high-precision analytical instruments. While the core microbial identification systems—such as MALDI-TOF mass spectrometers, next-generation sequencing (NGS) platforms, automated biochemical identification systems, and PCR analyzers—are often imported from manufacturing hubs in Europe and Asia, they are subject to U.S. import duties on scientific instruments, optical devices, biotechnology components, and certain electronic assemblies. Additionally, U.S. Section 301 tariffs on Chinese-origin laboratory consumables, reagents, plastics, and electronic subassemblies have increased procurement costs for American distributors and laboratories anywhere dependent on U.S.-based supply chains.
Key constraints include dependency on specialized reagents such as NGS chemistries and MALDI matrices, the regulatory burden of method validation at customer sites, and shortages of skilled microbiology personnel. These factors slow adoption when labs lack resources to perform validation internally. Conversely, demand accelerates for vendors offering turnkey validated systems, assay-specific documentation, and workflow automation that reduces training overhead. Centralized laboratory networks—strengthened by acquisitions and capacity expansions—create predictable demand for high-volume consumables and informatics licenses. This shift favors suppliers with integrated hardware-plus-reagent models and strong service portfolios.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
Microbial identification relies on physical products—NGS reagents, MALDI matrices, MALDI target plates, culture media, and specialized instrument components—justifying this section. Pricing is affected by proprietary chemistry, specialized plastics, cold-chain logistics, and concentrated OEM manufacturing. Volatility in reagent supply and tight capacity for MALDI plates raise procurement risk and encourage laboratories to secure long-term reagent agreements. Major vendors mitigate pricing exposure by offering bundled instrument-plus-consumable contracts with guaranteed replenishment schedules. These dynamics heighten demand for integrated supply solutions and shift purchasing from spot-buying to contracted consumables.
- Supply Chain Analysis
Production of instruments and reagents is concentrated in North America, Europe, and East Asia, with certain consumables produced by a limited number of OEMs. Cold-chain requirements for NGS reagents contribute to logistical complexity, while cross-border shipment of diagnostic kits demands strict regulatory documentation. At the laboratory level, episodic shortages of critical reagents drive greater reliance on regional contract laboratories and multi-supplier procurement strategies. Lab networks expand capacity to reduce import delays and ensure continuity, creating sustained demand for high-throughput consumables. Vendors that localize reagent production or provide validated alternatives benefit under these constraints.
Microbial Identification Market Government Regulations
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
United States |
FDA guidance on validation of microbiological methods; device oversight |
Increases demand for validated kits, instrument workflows, and vendor-supported regulatory documentation for pharmaceutical and clinical applications. |
|
European Union |
EMA and ICH Q4B microbiological testing expectations |
Creates demand for harmonized pharmacopoeia-compliant microbial identification systems and certified testing partners. |
|
Brazil |
ANVISA microbiological testing and surveillance frameworks |
Drives procurement of compliant assays and increases reliance on accredited testing laboratories capable of meeting national GMP microbiology requirements. |
Microbial Identification Market Segment Analysis
- By Application — Diagnostic Application
Diagnostic laboratories rely on speed, analytical precision, and traceable reporting, driving substantial demand for genotypic and proteomic platforms that surpass the capabilities of biochemical identification. MALDI-TOF systems and targeted NGS panels reduce diagnostic turnaround, enabling clinicians to make informed treatment decisions earlier—directly linking technology adoption with patient-care imperatives. These requirements create continual demand for validated reagent kits, software updates, and database subscriptions that maintain regulatory compliance and interoperability with national surveillance networks. Public-health laboratories further reinforce demand by requiring standardized outputs compatible with large-scale pathogen-tracking frameworks. As a result, purchasing priorities emphasize end-to-end solutions that minimize manual steps and reduce method-validation burdens. Vendors offering integrated wet-lab automation, curated microbial reference libraries, and compliant reporting tools benefit most within this segment.
- By End-User — Pharmaceutical
Pharmaceutical manufacturers adopt microbial identification platforms to meet stringent regulatory expectations for sterility testing, environmental monitoring, and product release. FDA and EMA frameworks require validated rapid microbiological methods, prompting companies to procure instruments, reagent kits, and vendor-supported validation services that can be documented during inspections. This environment elevates demand for suppliers offering qualification, method-transfer support, and traceability-ready informatics. Outsourcing trends reinforce this demand; Eurofins’ acquisition of Infinity Laboratories in 2024 demonstrates how testing networks scale microbiology capabilities that pharmaceutical companies cannot maintain cost-effectively in-house. When manufacturers outsource ID testing, demand shifts to standardized, high-throughput assay formats and stable consumables supply, benefiting vendors with reliable logistics and broad assay menus. End-to-end workflows that match GMP documentation needs have a competitive advantage.
Microbial Identification Market Geographical Analysis
- United States
Regulatory expectations for validated microbial methods and the scale of clinical demand create substantial procurement of NGS panels, MALDI-TOF systems, and FDA-aligned validation services. Pharmaceutical firms’ reliance on compliant RMM platforms reinforces sustained consumable usage.
- Brazil
ANVISA’s surveillance and GMP microbiology frameworks elevate demand for validated assays and accredited local laboratories. Limited domestic reagent production increases reliance on regional networks capable of rapid turnaround.
- Germany (Europe)
Strong hospital investment in MALDI-TOF and genomic systems and the requirement for pharmacopoeia-compliant release testing support high adoption of automated, validated ID workflows. The country’s established laboratory infrastructure sustains recurring consumable demand.
- United Arab Emirates
Healthcare investment programs and dependence on imported diagnostic products increase demand for partnerships with regional laboratory groups offering standardized microbial ID services. Procurement favors validated, turnkey workflows that reduce training requirements.
- China
A large clinical base, rapid expansion of domestic manufacturing, and alignment with international quality standards support broad demand for automated and cost-efficient microbial ID systems. Local production of selected consumables improves supply reliability and drives platform adoption.
Microbial Identification Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
The market includes integrated solution providers, global testing networks, and specialized sequencing or bioinformatics firms.
Eurofins Scientific maintains strong positioning through network expansion, including its 2024 acquisition of Infinity Laboratories, which increased US microbiology and pharmaceutical testing capacity. This expansion drives higher throughput and recurring demand for consumables and standardized assays.
Thermo Fisher Scientific provides integrated microbial identification workflows, including targeted NGS panels, validated chemistries, and software environments designed for regulated laboratory settings. Its emphasis on end-to-end solutions strengthens its position among clinical and pharmaceutical buyers requiring documented validation support.
Charles River Laboratories offers broad microbial detection and analytical services with established capabilities in manufacturing quality control, sterility assurance, and microbial identification. Its portfolio supports pharmaceutical clients requiring compliant and outsourced ID services.
Microbial Identification Market Developments
- September 2024 — Eurofins Scientific completed the acquisition of Infinity Laboratories, expanding its US microbiology and pharmaceutical testing network and increasing regional capacity for microbial identification services.
- 2024 — Thermo Fisher Scientific released updated microbial NGS workflow documentation and enhanced software support, strengthening validated sequencing-based microbial identification solutions in clinical and manufacturing environments.
Microbial Identification Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Microbial Identification Market Size in 2025 | US$4.411 billion |
| Microbial Identification Market Size in 2030 | US$6.564 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 8.28% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in the Microbial Identification Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Microbial Identification Market Segmentation:
- By Technique
- Genotypic Method
- Phenotypic Method
- By Components
- Consumables
- Instruments
- Software
- By Application
- Diagnostic Application
- Food and Beverages
- Pharmaceutical
- Other
- By Geography
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Others
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- France
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Australia
- South Korea
- Others
- North America