Report Overview
Global Model-Based Enterprise Market Highlights
Model-Based Enterprise Market Size:
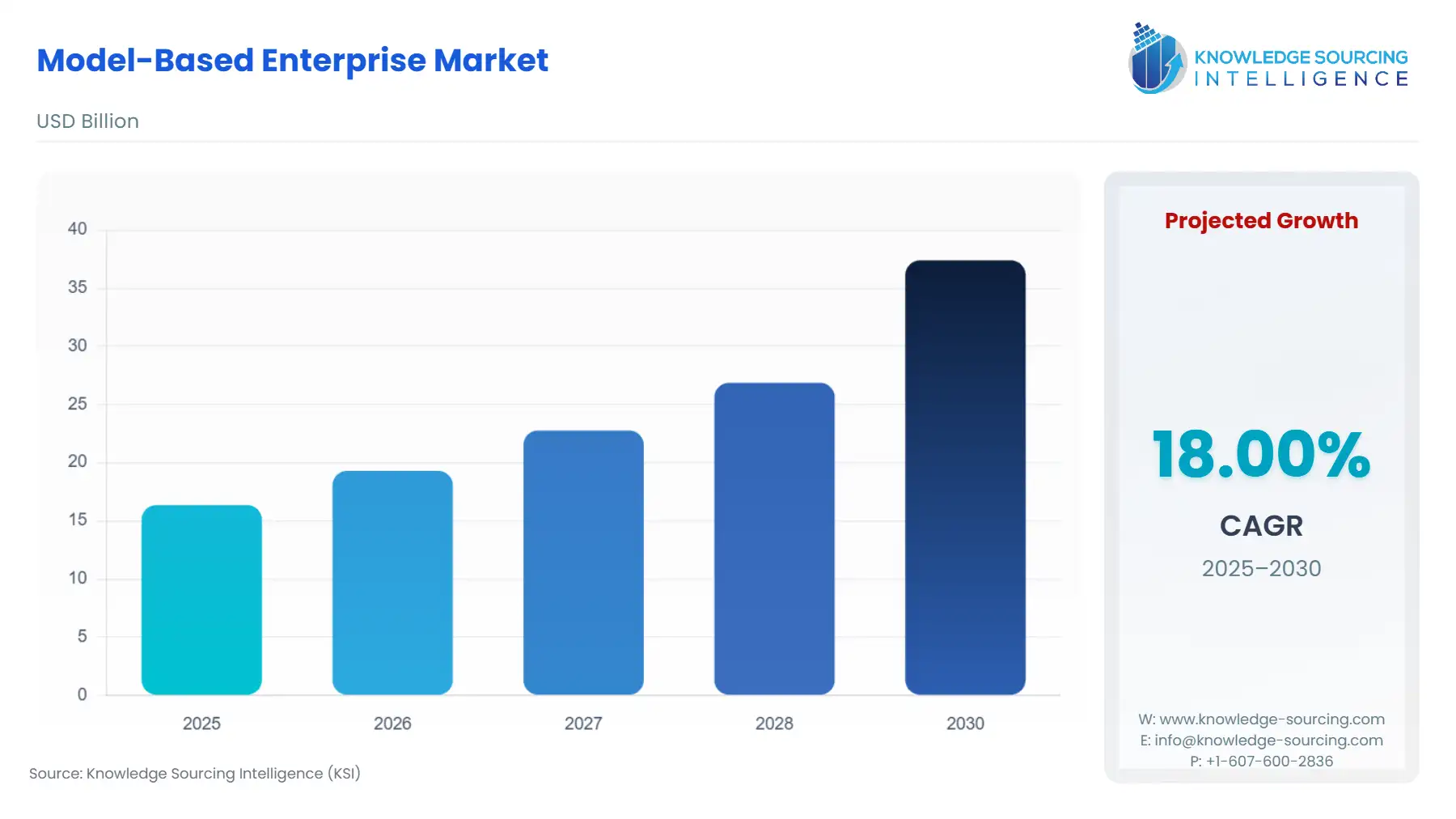
The Global Model-Based Enterprise Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18.3%, reaching a market size of USD 43.3 billion in 2031 from USD 18.7 billion in 2026.
Model-Based Enterprise Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Standards adoption and procurement mandates are the strongest lever for demand. U.S. DoD and allied defense programs increasingly require model-based technical data packages (MBTDP), forcing primes and their suppliers to invest in MBE-compliant toolchains. Standards organizations such as the DMSC, through its MBC 1.0 work, and QIF initiatives led by technical groups, lower the risk and cost of integrating model-based definitions across different PLM systems. Vendors’ introduction of cloud-native PLM platforms provides a lower-cost entry point for smaller suppliers, unlocking new demand. Finally, organizations implementing digital-thread or digital-twin strategies convert proof-of-concept MBE pilots into recurring enterprise service contracts, driving sustained demand for both software and managed services.
Challenges and Opportunities
For the Global Model-Based Enterprise market—where value is delivered primarily as software, services and hosted platforms—traditional customs duties have limited direct impact because intangible software and cross-border services are generally outside the scope of merchandise tariffs; only software supplied in a tangible medium and imported hardware (servers, workstations, networking equipment) are normally classed as dutiable goods under the Harmonized Tariff Schedule. Recent U.S. tariff actions and exclusions have, however, altered cost profiles for some hardware categories, meaning supplier decisions on server sourcing and on-premise infrastructure can affect implementation and hosting costs. Separately, export-control regimes (ITAR for defense-article technical data and EAR for dual-use technology and software) can restrict cross-border transfer of model-based technical data and tools where those tools or the data they contain relate to controlled defense or dual-use applications—this creates licensing and compliance burdens that materially affect demand from defense customers and their supply chains.
Major obstacles lie in data interoperability, entrenched drawing-centric processes, and governance and security complexities. Many suppliers continue to rely on 2D drawings, necessitating costly data-conversion projects and training initiatives. Confidentiality and cybersecurity requirements—especially in defense contexts—add further complexity and may slow adoption. On the opportunity side, mature standards (MBC 1.0 and QIF) and public technical guidance reduce integration risk and make large-scale enterprise rollouts more feasible. Vendors and system integrators can monetize this via migration services, training, and verification tools. There is also significant potential in verticalized solutions, such as model-based sustainment for aerospace or variant management for automotive, which offer higher-margin, repeatable service engagements.
Supply Chain Analysis
The MBE “supply chain” is predominantly software and service oriented. Core providers include major CAD/PLM vendors such as Siemens, Dassault Systèmes, PTC, and Autodesk, who supply authoring and lifecycle platforms. Complementary service providers—systems integrators and consultancies—offer model-conversion, data governance, training, and managed-hosting services. Key development centers are in North America, Western Europe, and India; engineering service delivery is concentrated near OEM clusters (for example, in the U.S. Midwest, Germany, and France). Significant logistical complexity arises from on-premises deployments at supplier locations, secure data exchanges in defense programs, and the need to certify suppliers’ model-based deliverables, thereby stimulating demand for secure cloud deployments and managed transformation services.
Government Regulations
Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
United States | NIST manufacturing programs & DoD digital-engineering guidance | Mandates from DoD and NIST create a baseline model-based data requirement in procurements, directly driving demand for certified MBE toolchains and supplier conversion services. |
International (Standards) | Digital Metrology Standards Consortium (DMSC) – MBC 1.0, QIF standards | The formal release of MBC 1.0 and QIF standards provides formal interoperability artifacts, reducing technical risk and encouraging cross-vendor enterprise adoption. |
Europe | OEM digital-engineering and platform strategies | Large European OEMs deploying cloud PLM (e.g., via Dassault or Siemens) stimulate regional demand for integrated model-based enterprise solutions and certified service partners. |
Model-Based Enterprise Market Segment Analysis
By Offering — Solution
Model-based enterprise solutions are the core purchased products: authoring tools (CAD), PLM systems, model-based inspection modules, and digital-thread orchestration. Demand arises primarily when enterprises—especially OEMs and primes—mandate model-based deliverables. For example, when a contract requires the authoritative 3D model with PMI for manufacturing or inspection, organizations must acquire and validate tools that support MBD workflows. Vendors that integrate model validation (e.g., QIF, MBC), automated publishing, and compliance checking reduce the effort and risk of deploying a digital thread. Cloud deployment options democratize access, enabling suppliers at tier-2 and tier-3 levels to adopt MBE without heavy upfront infrastructure. This drives recurring revenue through subscription-based PLM, migration, training, and managed-hosting services.
By Industry Vertical — Aerospace & Defense
Aerospace & Defense is the leading vertical for MBE demand, propelled by procurement policies and the long, regulated lifecycle of aerospace platforms. Defense agencies increasingly require model-based technical data packages (MBTDPs), including PMI and inspection characteristics, during acquisition. This translates to demand for authoring, PLM, validation, and conversion tools. Furthermore, the sustainment phase of aircraft and defense systems—especially for maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO)—creates ongoing demand: enterprises need digitally managed 3D models, inspection data, and configuration-management services. Suppliers that support the full lifecycle, from design to maintenance, win multi-year contracts. The complexity and risk of noncompliance encourage adoption of verified model-based workflows, making A&D an anchor market for MBE vendors.
Model-Based Enterprise Market Geographical Analysis
United States
In the U.S., DoD contracting is a prime driver. Defense procurement policies and the initiative for digital engineering (via NIST and the Defense Digital Service) push both primes and suppliers toward model-based deliverables. This procurement-driven demand ensures that MBE solutions remain part of major programs, especially in defense and aerospace. The large engineering software ecosystem in North America also supports integration and deployment capacity.
Brazil
Brazil has a growing aerospace supply chain and a developing manufacturing base. Adoption of model-based enterprise solutions is driven primarily by OEMs operating in global markets and by local suppliers engaged in export-oriented manufacturing. Demand is less prescriptive than in defense-led economies; uptake is driven more by cost savings, quality improvement, and exporting requirements than by formal procurement mandates.
Germany
Germany’s strong automotive and aerospace OEM clusters drive significant demand for MBE. Large manufacturers favor digital-engineering platforms from established vendors. The prevalence of high-precision manufacturing and regulated industries reinforces the need for validated, model-based workflows. Regional integrators and service providers address conversion and adoption challenges, particularly among tier-1 and tier-2 suppliers.
South Africa (MEA)
In South Africa and the broader Middle East & Africa region, MBE is emerging. Local manufacturing and defense sectors are increasingly investing in digital transformation, but adoption is constrained by skills shortages and limited certified integrators. Demand is often pilot-led, funded by public-private partnerships or modernization programs, and many companies rely on cloud-based solutions to circumvent infrastructure limitations.
China
China is witnessing rising MBE adoption as industrial manufacturers, automotive OEMs, and aerospace firms pursue digital-twin and model-based engineering strategies. Both global vendors and domestic integrators compete to deliver model-based PLM solutions tailored to local manufacturers. Demand is fueled by a growing export-oriented manufacturing base that must comply with global OEM standards, as well as by technology modernization initiatives within Chinese firms.
Model-Based Enterprise Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
The MBE market is highly competitive. Key players include Siemens AG, Dassault Systèmes SE, PTC Inc., Autodesk Inc., Aras Corporation, Anark Corporation, ANSYS, SAP, HCL Technologies, and General Electric. These companies differ by strength in core modeling, lifecycle management, standards support, cloud deployment, and ecosystem services.
Siemens AG: Through its NX and Xcelerator platform, Siemens offers strong model-based inspection and verification capabilities across its PLM suite. Its enterprise scale and engineering heritage position it well to support OEMs and suppliers in model-based deployments.
Dassault Systèmes SE: Leveraging its 3DEXPERIENCE platform, Dassault provides integrated cloud and on-premises PLM, enabling large OEMs to centralize model-based data and digital threads. Its platform strategy and services make it a go-to for companies with complex, regulated lifecycles.
PTC Inc.: PTC’s Creo suite (including cloud-native Creo+) supports authoring of MBD data, and its broad IoT and AR capabilities enable digital-thread applications. PTC integrates design-to-inspection workflows, positioning it to serve enterprises that need to unify engineering, manufacturing, and service.
These vendors compete not only on features, but also on certification, migration services, managed hosting, and long-term support. Service providers play a crucial role in facilitating adoption by converting legacy drawing-centric data, training teams, and ensuring compliance with model-based standards.
Model-Based Enterprise Market Developments
July 2024: Siemens released its NX Summer 2024 version, enhancing model-based inspection and MBD capabilities, thus strengthening its PLM offerings for manufacturing and quality workflows.
June 2024: Dassault Systèmes announced that Mahindra selected its 3DEXPERIENCE platform on cloud for its enterprise digital-engineering programs, reflecting strong demand for scalable MBE solutions outside traditional aerospace/defense markets.
February 2024: Anark Corporation rolled out version 4.5.82 of its software, advancing model-based publishing, collaboration, and validation capabilities, and meeting growing enterprise needs for digital thread orchestration.
Model-Based Enterprise Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 18.7 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 43.3 billion |
| Forecast Unit | Billion |
| Growth Rate | 18.3% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Offering, Deployment, Industry Vertical, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Model-Based Enterprise Market Segmentation:
By Offering
Solution
Service
By Deployment
On-premise
Cloud
By Industry Vertical
Aerospace & Defense
Automotive
Construction
Power & Energy
Retail
Food and Beverage
By Geography
North America
USA
Canada
Mexico
South America
Brazil
Argentina
Others
Europe
United Kingdom
Germany
France
Italy
Others
Middle East and Africa
Saudi Arabia
Israel
Others
Asia Pacific
China
Japan
India
South Korea
Indonesia
Thailand
Taiwan
Others