Report Overview
South Korea Nanotechnology Market Highlights
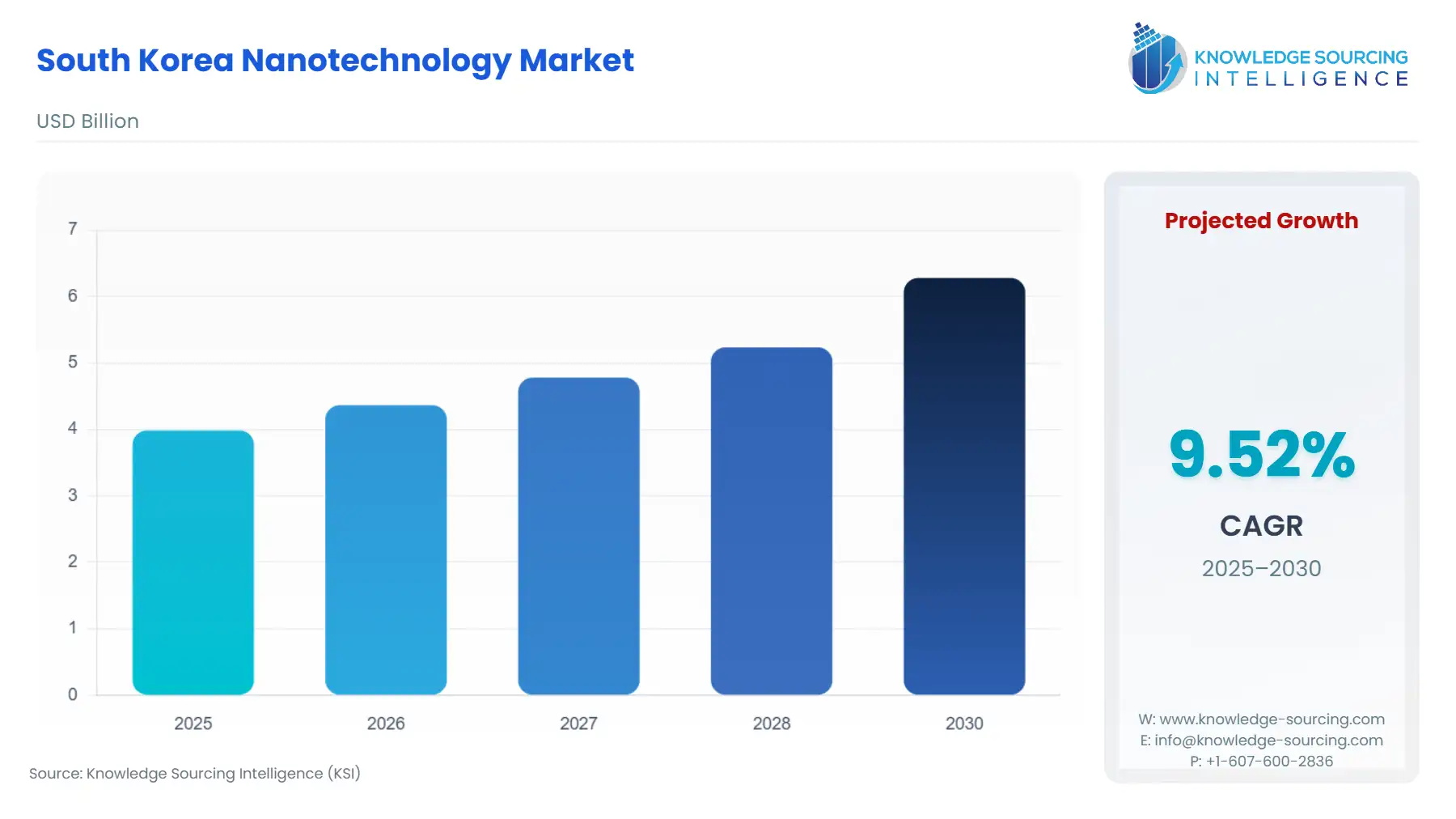
South Korea Nanotechnology Market Size:
The South Korea Nanotechnology Market is forecast to expand at a CAGR of 9.52%, attaining USD 6.28 billion in 2030 from USD 3.986 billion in 2025.
The South Korean Nanotechnology Market operates as a strategic imperative, not an ancillary sector, fundamentally embedded within the nation's export-oriented high-technology ecosystem. The government’s long-term planning, formalized through the Act on the Promotion of Nanotechnology, provides a clear, consistent framework that de-risks corporate investment.
This state-backed foundational support has allowed major industrial conglomerates to integrate nanotechnology directly into next-generation memory, display, and energy solutions, transitioning the market from a purely academic field to a high-volume industrial feedstock. The intense domestic competition and the global leadership position in capital-intensive sectors like semiconductors necessitate continuous, performance-driven innovation at the nanoscale, directly correlating R&D expenditure with commercial output.
South Korea Nanotechnology Market Growth Drivers:
The formidable expansion of the domestic semiconductor manufacturing base serves as the paramount driver, establishing a non-negotiable demand for ultra-precise Nanodevices and high-purity Nanomaterials. The race for superior memory capacity and processing speed, particularly for High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) used in Artificial Intelligence (AI) data centers, pushes the limits of lithography and stacking technology. This shift directly mandates the procurement of advanced Nanodevices for sub-10nm scale metrology, defect review, and fine-tuning, as exemplified by the need for precise Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) systems capable of sub-angstrom surface roughness measurement. Furthermore, the push for advanced chip packaging, which integrates multiple chips into a single, high-performance unit, exponentially increases the demand for specialized Nanocomposites and ultra-thin film materials for improved thermal management and power efficiency.
- Challenges and Opportunities:
The primary challenge is the capital and talent intensity inherent in nanoscale innovation. Sustaining a high level of technological advancement requires not only massive, continuous investment in R&D infrastructure but also a constant supply of highly specialized human capital. This constraint elevates operational costs and raises the barrier to entry for smaller firms. Concurrently, a significant opportunity lies in the convergence of nanotechnology with the burgeoning Biotechnology and Healthcare sectors. The focus on developing new medical diagnostics and drug delivery systems, leveraging advancements like biological Nanosensors and targeted Nanoparticles, presents a vast, untapped commercial market. Government initiatives, such as the establishment of specialized facilities like the National NanoFab Center (NNFC), provide a crucial infrastructure for start-ups, mitigating the capital burden and accelerating the commercialization timeline for medical applications, thereby creating new avenues of demand outside the electronics core.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis:
Nanotechnology involves the production and use of physical products, primarily Nanomaterials, necessitating a Raw Material and Pricing Analysis. The pricing dynamics of the market are critically tied to the purity and process-ability of precursor materials, such as specific metal oxides for nanoparticles or high-grade carbon sources for Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene. Raw material costs are often secondary to the sophisticated production and functionalization costs. The value driver shifts from the cost of the bulk precursor to the high capital expenditure required for precise synthesis equipment and the proprietary intellectual property required for consistent, high-volume production of functionalized nanomaterials. Pricing is premium-driven, reflecting the nanoscale functional superiority and the consistency required by high-reliability end-users like Samsung and SK Hynix.
- Supply Chain Analysis:
The Nanotechnology supply chain is complex, characterized by global dependencies for precursor chemicals and specialized equipment, even within a highly capable domestic market like South Korea. Key production hubs for high-end Nanodevices (e.g., advanced AFM systems) are often concentrated in specialized global manufacturers. Korea maintains a high dependency on foreign sources for certain essential components and sophisticated production tools. Logistical complexity arises from the stringent quality control and contamination risks associated with transporting ultra-high purity materials. The domestic supply chain, supported by government efforts to enhance self-sufficiency in materials, components, and equipment, concentrates on the final-stage manufacturing and integration of Nanomaterials, such as advanced coatings, into finished products like displays, batteries, and semiconductors.
South Korea Nanotechnology Market Government Regulations:
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| South Korea | Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) | MSIT orchestrates the National Comprehensive Development Plan of Nanotechnology, which directly fuels R&D funding and infrastructure development, systematically increasing market supply and commercialization readiness. |
| South Korea | Act on the Promotion of Nanotechnology | This act institutionalizes a long-term R&D investment strategy and mandates the establishment of NanoFab Centers, thereby lowering the initial capital barrier for R&D and encouraging the demand for advanced Nanodevices by providing shared access. |
| South Korea | Ministry of Environment / Ministry of Employment and Labor (Occupational Health) | Regulations concerning the Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) risks of Nanomaterials (e.g., nanoparticles) impose strict compliance and testing requirements, increasing material production costs but simultaneously driving demand for safer, encapsulated, or inherently less toxic Nanomaterials. |
South Korea Nanotechnology Market Segment Analysis:
- By Technology: Nanodevices The Nanodevices segment’s growth is directly correlated with the continued miniaturization imperative across the domestic electronics and semiconductor industries. As feature sizes shrink to the sub-10nm range, traditional macro-scale inspection and fabrication tools become obsolete. The intense competition in memory fabrication necessitates new metrology tools for precise measurement of critical dimensions and rapid detection of minute defects, which are only possible with advanced Nanodevices like sophisticated Atomic Force Microscopes (AFMs) and Nanoscale Infrared Spectrometers. The introduction of 3D-stacked memory (e.g., HBM) requires non-destructive internal analysis, directly driving demand for high-resolution nanomechanical test instruments to ensure mechanical integrity at the layer interface. The transition to mass production of next-generation chips means South Korean foundries are now the world’s most arduous consumers of these ultra-precision Nanodevices, translating every new technological hurdle into a specific equipment procurement cycle.
- By End-User: Electronics The Electronics sector, specifically consumer electronics and semiconductor manufacturing, acts as the foundational off-taker, generating high-volume, high-value demand for nanotechnology products. This necessity is not generic growth but a direct consequence of product roadmaps focusing on superior performance metrics. For example, the pervasive integration of flexible and foldable displays in flagship smartphones drives the demand for flexible, transparent electrode materials based on Graphene and Nanowires. The push for extended battery life and faster charging in all consumer devices, from wearables to electric vehicles, simultaneously creates immense demand for advanced Nanomaterials (e.g., silicon-based Nanoparticles for high-capacity anodes) to improve energy density. Therefore, the core growth driver in the Electronics end-user segment is the cyclical introduction of next-generation consumer and enterprise hardware that mandates nanoscale innovation to achieve performance differentiation.
South Korea Nanotechnology Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The competitive landscape is dominated by large, vertically integrated Korean conglomerates (Chaebols) and a specialized ecosystem of spin-off or SME firms focused on specific nanomaterial synthesis or nanodevice components. The strategic positioning is largely defined by the degree of control over the nanoscale manufacturing process.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.: Samsung’s nanotechnology strategy is defensive and highly integrated, focusing on securing a technological edge in its core businesses: semiconductors and displays. Its positioning centers on advanced nanoscale process technology, exemplified by its use of Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) lithography for sub-5nm chip production. Key products and services include High-K dielectric thin films deposited at the nanoscale and proprietary manufacturing processes for High Bandwidth Memory (HBM), which relies heavily on advanced material science at the nanoscale to manage thermal and electrical challenges.
- SK Hynix Inc.: SK Hynix focuses its nanotechnology efforts on memory chip performance and density, directly addressing the exploding demand from AI and data centers. The company's strategic positioning is anchored in the development and mass production of advanced HBM, which uses through-silicon via (TSV) technology—a nanotech application for vertical stacking—to achieve unprecedented bandwidth. Its key product development includes the integration of advanced Nanomaterials to increase cell capacity and reliability in its DRAM and NAND flash products.
South Korea Nanotechnology Market Developments:
- October 2025: Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix signed preliminary agreements with OpenAI to supply a significant volume of high-performance DRAM, including HBM, for the company’s Stargate project. This development signals a direct, massive injection of demand for advanced Nanomaterials and the ultra-precise Nanodevices required for the production of these high-value-added AI semiconductors.
- September 2025: Finland-based nanomedicine company Nanoform announced a significant expansion of its commercial presence in Asia by signing a distributor agreement with Ageing & Life Science Corp. (A&LS Pharma), a South Korean pharmaceutical products and services distribution company. Under this partnership, A&LS Pharma will act as Nanoform's local representative, providing South Korean pharmaceutical and biotech innovators access to Nanoform's proprietary nanoparticle engineering services. These services are designed to improve the bioavailability of small and large molecules, enhance drug performance, and accelerate the development of next-generation therapies. This move is critical for bringing advanced nanotech drug development capabilities directly into South Korea's rapidly growing and government-supported life science sector.
South Korea Nanotechnology Market Sope:
South Korea Nanotechnology Market Segmentation:
- BY TECHNOLOGY
- Nanodevices
- Nanomanipulators
- Nanomechanical Test Instruments
- Nanoscale Infrared Spectrometers
- Others
- Nanosensors
- Optical Nanosensors
- Biological Nanosensors
- Chemical Nanosensors
- Physical Nanosensors
- Others
- Nanotools
- Nanomaterials
- Fullerenes
- Nanoparticles
- Nanoshells
- Carbon-based Nanotubes
- Nanocomposites
- Graphene
- Quantum Dots
- Nanocomposites
- Other Nanotechnologies
- Nanodevices
- BY APPLICATION
- Aerospace & Defense
- Energy
- Electronics
- Chemical Manufacturing
- Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals
- Automobiles
- Biotechnology
- IT & Telecom
- Textile
- Others
- BY END-USER
- Electronics
- Cosmetics
- Pharmaceutical
- Biotechnology
- Others