Top 10 Cybersecurity Applications

Cybersecurity is a comprehensive discipline aimed at safeguarding computer systems, networks, and data against malicious attacks and unauthorized access. This multifaceted field encompasses a diverse array of technologies, processes, and practices meticulously designed to guarantee the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information. The paramount objective of cybersecurity is to fortify digital infrastructure and prevent the exploitation of vulnerabilities that could compromise the security of individuals, organizations, or even nations. Through a continuous and dynamic approach, cybersecurity professionals employ cutting-edge tools and strategies to detect, respond to, and mitigate evolving cyber threats, thus fortifying the resilience of the digital landscape in an ever-evolving technological era. As per the latest report released by the Press Information Bureau, the incidents of cybercrimes reported in India have been increasing steadily. The report highlights the alarming rise in various types of online criminal activities such as phishing scams, identity theft, cyberbullying, online financial frauds, ransomware attacks, and hacking attempts.
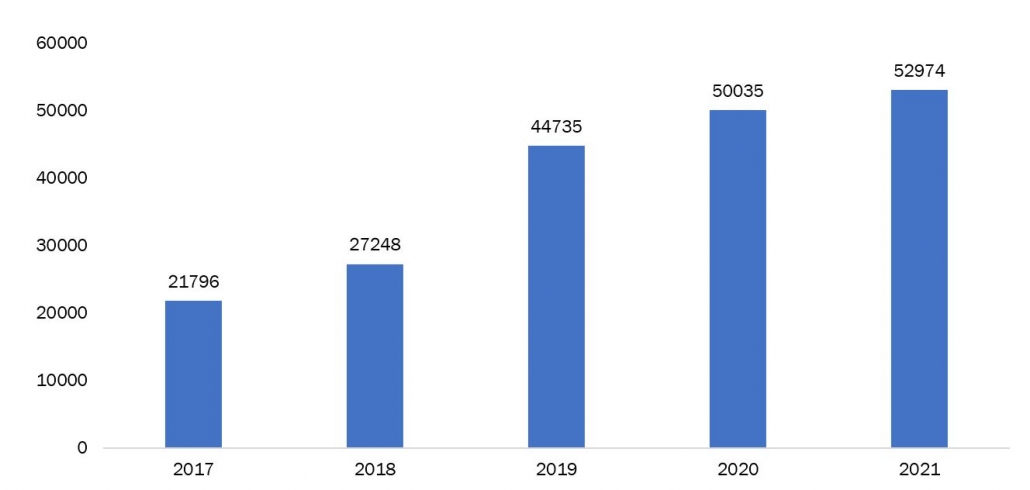 Source: Press Information Bureau, Government of India
The top 10 applications of cybersecurity are mentioned below:
Network Security Surveillance
Network security surveillance stands as a vital sentinel in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity. Its purpose is unwavering: to continuously monitor and safeguard a network from misuse, unauthorized access, and malicious alterations. This vigilant practice plays a crucial role in safeguarding data transfers, shielding them from the prying eyes and opportunistic actions of cybercriminals. Equipped with the latest threat intelligence, network security monitoring tools act as digital detectives, meticulously scanning networks for suspicious activity. They tirelessly analyze every byte of data, uncovering anomalies and identifying potential threats before they can wreak havoc. This proactive approach allows organizations to anticipate both authorized and unauthorized user actions, significantly reducing the time it takes to respond to security breaches.
Identification and Access Management (IAM)
In the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape, Identity and Access Management (IAM) stands as a cornerstone, overseeing the digital identities and access controls that safeguard critical corporate information. IAM operates within a framework of policies, processes, and technologies, meticulously designed to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to specific resources, with appropriate justification, for a limited duration. These solutions play a pivotal role in enhancing overall security and mitigating potential risks by employing a multi-pronged approach:
User Identification & Authentication: IAM systems meticulously identify and verify users before granting access, ensuring that only authorized individuals can enter the digital fortress.
Authorization Control: Access privileges are meticulously assigned based on each user's role and responsibilities, preventing unauthorized individuals from reaching sensitive data or performing restricted actions.
User Provisioning & Lifecycle Management: IAM solutions efficiently automate user onboarding and grant access privileges based on their roles. This ensures users have the precise level of access required to fulfill their duties.
Activity Monitoring & Threat Detection: Continuous monitoring of user activities allows for the identification and prevention of potential security breaches or unauthorized access attempts.
Software Security
In today's interconnected world, software security has emerged as a critical pillar of cybersecurity, safeguarding software applications and digital solutions from malicious actors. Developers play a pivotal role in this endeavor, seamlessly integrating security practices into the software development lifecycle (SDLC) and testing procedures. This meticulous approach ensures that digital solutions are built with robust defenses, enabling them to withstand and effectively respond to cyberattacks. By prioritizing software security, developers contribute to a safer digital environment, fostering trust and mitigating the potential harm caused by data breaches and system disruptions.
Source: Press Information Bureau, Government of India
The top 10 applications of cybersecurity are mentioned below:
Network Security Surveillance
Network security surveillance stands as a vital sentinel in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity. Its purpose is unwavering: to continuously monitor and safeguard a network from misuse, unauthorized access, and malicious alterations. This vigilant practice plays a crucial role in safeguarding data transfers, shielding them from the prying eyes and opportunistic actions of cybercriminals. Equipped with the latest threat intelligence, network security monitoring tools act as digital detectives, meticulously scanning networks for suspicious activity. They tirelessly analyze every byte of data, uncovering anomalies and identifying potential threats before they can wreak havoc. This proactive approach allows organizations to anticipate both authorized and unauthorized user actions, significantly reducing the time it takes to respond to security breaches.
Identification and Access Management (IAM)
In the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape, Identity and Access Management (IAM) stands as a cornerstone, overseeing the digital identities and access controls that safeguard critical corporate information. IAM operates within a framework of policies, processes, and technologies, meticulously designed to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to specific resources, with appropriate justification, for a limited duration. These solutions play a pivotal role in enhancing overall security and mitigating potential risks by employing a multi-pronged approach:
User Identification & Authentication: IAM systems meticulously identify and verify users before granting access, ensuring that only authorized individuals can enter the digital fortress.
Authorization Control: Access privileges are meticulously assigned based on each user's role and responsibilities, preventing unauthorized individuals from reaching sensitive data or performing restricted actions.
User Provisioning & Lifecycle Management: IAM solutions efficiently automate user onboarding and grant access privileges based on their roles. This ensures users have the precise level of access required to fulfill their duties.
Activity Monitoring & Threat Detection: Continuous monitoring of user activities allows for the identification and prevention of potential security breaches or unauthorized access attempts.
Software Security
In today's interconnected world, software security has emerged as a critical pillar of cybersecurity, safeguarding software applications and digital solutions from malicious actors. Developers play a pivotal role in this endeavor, seamlessly integrating security practices into the software development lifecycle (SDLC) and testing procedures. This meticulous approach ensures that digital solutions are built with robust defenses, enabling them to withstand and effectively respond to cyberattacks. By prioritizing software security, developers contribute to a safer digital environment, fostering trust and mitigating the potential harm caused by data breaches and system disruptions.
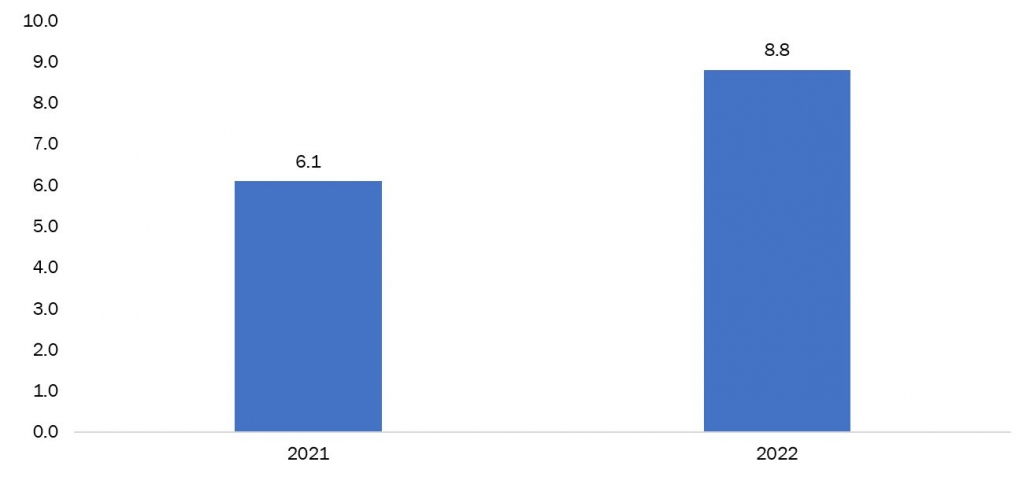 Source: Federal Trade Commission
US consumers lost nearly $8.8 billion to fraud in 2022, up over 30% YoY. Investment and imposter scams accounted for more than $6.4 billion of the losses. The FTC received 2.4 million fraud reports with imposter scams being the most commonly reported.
Malware Detection and Prevention
In the increasingly interconnected world, protecting our digital systems from malicious actors is paramount. This is where malware detection and prevention come into play, acting as essential shields against harmful software designed to wreak havoc on our devices and data. Malware, short for malicious software, encompasses a diverse range of programs with nefarious intent. From stealing sensitive information and hijacking systems to disrupting operations and compromising privacy, the consequences of malware infections can be devastating. Fortunately, a robust arsenal of tools and techniques exists to combat this threat. Malware detection systems utilize sophisticated algorithms to analyze code and identify suspicious behavior.
Threat Hunting
Threat hunting, a cornerstone of effective defense, goes beyond passively monitoring for threats and actively seeks out hidden dangers lurking within networks, systems, and devices. Unlike automated security tools and the initial layers of security operations centers (SOCs), threat hunting is human-driven. This involves skilled professionals employing a unique blend of intuition, strategic thinking, ethical decision-making, and creative problem-solving to uncover potential threats. Through meticulous analysis of data and usage patterns, these "cyber hunters" identify anomalies and suspicious activities that might otherwise go unnoticed. Crucially, threat hunting is distinct from threat detection. While the latter focuses on passively monitoring for known threats, threat hunting takes a preemptive stance, actively searching for potential threats that may not yet be identified.
Security Compliance
Cybersecurity compliance transcends mere adherence to legal mandates. It's the active implementation of risk management systems incorporating security regulations and standards to safeguard information's integrity, availability, and confidentiality. This goes beyond ticking boxes on government checklists; it's a proactive approach to fortifying organizations against a constantly evolving landscape of cyber threats. Compliance serves as a powerful shield against digital attacks like DDoS, phishing, malware, and ransomware. By aligning with established security frameworks, organizations build robust defenses that minimize vulnerabilities and bolster their resilience against cyber intrusions. This proactive stance not only mitigates potential financial and reputational damage from breaches but also fosters trust with stakeholders, including customers, partners, and investors. Cybersecurity compliance provides a structured path to securing this valuable asset, ensuring its integrity and availability for critical operations. By prioritizing compliance, organizations can proactively address security risks, bolstering their digital infrastructure and fostering a culture of security awareness within their workforce. As per the Federal Trade Commission, cases of Identity theft are on the rise with maximum related to Credit card frauds, increasing the incidence of cybercrimes.
Source: Federal Trade Commission
US consumers lost nearly $8.8 billion to fraud in 2022, up over 30% YoY. Investment and imposter scams accounted for more than $6.4 billion of the losses. The FTC received 2.4 million fraud reports with imposter scams being the most commonly reported.
Malware Detection and Prevention
In the increasingly interconnected world, protecting our digital systems from malicious actors is paramount. This is where malware detection and prevention come into play, acting as essential shields against harmful software designed to wreak havoc on our devices and data. Malware, short for malicious software, encompasses a diverse range of programs with nefarious intent. From stealing sensitive information and hijacking systems to disrupting operations and compromising privacy, the consequences of malware infections can be devastating. Fortunately, a robust arsenal of tools and techniques exists to combat this threat. Malware detection systems utilize sophisticated algorithms to analyze code and identify suspicious behavior.
Threat Hunting
Threat hunting, a cornerstone of effective defense, goes beyond passively monitoring for threats and actively seeks out hidden dangers lurking within networks, systems, and devices. Unlike automated security tools and the initial layers of security operations centers (SOCs), threat hunting is human-driven. This involves skilled professionals employing a unique blend of intuition, strategic thinking, ethical decision-making, and creative problem-solving to uncover potential threats. Through meticulous analysis of data and usage patterns, these "cyber hunters" identify anomalies and suspicious activities that might otherwise go unnoticed. Crucially, threat hunting is distinct from threat detection. While the latter focuses on passively monitoring for known threats, threat hunting takes a preemptive stance, actively searching for potential threats that may not yet be identified.
Security Compliance
Cybersecurity compliance transcends mere adherence to legal mandates. It's the active implementation of risk management systems incorporating security regulations and standards to safeguard information's integrity, availability, and confidentiality. This goes beyond ticking boxes on government checklists; it's a proactive approach to fortifying organizations against a constantly evolving landscape of cyber threats. Compliance serves as a powerful shield against digital attacks like DDoS, phishing, malware, and ransomware. By aligning with established security frameworks, organizations build robust defenses that minimize vulnerabilities and bolster their resilience against cyber intrusions. This proactive stance not only mitigates potential financial and reputational damage from breaches but also fosters trust with stakeholders, including customers, partners, and investors. Cybersecurity compliance provides a structured path to securing this valuable asset, ensuring its integrity and availability for critical operations. By prioritizing compliance, organizations can proactively address security risks, bolstering their digital infrastructure and fostering a culture of security awareness within their workforce. As per the Federal Trade Commission, cases of Identity theft are on the rise with maximum related to Credit card frauds, increasing the incidence of cybercrimes.
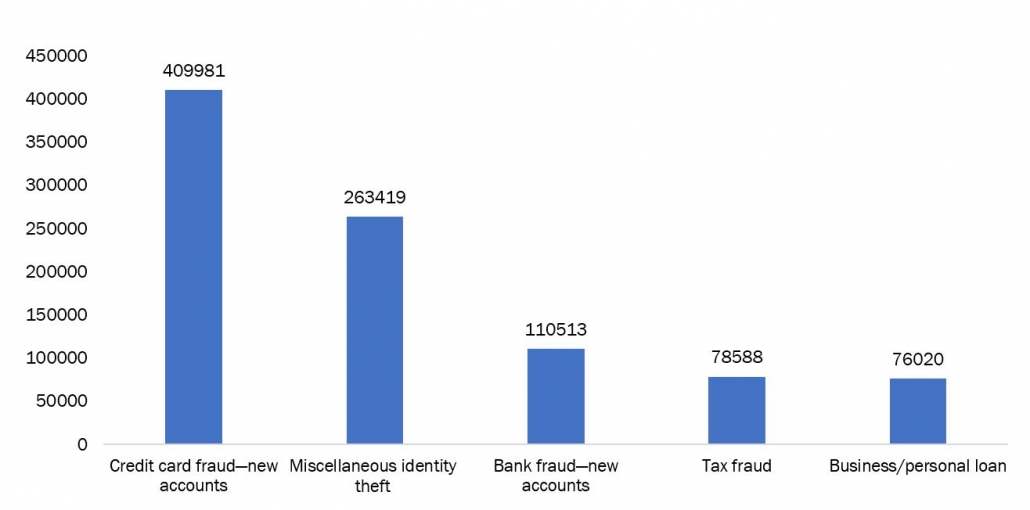 Source: Federal Trade Commission
Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management stands as a vital shield against cyberattacks. It's a continuous process of identifying, prioritizing, and resolving security vulnerabilities within an organization's IT infrastructure and software. This risk-based approach systematically identifies weaknesses and misconfigurations, allowing for proactive mitigation strategies that keep systems, networks, and applications secure. The core objective of vulnerability management is to minimize an organization's overall risk exposure. By tackling identified vulnerabilities, organizations build resilience against potential attacks and minimize potential damage if breaches occur. Vulnerability management isn't just a technical exercise; it's a strategic imperative for any organization that relies on information technology. By proactively identifying, evaluating, and addressing vulnerabilities, organizations can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect their critical data assets from known and unknown threats.
Incident Response
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, incident response plays a critical role in protecting businesses from the devastating effects of cyberattacks. Defined as the organized and methodical approach to detecting and managing these attacks, incident response aims to minimize damage, expedite recovery, and reduce costs incurred during such events. At the heart of effective incident response lies the incident response plan, a documented roadmap outlining the step-by-step procedures for each critical phase. This includes detection, investigation, containment, eradication, recovery, and breach notification, providing a clear and comprehensive framework for dealing with security incidents.
The Department of Financial Services (DFS), the government of India, conducted a meeting in November 2023 to discuss cybersecurity issues in the financial services sector. The meeting shared that 70 lakh mobile connections have been disconnected so far for involvement in cybercrime/financial frauds, and the sum of 900 crore rupees, which was fraudulently taken, has been recovered successfully, resulting in the benefit of 3.5 lakh victims.
User Authentication
User authentication stands as the gatekeeper of digital spaces, ensuring only authorized individuals gain access to systems, applications, and networks. This crucial process verifies a user's identity before granting them entry, requiring them to present credentials like usernames and passwords. These credentials are then compared against a secured database of authorized users, acting as a filter against unauthorized access. User authentication plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information and preventing malicious actors from exploiting vulnerabilities. By verifying identities, it helps to safeguard critical data, maintain system integrity, and ensure the overall security of digital platforms.
Source: Federal Trade Commission
Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management stands as a vital shield against cyberattacks. It's a continuous process of identifying, prioritizing, and resolving security vulnerabilities within an organization's IT infrastructure and software. This risk-based approach systematically identifies weaknesses and misconfigurations, allowing for proactive mitigation strategies that keep systems, networks, and applications secure. The core objective of vulnerability management is to minimize an organization's overall risk exposure. By tackling identified vulnerabilities, organizations build resilience against potential attacks and minimize potential damage if breaches occur. Vulnerability management isn't just a technical exercise; it's a strategic imperative for any organization that relies on information technology. By proactively identifying, evaluating, and addressing vulnerabilities, organizations can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect their critical data assets from known and unknown threats.
Incident Response
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, incident response plays a critical role in protecting businesses from the devastating effects of cyberattacks. Defined as the organized and methodical approach to detecting and managing these attacks, incident response aims to minimize damage, expedite recovery, and reduce costs incurred during such events. At the heart of effective incident response lies the incident response plan, a documented roadmap outlining the step-by-step procedures for each critical phase. This includes detection, investigation, containment, eradication, recovery, and breach notification, providing a clear and comprehensive framework for dealing with security incidents.
The Department of Financial Services (DFS), the government of India, conducted a meeting in November 2023 to discuss cybersecurity issues in the financial services sector. The meeting shared that 70 lakh mobile connections have been disconnected so far for involvement in cybercrime/financial frauds, and the sum of 900 crore rupees, which was fraudulently taken, has been recovered successfully, resulting in the benefit of 3.5 lakh victims.
User Authentication
User authentication stands as the gatekeeper of digital spaces, ensuring only authorized individuals gain access to systems, applications, and networks. This crucial process verifies a user's identity before granting them entry, requiring them to present credentials like usernames and passwords. These credentials are then compared against a secured database of authorized users, acting as a filter against unauthorized access. User authentication plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information and preventing malicious actors from exploiting vulnerabilities. By verifying identities, it helps to safeguard critical data, maintain system integrity, and ensure the overall security of digital platforms.
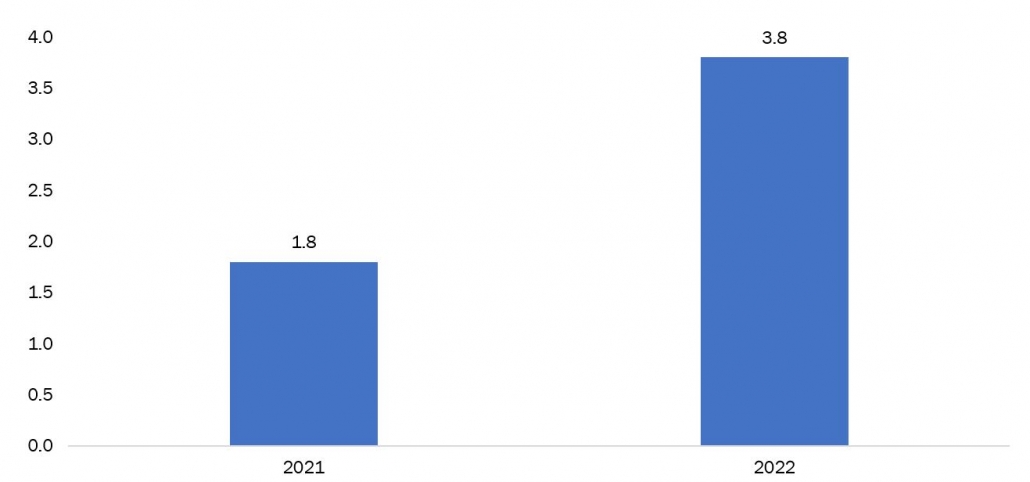 Source: Federal Trade Commission
According to recent reports investment scams in the United States have caused a staggering loss of $3.8 billion in 2022, marking a significant increase from the previous year's figures. This rise in fraudulent activities has resulted in a financial burden on consumers, who have had to bear the brunt of the scams.
Security Logging and Monitoring
Security logging and monitoring are the unsung heroes of cybersecurity, working tirelessly in the background to protect systems and data from harm. These vital processes work in tandem to collect, analyze, and retain security-related data, providing invaluable insights into potential threats and security incidents. Imagine a digital trail of breadcrumbs. That's what security logging offers. It meticulously records specific activities, events, errors, and system states, capturing the intricate details of an organization's digital landscape. This information becomes the foundation for security monitoring, which involves continuously analyzing these logs for suspicious patterns and potential security breaches.
Source: Federal Trade Commission
According to recent reports investment scams in the United States have caused a staggering loss of $3.8 billion in 2022, marking a significant increase from the previous year's figures. This rise in fraudulent activities has resulted in a financial burden on consumers, who have had to bear the brunt of the scams.
Security Logging and Monitoring
Security logging and monitoring are the unsung heroes of cybersecurity, working tirelessly in the background to protect systems and data from harm. These vital processes work in tandem to collect, analyze, and retain security-related data, providing invaluable insights into potential threats and security incidents. Imagine a digital trail of breadcrumbs. That's what security logging offers. It meticulously records specific activities, events, errors, and system states, capturing the intricate details of an organization's digital landscape. This information becomes the foundation for security monitoring, which involves continuously analyzing these logs for suspicious patterns and potential security breaches.
Figure 1: Number Of Cyber Crime Cases Registered– India (2017-2021)
 Source: Press Information Bureau, Government of India
The top 10 applications of cybersecurity are mentioned below:
Network Security Surveillance
Network security surveillance stands as a vital sentinel in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity. Its purpose is unwavering: to continuously monitor and safeguard a network from misuse, unauthorized access, and malicious alterations. This vigilant practice plays a crucial role in safeguarding data transfers, shielding them from the prying eyes and opportunistic actions of cybercriminals. Equipped with the latest threat intelligence, network security monitoring tools act as digital detectives, meticulously scanning networks for suspicious activity. They tirelessly analyze every byte of data, uncovering anomalies and identifying potential threats before they can wreak havoc. This proactive approach allows organizations to anticipate both authorized and unauthorized user actions, significantly reducing the time it takes to respond to security breaches.
Identification and Access Management (IAM)
In the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape, Identity and Access Management (IAM) stands as a cornerstone, overseeing the digital identities and access controls that safeguard critical corporate information. IAM operates within a framework of policies, processes, and technologies, meticulously designed to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to specific resources, with appropriate justification, for a limited duration. These solutions play a pivotal role in enhancing overall security and mitigating potential risks by employing a multi-pronged approach:
User Identification & Authentication: IAM systems meticulously identify and verify users before granting access, ensuring that only authorized individuals can enter the digital fortress.
Authorization Control: Access privileges are meticulously assigned based on each user's role and responsibilities, preventing unauthorized individuals from reaching sensitive data or performing restricted actions.
User Provisioning & Lifecycle Management: IAM solutions efficiently automate user onboarding and grant access privileges based on their roles. This ensures users have the precise level of access required to fulfill their duties.
Activity Monitoring & Threat Detection: Continuous monitoring of user activities allows for the identification and prevention of potential security breaches or unauthorized access attempts.
Software Security
In today's interconnected world, software security has emerged as a critical pillar of cybersecurity, safeguarding software applications and digital solutions from malicious actors. Developers play a pivotal role in this endeavor, seamlessly integrating security practices into the software development lifecycle (SDLC) and testing procedures. This meticulous approach ensures that digital solutions are built with robust defenses, enabling them to withstand and effectively respond to cyberattacks. By prioritizing software security, developers contribute to a safer digital environment, fostering trust and mitigating the potential harm caused by data breaches and system disruptions.
Source: Press Information Bureau, Government of India
The top 10 applications of cybersecurity are mentioned below:
Network Security Surveillance
Network security surveillance stands as a vital sentinel in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity. Its purpose is unwavering: to continuously monitor and safeguard a network from misuse, unauthorized access, and malicious alterations. This vigilant practice plays a crucial role in safeguarding data transfers, shielding them from the prying eyes and opportunistic actions of cybercriminals. Equipped with the latest threat intelligence, network security monitoring tools act as digital detectives, meticulously scanning networks for suspicious activity. They tirelessly analyze every byte of data, uncovering anomalies and identifying potential threats before they can wreak havoc. This proactive approach allows organizations to anticipate both authorized and unauthorized user actions, significantly reducing the time it takes to respond to security breaches.
Identification and Access Management (IAM)
In the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape, Identity and Access Management (IAM) stands as a cornerstone, overseeing the digital identities and access controls that safeguard critical corporate information. IAM operates within a framework of policies, processes, and technologies, meticulously designed to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to specific resources, with appropriate justification, for a limited duration. These solutions play a pivotal role in enhancing overall security and mitigating potential risks by employing a multi-pronged approach:
User Identification & Authentication: IAM systems meticulously identify and verify users before granting access, ensuring that only authorized individuals can enter the digital fortress.
Authorization Control: Access privileges are meticulously assigned based on each user's role and responsibilities, preventing unauthorized individuals from reaching sensitive data or performing restricted actions.
User Provisioning & Lifecycle Management: IAM solutions efficiently automate user onboarding and grant access privileges based on their roles. This ensures users have the precise level of access required to fulfill their duties.
Activity Monitoring & Threat Detection: Continuous monitoring of user activities allows for the identification and prevention of potential security breaches or unauthorized access attempts.
Software Security
In today's interconnected world, software security has emerged as a critical pillar of cybersecurity, safeguarding software applications and digital solutions from malicious actors. Developers play a pivotal role in this endeavor, seamlessly integrating security practices into the software development lifecycle (SDLC) and testing procedures. This meticulous approach ensures that digital solutions are built with robust defenses, enabling them to withstand and effectively respond to cyberattacks. By prioritizing software security, developers contribute to a safer digital environment, fostering trust and mitigating the potential harm caused by data breaches and system disruptions.
Figure 2: Reported Fraud Losses In United States (USD Billions)
 Source: Federal Trade Commission
US consumers lost nearly $8.8 billion to fraud in 2022, up over 30% YoY. Investment and imposter scams accounted for more than $6.4 billion of the losses. The FTC received 2.4 million fraud reports with imposter scams being the most commonly reported.
Malware Detection and Prevention
In the increasingly interconnected world, protecting our digital systems from malicious actors is paramount. This is where malware detection and prevention come into play, acting as essential shields against harmful software designed to wreak havoc on our devices and data. Malware, short for malicious software, encompasses a diverse range of programs with nefarious intent. From stealing sensitive information and hijacking systems to disrupting operations and compromising privacy, the consequences of malware infections can be devastating. Fortunately, a robust arsenal of tools and techniques exists to combat this threat. Malware detection systems utilize sophisticated algorithms to analyze code and identify suspicious behavior.
Threat Hunting
Threat hunting, a cornerstone of effective defense, goes beyond passively monitoring for threats and actively seeks out hidden dangers lurking within networks, systems, and devices. Unlike automated security tools and the initial layers of security operations centers (SOCs), threat hunting is human-driven. This involves skilled professionals employing a unique blend of intuition, strategic thinking, ethical decision-making, and creative problem-solving to uncover potential threats. Through meticulous analysis of data and usage patterns, these "cyber hunters" identify anomalies and suspicious activities that might otherwise go unnoticed. Crucially, threat hunting is distinct from threat detection. While the latter focuses on passively monitoring for known threats, threat hunting takes a preemptive stance, actively searching for potential threats that may not yet be identified.
Security Compliance
Cybersecurity compliance transcends mere adherence to legal mandates. It's the active implementation of risk management systems incorporating security regulations and standards to safeguard information's integrity, availability, and confidentiality. This goes beyond ticking boxes on government checklists; it's a proactive approach to fortifying organizations against a constantly evolving landscape of cyber threats. Compliance serves as a powerful shield against digital attacks like DDoS, phishing, malware, and ransomware. By aligning with established security frameworks, organizations build robust defenses that minimize vulnerabilities and bolster their resilience against cyber intrusions. This proactive stance not only mitigates potential financial and reputational damage from breaches but also fosters trust with stakeholders, including customers, partners, and investors. Cybersecurity compliance provides a structured path to securing this valuable asset, ensuring its integrity and availability for critical operations. By prioritizing compliance, organizations can proactively address security risks, bolstering their digital infrastructure and fostering a culture of security awareness within their workforce. As per the Federal Trade Commission, cases of Identity theft are on the rise with maximum related to Credit card frauds, increasing the incidence of cybercrimes.
Source: Federal Trade Commission
US consumers lost nearly $8.8 billion to fraud in 2022, up over 30% YoY. Investment and imposter scams accounted for more than $6.4 billion of the losses. The FTC received 2.4 million fraud reports with imposter scams being the most commonly reported.
Malware Detection and Prevention
In the increasingly interconnected world, protecting our digital systems from malicious actors is paramount. This is where malware detection and prevention come into play, acting as essential shields against harmful software designed to wreak havoc on our devices and data. Malware, short for malicious software, encompasses a diverse range of programs with nefarious intent. From stealing sensitive information and hijacking systems to disrupting operations and compromising privacy, the consequences of malware infections can be devastating. Fortunately, a robust arsenal of tools and techniques exists to combat this threat. Malware detection systems utilize sophisticated algorithms to analyze code and identify suspicious behavior.
Threat Hunting
Threat hunting, a cornerstone of effective defense, goes beyond passively monitoring for threats and actively seeks out hidden dangers lurking within networks, systems, and devices. Unlike automated security tools and the initial layers of security operations centers (SOCs), threat hunting is human-driven. This involves skilled professionals employing a unique blend of intuition, strategic thinking, ethical decision-making, and creative problem-solving to uncover potential threats. Through meticulous analysis of data and usage patterns, these "cyber hunters" identify anomalies and suspicious activities that might otherwise go unnoticed. Crucially, threat hunting is distinct from threat detection. While the latter focuses on passively monitoring for known threats, threat hunting takes a preemptive stance, actively searching for potential threats that may not yet be identified.
Security Compliance
Cybersecurity compliance transcends mere adherence to legal mandates. It's the active implementation of risk management systems incorporating security regulations and standards to safeguard information's integrity, availability, and confidentiality. This goes beyond ticking boxes on government checklists; it's a proactive approach to fortifying organizations against a constantly evolving landscape of cyber threats. Compliance serves as a powerful shield against digital attacks like DDoS, phishing, malware, and ransomware. By aligning with established security frameworks, organizations build robust defenses that minimize vulnerabilities and bolster their resilience against cyber intrusions. This proactive stance not only mitigates potential financial and reputational damage from breaches but also fosters trust with stakeholders, including customers, partners, and investors. Cybersecurity compliance provides a structured path to securing this valuable asset, ensuring its integrity and availability for critical operations. By prioritizing compliance, organizations can proactively address security risks, bolstering their digital infrastructure and fostering a culture of security awareness within their workforce. As per the Federal Trade Commission, cases of Identity theft are on the rise with maximum related to Credit card frauds, increasing the incidence of cybercrimes.
Figure 3: Different Categories of Identity Theft in United States (USD Billions)
 Source: Federal Trade Commission
Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management stands as a vital shield against cyberattacks. It's a continuous process of identifying, prioritizing, and resolving security vulnerabilities within an organization's IT infrastructure and software. This risk-based approach systematically identifies weaknesses and misconfigurations, allowing for proactive mitigation strategies that keep systems, networks, and applications secure. The core objective of vulnerability management is to minimize an organization's overall risk exposure. By tackling identified vulnerabilities, organizations build resilience against potential attacks and minimize potential damage if breaches occur. Vulnerability management isn't just a technical exercise; it's a strategic imperative for any organization that relies on information technology. By proactively identifying, evaluating, and addressing vulnerabilities, organizations can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect their critical data assets from known and unknown threats.
Incident Response
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, incident response plays a critical role in protecting businesses from the devastating effects of cyberattacks. Defined as the organized and methodical approach to detecting and managing these attacks, incident response aims to minimize damage, expedite recovery, and reduce costs incurred during such events. At the heart of effective incident response lies the incident response plan, a documented roadmap outlining the step-by-step procedures for each critical phase. This includes detection, investigation, containment, eradication, recovery, and breach notification, providing a clear and comprehensive framework for dealing with security incidents.
The Department of Financial Services (DFS), the government of India, conducted a meeting in November 2023 to discuss cybersecurity issues in the financial services sector. The meeting shared that 70 lakh mobile connections have been disconnected so far for involvement in cybercrime/financial frauds, and the sum of 900 crore rupees, which was fraudulently taken, has been recovered successfully, resulting in the benefit of 3.5 lakh victims.
User Authentication
User authentication stands as the gatekeeper of digital spaces, ensuring only authorized individuals gain access to systems, applications, and networks. This crucial process verifies a user's identity before granting them entry, requiring them to present credentials like usernames and passwords. These credentials are then compared against a secured database of authorized users, acting as a filter against unauthorized access. User authentication plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information and preventing malicious actors from exploiting vulnerabilities. By verifying identities, it helps to safeguard critical data, maintain system integrity, and ensure the overall security of digital platforms.
Source: Federal Trade Commission
Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management stands as a vital shield against cyberattacks. It's a continuous process of identifying, prioritizing, and resolving security vulnerabilities within an organization's IT infrastructure and software. This risk-based approach systematically identifies weaknesses and misconfigurations, allowing for proactive mitigation strategies that keep systems, networks, and applications secure. The core objective of vulnerability management is to minimize an organization's overall risk exposure. By tackling identified vulnerabilities, organizations build resilience against potential attacks and minimize potential damage if breaches occur. Vulnerability management isn't just a technical exercise; it's a strategic imperative for any organization that relies on information technology. By proactively identifying, evaluating, and addressing vulnerabilities, organizations can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect their critical data assets from known and unknown threats.
Incident Response
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, incident response plays a critical role in protecting businesses from the devastating effects of cyberattacks. Defined as the organized and methodical approach to detecting and managing these attacks, incident response aims to minimize damage, expedite recovery, and reduce costs incurred during such events. At the heart of effective incident response lies the incident response plan, a documented roadmap outlining the step-by-step procedures for each critical phase. This includes detection, investigation, containment, eradication, recovery, and breach notification, providing a clear and comprehensive framework for dealing with security incidents.
The Department of Financial Services (DFS), the government of India, conducted a meeting in November 2023 to discuss cybersecurity issues in the financial services sector. The meeting shared that 70 lakh mobile connections have been disconnected so far for involvement in cybercrime/financial frauds, and the sum of 900 crore rupees, which was fraudulently taken, has been recovered successfully, resulting in the benefit of 3.5 lakh victims.
User Authentication
User authentication stands as the gatekeeper of digital spaces, ensuring only authorized individuals gain access to systems, applications, and networks. This crucial process verifies a user's identity before granting them entry, requiring them to present credentials like usernames and passwords. These credentials are then compared against a secured database of authorized users, acting as a filter against unauthorized access. User authentication plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information and preventing malicious actors from exploiting vulnerabilities. By verifying identities, it helps to safeguard critical data, maintain system integrity, and ensure the overall security of digital platforms.
Figure 4: Investment Scams Related Losses In United States (USD Billions)
 Source: Federal Trade Commission
According to recent reports investment scams in the United States have caused a staggering loss of $3.8 billion in 2022, marking a significant increase from the previous year's figures. This rise in fraudulent activities has resulted in a financial burden on consumers, who have had to bear the brunt of the scams.
Security Logging and Monitoring
Security logging and monitoring are the unsung heroes of cybersecurity, working tirelessly in the background to protect systems and data from harm. These vital processes work in tandem to collect, analyze, and retain security-related data, providing invaluable insights into potential threats and security incidents. Imagine a digital trail of breadcrumbs. That's what security logging offers. It meticulously records specific activities, events, errors, and system states, capturing the intricate details of an organization's digital landscape. This information becomes the foundation for security monitoring, which involves continuously analyzing these logs for suspicious patterns and potential security breaches.
Source: Federal Trade Commission
According to recent reports investment scams in the United States have caused a staggering loss of $3.8 billion in 2022, marking a significant increase from the previous year's figures. This rise in fraudulent activities has resulted in a financial burden on consumers, who have had to bear the brunt of the scams.
Security Logging and Monitoring
Security logging and monitoring are the unsung heroes of cybersecurity, working tirelessly in the background to protect systems and data from harm. These vital processes work in tandem to collect, analyze, and retain security-related data, providing invaluable insights into potential threats and security incidents. Imagine a digital trail of breadcrumbs. That's what security logging offers. It meticulously records specific activities, events, errors, and system states, capturing the intricate details of an organization's digital landscape. This information becomes the foundation for security monitoring, which involves continuously analyzing these logs for suspicious patterns and potential security breaches.Get in Touch
Interested in this topic? Contact our analysts for more details.
Latest Thought Articles

Top OSAT Companies Driving Semiconductor Assembly and Test Services Worldwide
Recently
EV Charging Stations Market Outlook: Smart Charging, Fast Charging, and Regional Expansion
Recently
Future of Corporate Wellness: Global Trends and Regional Outlook
Recently
Regional Breakdown of the Mechanical Keyboard Market: Who Leads and Why?
Recently