Report Overview
Automotive Battery Market - Highlights
Automotive Battery Market Size:
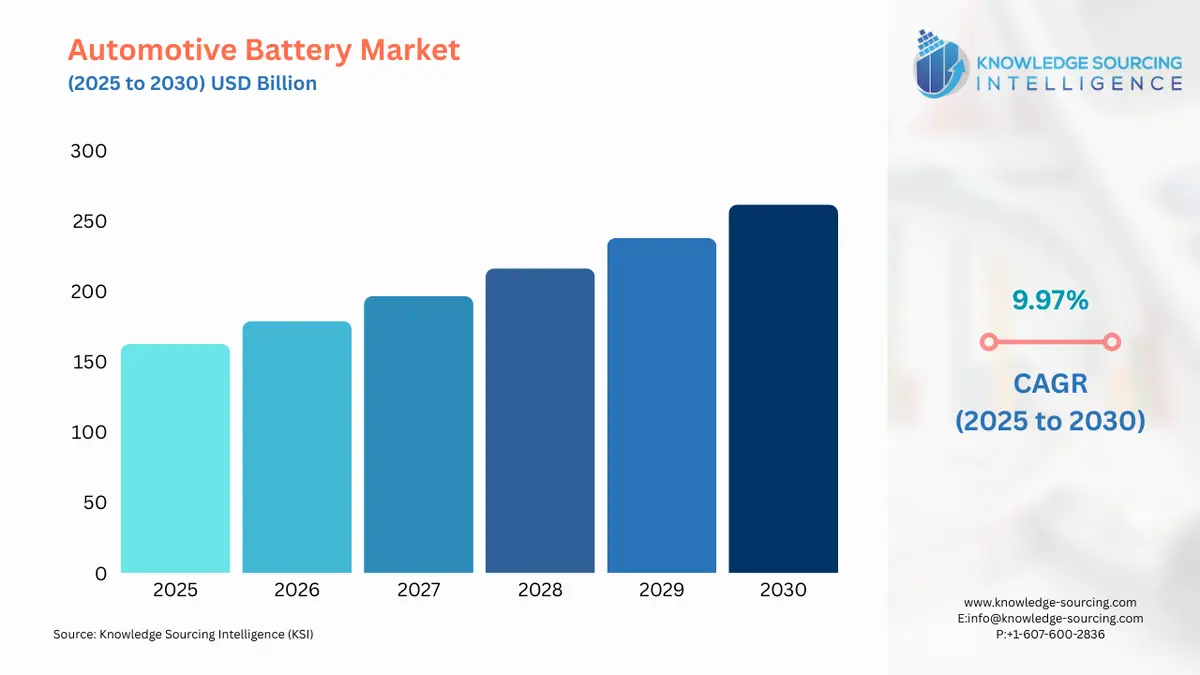
The Automotive Battery Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.97%, reaching USD 261.555 billion in 2030 from USD 162.650 billion in 2025.
The automotive battery market is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by an accelerating global shift toward vehicle electrification and persistent demand from the traditional automotive sector. This market is a critical pillar of the broader automotive industry, supplying the essential energy storage systems that power everything from standard internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to advanced battery electric vehicles (BEVs). The dual nature of this demand—servicing the long-established ICE market with lead-acid batteries for starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) applications, while simultaneously addressing the exponential growth of the EV market with lithium-ion technology—defines its current state. The trajectory of this market is directly tied to global and regional vehicle production trends, technological advancements, and the complex interplay of raw material supply and regulatory policies.
Automotive Battery Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
The primary factor propelling demand in the automotive battery market is the consistent expansion of global vehicle production. This growth is not limited to a single vehicle type but encompasses both traditional ICE vehicles and the rapidly expanding fleet of electric vehicles. For ICE vehicles, every new car, truck, or two-wheeler manufactured by OEMs requires a battery for SLI functions. This foundational demand provides a steady, high-volume baseline for the market. Simultaneously, the aftermarket segment—driven by the finite lifespan of these batteries—creates a continuous replacement cycle, ensuring a sustained stream of revenue and demand.
The rising adoption of electric vehicles directly increases the need for high-capacity, high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Governments worldwide are implementing policies that encourage the transition to EVs, including subsidies, tax incentives, and stringent emission standards. These policies directly translate into a greater consumer and fleet demand for electric cars, which in turn necessitates a proportional increase in the production of EV batteries. This structural shift in the automotive landscape makes the demand for lithium-ion batteries a high-growth segment of the overall market.
Technological advancements, particularly in start-stop systems and micro-hybrids, also serve as a key growth driver. These fuel-saving technologies, which automatically shut off the engine when the vehicle is stationary and restart it upon releasing the brake, require more robust batteries. Enhanced flooded batteries (EFBs) and absorbent glass mat (AGM) batteries are specifically designed to handle the frequent cycling and deep discharge cycles associated with these systems. The widespread integration of start-stop technology across new vehicle models directly increases the demand for these advanced lead-acid battery chemistries.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The automotive battery market faces significant challenges, primarily centered around supply chain vulnerabilities and raw material constraints. The geopolitical concentration of critical raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, exposes the market to supply chain bottlenecks and price volatility. This reliance on a limited number of regions for raw material extraction and processing creates a risk of supply shortages that could impede production and increase manufacturing costs. The high production costs of lithium-ion batteries, stemming from the complex extraction and refining processes, remain a persistent challenge that directly impacts the final price of electric vehicles, which can deter consumer adoption and thus dampen demand.
However, these challenges also create opportunities. The imperative to mitigate supply chain risks has spurred investments in battery recycling and second-life applications. Recycling infrastructure, while still nascent, presents a long-term opportunity to create a circular economy for batteries, reducing reliance on primary raw material mining and stabilizing supply. This also provides an opportunity for new business models and technologies focused on urban mining and material recovery. The push for diversification in the supply chain has also led to new investments in refining and processing facilities outside of traditional hubs. For example, countries are actively seeking to secure their own supply chains for battery materials to reduce geopolitical risks and ensure sustained access to these critical resources.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The automotive battery is a physical product, and its pricing is inextricably linked to the cost and availability of key raw materials. For lithium-ion batteries, the primary cost drivers are lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite. The price of these commodities is subject to global market forces, geopolitical tensions, and mining capacity. For instance, the price of lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide, essential for battery cathodes, has experienced significant volatility. This variability is directly influenced by the speed of new mining and processing projects coming online versus the rate of demand from the accelerating EV market.
Similarly, the price of cobalt, often a subject of ethical sourcing scrutiny, remains a critical cost factor. The concentration of cobalt mining in the Democratic Republic of Congo poses a significant risk to the supply chain. In response, manufacturers are actively exploring alternative battery chemistries, such as those with reduced or zero cobalt content, which directly impacts the demand for different raw materials. The pricing of traditional lead-acid batteries, while more stable, is still tied to the global price of lead. The high recyclability of lead-acid batteries, with a well-established recycling chain, helps to stabilize the raw material supply and mitigate price shocks.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global automotive battery supply chain is complex and geographically concentrated. The upstream segment, involving the mining and refining of raw materials, is dominated by a few key regions. Chile and Australia lead in lithium extraction, while the Democratic Republic of Congo is the largest source of cobalt. China holds a near-monopoly on the processing and refining of many of these materials into battery-grade chemicals.
The midstream of the supply chain, cell manufacturing, is heavily concentrated in Asia, with China, South Korea, and Japan serving as major production hubs. This concentration creates a logistical challenge for automakers in North America and Europe, who must import a significant portion of their battery cells. In response, these regions are aggressively pursuing domestic and regional battery manufacturing capabilities, often referred to as "gigafactories," to reduce dependency and localize their supply chains. The downstream segment, module and pack assembly, is often handled closer to the final vehicle assembly plants to minimize the complexities and costs associated with transporting large, heavy battery packs.
- Government Regulations
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) Standards & Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) | CAFE standards compel automakers to improve fuel efficiency, which directly increases the adoption of start-stop systems and micro-hybrids, thereby raising demand for enhanced lead-acid batteries. The IRA provides tax credits for consumers purchasing EVs and for manufacturers producing batteries and their components in North America, accelerating consumer demand for EVs and incentivizing the localization of the battery supply chain. |
| European Union | EU Battery Regulation & Green Deal | The EU Battery Regulation mandates strict recycling targets and requires due diligence on the sourcing of raw materials, which directly shapes the competitive landscape by rewarding manufacturers with sustainable supply chains. The Green Deal's push for a carbon-neutral economy accelerates the demand for EVs and, consequently, their batteries, by setting aggressive emission reduction targets for the automotive sector. |
| China | New Energy Vehicle (NEV) Mandates & Battery Recycling Policies | The NEV mandate requires automakers to produce a certain percentage of EVs, creating a direct and non-negotiable demand for lithium-ion batteries. The government's focus on battery recycling, including the "Extended Producer Responsibility" (EPR) policy, compels manufacturers to establish a comprehensive battery recovery system, which creates a new segment for battery lifecycle management services. |
| India | Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) Scheme | The FAME scheme offers subsidies for the purchase of EVs, reducing the cost of ownership for consumers and thereby stimulating demand for electric two-wheelers and three-wheelers, which are a major market segment for batteries in the country. This policy directly lowers the price barrier to EV adoption. |
| Japan | Clean Energy Vehicle (CEV) Subsidies & Emissions Standards | CEV subsidies incentivize the purchase of hybrid and electric vehicles, thereby boosting demand for advanced battery technologies. Japan's stringent emissions standards, which are continuously tightened, encourage automakers to integrate fuel-saving technologies like start-stop systems, sustaining demand for advanced lead-acid and other auxiliary battery types. |
Automotive Battery Market Segmentation Analysis:
- By Technology: Lithium-Ion Battery Analysis
The lithium-ion battery segment is a dynamic growth engine of the automotive battery market, with its demand drivers uniquely tied to the proliferation of electric and hybrid vehicles. The primary driver is the global transition away from internal combustion engines. Governments and consumers are increasingly prioritizing zero-emission and fuel-efficient vehicles, which rely exclusively on lithium-ion batteries for propulsion. This trend is amplified by a continuous reduction in battery pack costs, which makes EVs more price-competitive with their ICE counterparts. The demand for lithium-ion batteries is a function of their superior energy density, power-to-weight ratio, and long cycle life, which are essential for achieving the required range and performance in modern EVs. The segment also benefits from the accelerating demand for high-performance vehicles, as automakers integrate these batteries into sports cars and luxury models to enable rapid acceleration and advanced functionality. This growth is further fueled by the integration of more sophisticated electronic systems within all vehicles, as lithium-ion batteries serve as a reliable, lightweight power source for infotainment, safety, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
- By Application: Electric Vehicle (EV) Analysis
The Electric Vehicle (EV) segment is the most significant demand-side force shaping the automotive battery market. The demand for batteries in this application is not driven by simple replacement cycles but by the fundamental and sustained growth in EV production and sales. This is a direct consequence of policy support, such as subsidies and tax credits, which directly lower the cost of entry for consumers. As the global EV fleet expands, so too does the demand for the original equipment batteries. This growth is further propelled by ongoing advancements in battery technology that promise longer range and faster charging times, which directly address consumer range anxiety and accelerate adoption. The market for EV batteries is also a long-term play, as a new aftermarket for battery replacements and second-life applications will emerge as the installed base of EVs matures. Fleet electrification—from public transit buses to commercial delivery vans—is another powerful demand driver, as corporations and municipalities seek to lower operating costs and meet sustainability goals.
Automotive Battery Market Geographical Outlook:
- US Market Analysis
The US automotive battery market is characterized by a high volume of demand from the traditional automotive sector and a rapidly expanding EV segment. The market for lead-acid batteries remains robust, driven by the country's large vehicle parc and the consistent demand for replacement batteries. The need for advanced lead-acid batteries, such as AGMs, is growing as automakers integrate start-stop technology across a wider range of vehicles to meet increasingly stringent fuel economy standards. The necessity for EV batteries is accelerating, propelled by federal and state-level incentives, including the tax credits provided by the Inflation Reduction Act. This policy has spurred significant investment in localized battery manufacturing, with major companies establishing "gigafactories" to meet the growing domestic demand for EVs and to comply with the IRA's sourcing requirements. - Brazil Market Analysis
Brazil’s automotive battery market is primarily shaped by its large fleet of flexible-fuel vehicles and its position as a major automotive production hub in South America. The market for lead-acid batteries is the dominant segment, driven by the high volume of new vehicle production and the substantial aftermarket demand. Economic fluctuations and high interest rates have at times constrained consumer spending on new vehicles, which directly impacts OEM demand. However, the country's large vehicle parc ensures a steady and resilient aftermarket for replacement batteries. The necessity for EV batteries is still in its nascent stages, but is gaining momentum. Government policies promoting biofuels, such as Brazil's E30 mandate, have historically prioritized a different approach to clean transportation, but a growing number of automakers are introducing EV models, and localized production is beginning to emerge to narrow the price gap with traditional vehicles. - German Market Analysis
The German automotive battery market is a key hub for both conventional and advanced battery technologies. As a powerhouse of the European automotive industry, Germany drives substantial demand for traditional lead-acid batteries for its domestic vehicle production. Simultaneously, the country is at the forefront of the European transition to electric mobility. The need for EV batteries is exceptionally high, driven by the German government's ambitious electrification targets, strong consumer incentives, and a robust charging infrastructure. The German market is a major locus of research and development for next-generation battery technologies, including solid-state batteries, and is home to a growing number of large-scale battery production facilities being established by both domestic and international players. - Saudi Arabian Market Analysis
The automotive battery market in Saudi Arabia is heavily influenced by its reliance on a large fleet of ICE vehicles and a nascent but ambitious push toward vehicle electrification. The need for traditional lead-acid batteries is strong and stable, driven by the constant need for replacement batteries in a challenging climate that can shorten battery life. The government’s Vision 2030 plan, which includes economic diversification and sustainability goals, is beginning to create a new demand segment for EV batteries. While EV penetration is currently low, government initiatives to develop charging infrastructure and attract foreign direct investment in EV manufacturing signal a future increase in demand. For instance, an EV manufacturing facility is being established to cater to both domestic and export markets, which will directly catalyze local demand for batteries. - Chinese Market Analysis
China is the largest and most dominant force in the global automotive battery market, both in terms of production and demand. The country's necessity for automotive batteries is fueled by two colossal segments: the world’s largest vehicle manufacturing industry and its unparalleled commitment to electric mobility. The Chinese government's aggressive NEV mandates and extensive consumer subsidies have created an explosive demand for lithium-ion batteries, which has, in turn, spurred the establishment of a vast network of domestic battery manufacturers. This has positioned China not only as the largest consumer but also as the primary global supplier of EV batteries. The market is further solidified by stringent battery recycling and management policies, which are creating a structured, long-term market for battery lifecycle services.
List of Top Automotive Battery Market Companies:
The automotive battery market is a highly competitive landscape dominated by a few key global players and a growing number of regional specialists. Competition is centered on achieving economies of scale, investing in advanced battery chemistry research, and securing long-term supply agreements with major automotive OEMs.
- LG Energy Solution
As a leading global provider of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles, LG Energy Solution has established a formidable presence in the market. The company's strategic positioning is built on its extensive R&D capabilities and a global manufacturing footprint that includes facilities in the United States, South Korea, China, and Poland. The company has secured numerous long-term supply contracts with major global automakers, solidifying its position as a preferred partner for EV battery technology. Its product portfolio is defined by high energy density and a focus on safety, making it a key player in the high-growth EV segment. - CATL (Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited)
Based in China, CATL has emerged as the world's largest automotive battery manufacturer. The company’s strategic positioning is predicated on its massive production capacity, which allows it to achieve significant economies of scale and offer competitive pricing. CATL has a strong focus on innovation, particularly in developing new cell-to-pack technologies that increase battery energy density and reduce manufacturing complexity. Its dominant position in the Chinese market, combined with expanding partnerships with global automakers, makes it a critical competitor shaping the future of the industry. - Clarios
Clarios is a global leader in advanced battery solutions, with a strong emphasis on the lead-acid segment. The company's strategic advantage lies in its well-established brand reputation and its comprehensive global distribution network, which services both OEM and aftermarket customers. Clarios has maintained its market relevance by focusing on technologies like Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) and Enhanced Flooded Batteries (EFBs), which are essential for vehicles with start-stop systems. The company's business model is also anchored in a commitment to sustainability, operating a closed-loop recycling system where 99% of its batteries are collected and repurposed.
Automotive Battery Market Developments:
- July 2025: Panasonic Announces New EV Battery Plant in Kansas, US
Panasonic announced the opening of its new $4 billion EV battery plant in De Soto, Kansas. The facility, which has a planned capacity of 32 GWh, is Panasonic's second in the United States and is a direct move to strengthen the domestic EV battery supply chain. This investment expands the company's presence beyond its partnership with Tesla, and the new facility will produce 2170 cylindrical cells, a common format for high-performance EVs. The development signifies a major capacity addition in North America, aimed at meeting the increasing demand for locally sourced EV components. - July 2025: BYD Begins Production at Former Ford Plant in Brazil
BYD began the production of electric and hybrid vehicles at a former Ford plant in Brazil. This move represents a significant capacity addition for EV manufacturing in South America. By localizing production, BYD aims to serve the Brazilian and broader South American markets more effectively. This strategic development is expected to reduce import-related costs and improve supply chain efficiency for the company in the region.
Automotive Battery Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Automotive Battery Market Size in 2025 | USD 162.650 billion |
| Automotive Battery Market Size in 2030 | USD 261.555 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 9.97% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in the Automotive Battery Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Automotive Battery Market Segmentation:
- By Technology
- Lead-Acid
- Lithium-Ion
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH)
- Other Technologies
- By Vehicle Type
- Passenger Cars
- Commercial Vehicles
- Two-Wheelers
- Three-Wheelers
- By Application
- Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV)
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV)
- By End-User
- Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM)
- Aftermarket
- By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- South America
- Middle East & Africa