Report Overview
Chemical Recycling Market Size, Highlights
Chemical Recycling Market Size:
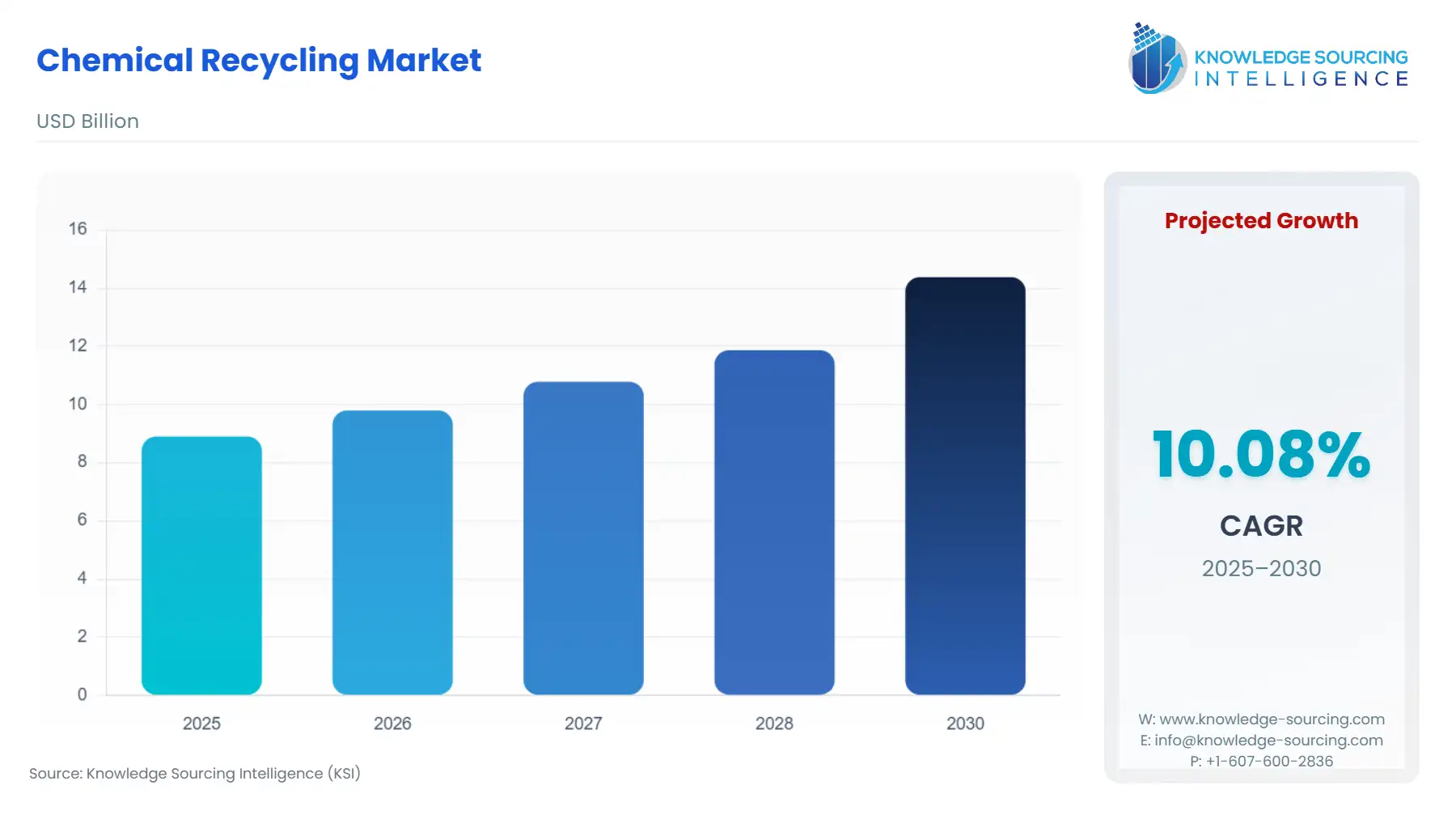
The chemical recycling market is estimated to grow from US$8.90 billion in 2025 to US$14.383 billion in 2030 at 10.05% CAGR.
Chemical recycling breaks down plastic waste to its molecular building blocks through advanced processes such as pyrolysis or solvolysis. This allows the production of high-quality raw materials to manufacture new plastics, reducing the dependency on virgin resources and dealing with hard-to-recycle plastics that support the circular economy and sustainability goals.
The OECD reports that global policy changes will decrease 96% of plastic leakage in 2040. If effective regulations are not more comprehensive, while the production of plastics has increased by 70%, the mismanagement of waste has escalated by 50%, resulting in negative environmental impacts. Effective policy imparts significant competitive and ecological advantages.
Chemical Recycling Market Growth Drivers:
- Environmental regulations are driving the chemical recycling market growth
Stricter waste management laws, extended producer responsibility policies, and increased consumer demand for sustainable products force industries to turn to chemical recycling to reduce plastic waste and environmental pollution.
In 2024, the Indian government issued new National Guidelines addressing plastic pollution, the Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016, and created new standards for these decrees. These guidelines bring in new regulations about extended producer responsibility, labeling biodegradable plastics, and reporting requirements. In doing so, the EPR targets will be achieved effectively, with increased recycling performances ranging from 50-80% for individual categories.
- Technological advancements are propelling the chemical recycling market expansion
Technological strides, economies of scale, and new business opportunities from a circular economy increasingly make chemical recycling attractive. These make it increasingly viable to manage plastic waste and thus enable industries to move toward sustainability while harvesting new market potential.
Among the promising chemical recycling technologies is hydrothermal treatment (HTT), which uses water to dissolve mixed plastics without combustion, especially under supercritical conditions. Hence, no toxic by-products are made. It has better product yields than pyrolysis and gasification, but requires some process methods to be further optimized for full commercialization.
Chemical Recycling Market Segment Analysis:
- By type, the depolymerization process is anticipated to grow fastest during the forecasted period
In chemical recycling, depolymerization is breaking polymers, like plastics, into their monomeric building blocks, usually through hydrolysis, glycolysis, or pyrolysis. This enables raw material recovery to produce new polymers, supporting a circularity reduction in waste and dependence on virgin fossil-based resources.
The world economy faces increasing responsibility for textile waste; polyester is at the center because it's the most used textile fiber, representing 54% of global fiber production. Almost 73% of polyester gets lost in landfilling or incineration. Effective, closed-loop chemical recycling solutions have not yet been commercially established.
Chemical Recycling Market Geographical Outlook:
- By geography, North America will be the fastest-growing region during the forecasted period.
This growth is due to stringent environmental regulations, strong consumer awareness, and significant investment in recycling technologies. Chemical recycling is being compelled by the Save Our Seas Act, among other initiatives, and bans at the state level in the United States against plastic bags. Leading chemical and petrochemical companies are heavily investing in advanced recycling technologies to meet the growing demand for sustainable packaging and automotive components. Similarly, Canada focuses on sustainable waste management practices where government initiatives strongly encourage a circular economy and waste reduction.
American Chemistry Council and its members advocate for this circular economy towards resource conservation, product lifespan innovations, and advanced recycling technologies. The chemical industry is targeting 100% recycling, recovery, or reuse of U.S. plastic packaging by 2040. It is working on the principle that no trash will ever be sent to landfills or the environment anymore using advanced recycling.
List of Top Chemical Recycling Companies:
- Aduro Clean Technologies
- Agilyx
- BASF ChemCycling
- BiologioQ
These companies are at the forefront of developing and supplying the chemical recycling market, contributing to the growth and innovation of monomers and oligomers. Aduro Clean Technologies, Aglix, BASF Chemcycling, and BiologioQ are major companies in the chemical recycling market.
Chemical Recycling Market Key Developments:
- In November 2024, Aduro Clean Technologies signed an MOU with GF Building Flow Solutions Americas to explore the conversion of Uponor crosslinked polyethylene (PEX) waste into valuable raw materials using Aduro's Hydrochemolytic Technology (HCT). The collaboration aims to further sustainable product manufacturing and chemical recycling products.
- In February 2024, BASF introduced Chemcycled products to the US market, using feedstock from plastic waste through its ChemCycling process. The ISCC+-certified advanced recycled building blocks are being produced at BASF TotalEnergies Petrochemicals Port Arthur site. They will substitute fossil resources in end products like super absorbent polymers, engineered plastics, and polyurethanes.
Chemical Recycling Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Chemical Recycling Market Size in 2025 | US$8.90 billion |
| Chemical Recycling Market Size in 2030 | US$14.383 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 10.05% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in the Chemical Recycling Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
The Chemical Recycling market is analyzed into the following segments:
- By Process Type
- Depolymerization
- Pyrolysis
- Gasification
- Solvolysis
- Others
- By Product
- Monomers
- Oligomers
- Syngas
- Oil and Wax
- By End-User
- Chemical
- Automotive
- Packaging
- Construction
- Textile
- Others
- By Geography
- North America
- USA
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Spain
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Indonesia
- Thailand
- Others
- North America
Our Best-Performing Industry Reports: