Report Overview
China AI in Transportation Highlights
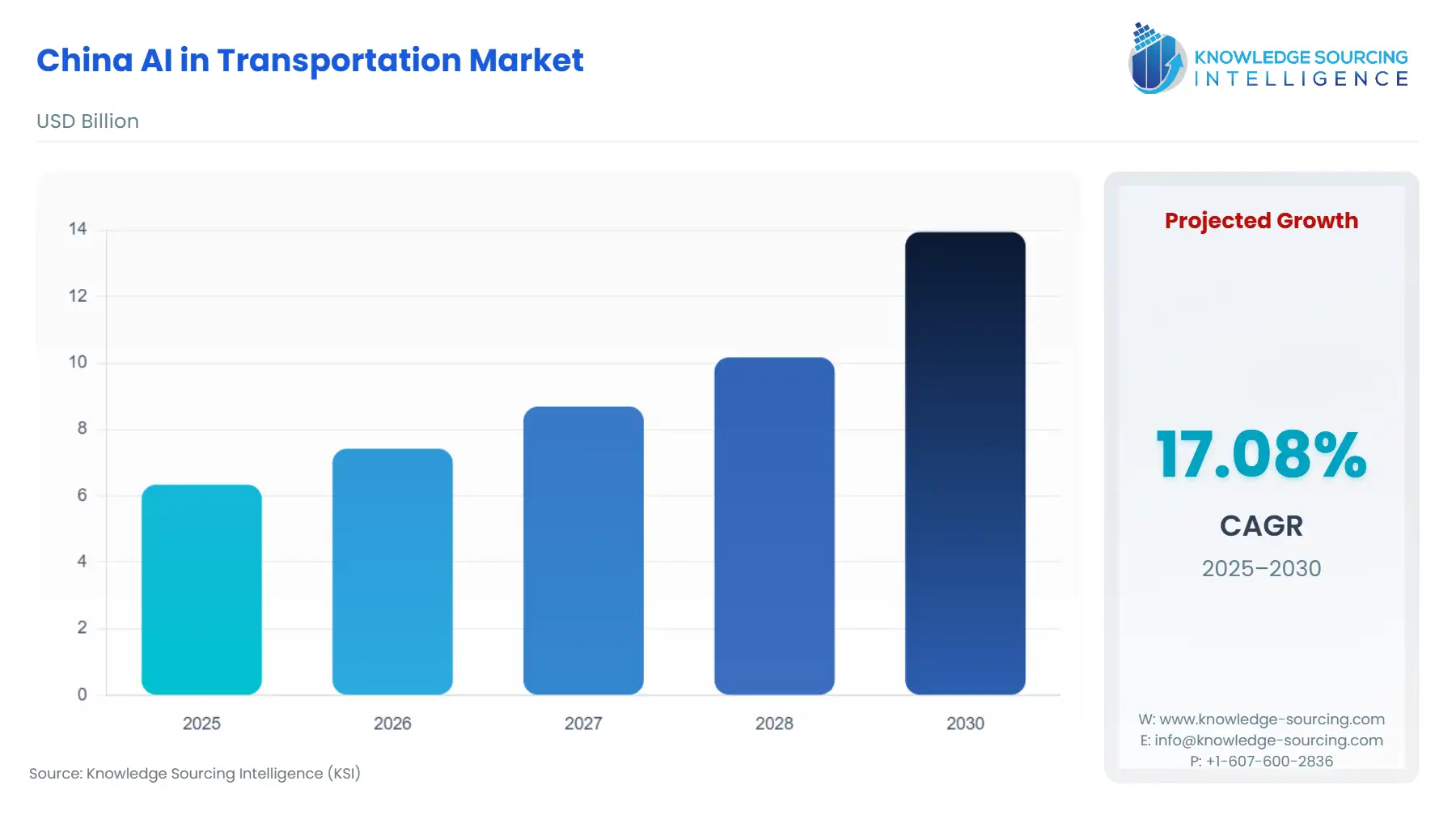
China AI in Transportation Market Size:
The China AI in Transportation Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 17.08%, rising from USD 6.338 billion in 2025 to USD 13.944 billion by 2030.
China AI in Transportation Market Key Highlights:
- The establishment of the National Data Administration (NDA) and the subsequent "Data Element X" action plan signify a top-down national strategy to activate the data market, directly propelling the availability and quality of training data, which is foundational for the performance and commercial viability of AI-driven transportation systems.
- China's comprehensive regulatory framework, including the Generative AI Measures and the algorithm registration requirements, balances innovation encouragement with safety and information control, imposing a necessity for traceable and compliant AI solutions, thus increasing demand for 'responsible AI' development services.
- By the end of September 2025, over 60% of new passenger vehicles sold in China featured Level 2 driving-assistance functions, creating a massive, immediately addressable market for the integration of higher-level AI software into production vehicles, shifting the industry focus from pure R&D to mass commercialization and scale.
- Market leaders like Baidu's Apollo Go have advanced operational metrics, recording 14 million autonomous rides provided to the public and achieving 100% fully driverless urban deployment in some Chinese cities, demonstrating the technical maturity and immediate scaling potential of the Robotaxi segment within the domestic ecosystem.
The intersection of artificial intelligence and the transportation sector in China represents a strategic convergence of national industrial policy and technological capability. This market is not simply adopting global AI trends; it is being fundamentally shaped by the central government's designation of data as a core factor of production and its strategic goal of building an intelligent, multilayered transport system.
The rapid expansion of urban centers and the imperative for optimizing logistics, compounded by the sheer volume of data generated by the world's largest connected population, provide a unique proving ground for large-scale AI deployment. This environment ensures a shift from theoretical research to the practical, commercial application of machine learning, deep learning, and computer vision across the entire mobility value chain, spanning public transport, autonomous ride-hailing, and commercial logistics.
China AI in Transportation Market Analysis:
Growth Drivers
Top-tier governmental support for "vehicle-road-cloud" integration acts as the primary catalyst, directly creating demand for AI-powered cloud platform services capable of aggregating, processing, and disseminating real-time data between vehicles and infrastructure. Furthermore, the high penetration rate of Level 2 driving-assistance functions in new passenger cars—exceeding 60% as of September 2025—stimulates immediate consumer demand for Level 3 and Level 4 AI software upgrades that leverage existing in-vehicle hardware for enhanced hands-off capabilities. The explicit policy to integrate AI into transportation by the Ministry of Transport, focusing on a comprehensive transport mega-model, mandates the development and deployment of sophisticated AI agent technologies for network-wide optimization, thereby pushing transportation operators to procure advanced, deep learning-based solutions.
Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge constraining market expansion is the regulatory necessity for algorithm registration and rigorous security assessments, which increases the time-to-market and development cost for new AI applications, consequently dampening demand for experimental, non-compliant solutions. However, this same regulatory environment creates a significant opportunity: the imposition of strict data privacy and security requirements directly fuels demand for domestic 'trusted' cloud and data governance platforms that can ensure compliance with national data laws. The mass recall of over 2.5 million vehicles in 2024 due to driver-assist system issues highlights the prevailing safety and liability constraint, but simultaneously drives a massive market opportunity for AI-driven validation, simulation, and predictive maintenance software that can proactively identify and mitigate system failures before deployment, shifting demand from reactive fixes to preventative, AI-based quality assurance.
Supply Chain Analysis
The AI in Transportation market's supply chain is fundamentally bifurcated into a domestic hardware pipeline and a globally interdependent software stack. Key hardware components for L2-L4 systems—specifically high-performance semiconductors (GPUs/ASICs) and certain high-resolution sensor modules (LiDAR)—retain a dependency on international suppliers, creating a logistical vulnerability that can constrain the mass production of autonomous vehicles. Conversely, the core value proposition, the AI software itself, is domestically dominated, leveraging local cloud infrastructure and massive, China-specific datasets. Logistical complexities center on the secure and low-latency transmission of real-time data between the vehicle, roadside units (RSUs), and central cloud control centers, necessitating heavy investment in high-bandwidth 5G and C-V2X (Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything) networks to support the deployment and continuous operation of AI models for fleet management, route optimization, and predictive maintenance.
Government Regulations
The central government's regulatory approach is characterized by a "pro-growth, coordinated control" strategy, directly impacting the compliance cost and operational scale for AI service providers.
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| National | Generative AI Measures (CAC, 2023) | Requires algorithm security assessment and registration for services that influence public opinion, including ride-hailing optimization. Directly increases compliance costs, but favors established firms capable of centralized auditing and transparent disclosure, thus consolidating demand toward mature, heavily capitalized vendors. |
| Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) | Intelligent Connected Vehicle Standards | Rapid acceleration of urgently needed standards for combined driving-assistance (L2) and automated driving (L3/L4) systems. The move legitimizes the technology, creating predictable development pathways and acting as a clear demand signal for automakers to adopt compliant, high-level AI modules. |
| Ministry of Transport (MoT) | "AI + Transport" Action Plan (Planned issuance) | Focuses on integrating AI across the entire transport network and developing a comprehensive transport mega-model. Creates guaranteed public-sector demand for AI solutions in traffic management, logistics planning, and infrastructure monitoring, shifting provider focus from merely private vehicles to large-scale, municipal-level contracts. |
China AI in Transportation Market Segment Analysis:
By Technology: Deep Learning
Deep Learning (DL) is the fundamental technology underpinning the majority of high-value AI in Transportation applications, driving demand for both specialized hardware and high-performance cloud computing resources. The primary growth driver for DL stems from the complexity of China's urban environments—dense, non-standardized traffic patterns, diverse road furniture, and unpredictable pedestrian behavior—which mandate extremely robust, non-rule-based perception and prediction systems. DL models, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Transformers, are the sole practical solution for processing the immense, multi-modal sensor data (LiDAR, camera, radar) required for L4 autonomous systems to perform highly accurate object detection, semantic segmentation, and intent prediction in these complex scenarios. The rapid closure of the quality gap between Chinese and US-based AI models in 2024, as cited in the Stanford AI Index Report, validates the maturity of domestic DL capabilities. This performance parity directly increases demand for domestic DL-powered autonomous driving software suites (e.g., Baidu Apollo), as they are proven to handle local road conditions effectively while adhering to China's strict data localization laws. The shift from basic L2 features to L4 robotaxis is entirely predicated on scaling the performance of DL algorithms, directly translating performance improvements into commercial demand.
By Application: Predictive Fleet Maintenance
The Predictive Fleet Maintenance (PFM) solutions segment is driven directly by the massive scale and economic constraints of commercial logistics and public transportation operators. With the number of connected IoT devices exceeding connected people in China as of August 2022, the prerequisite data stream from vehicle sensors is immense and readily available. PFM leverages Machine Learning (ML) to analyze real-time operational data, identifying subtle patterns indicative of component failure—for example, anomalies in battery temperature, motor vibration signatures, or tire pressure deviations—long before a human technician or a conventional diagnostic system would. This capability addresses the crucial commercial imperative of minimizing vehicle downtime. In large-scale operations, such as DiDi Chuxing's ride-hailing fleet or SAIC Motor's logistics division, every hour a vehicle is out of service represents a quantifiable revenue loss. Therefore, PFM creates immediate, calculable economic value by shifting maintenance from a costly, scheduled interval to an optimized, demand-driven event, directly increasing the procurement need for cloud-based, ML-powered fleet management platforms that promise verifiable reductions in operational expenditure and improvements in fleet utilization rates.
China AI in Transportation Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The Chinese AI in Transportation market is highly competitive, structured as a battle between established technology conglomerates, focused autonomous driving startups, and legacy automotive OEMs. This landscape features a core dynamic of platform-centric, full-stack providers vying against modular component suppliers. Key players leverage their core competencies—either data aggregation and software expertise or vehicle manufacturing capability—to secure their market position.
Baidu Apollo: Baidu's Apollo platform is strategically positioned as a comprehensive, open-source ecosystem that offers both a full-stack AI solution and modular services for various partners, from OEMs to local governments. Its strength lies in its data moat derived from providing over 14 million autonomous rides and recording 200 million kilometers of safe driving in China, as of late 2025. This vast, real-world operational data is crucial for continuously refining its deep learning models. Key product focus includes the Apollo Go autonomous ride-hailing service, which has achieved fully driverless urban deployment in some domestic areas. Baidu's strategy is to establish its platform as the foundational operating system for Intelligent Connected Vehicles (ICVs) nationwide.
Pony.ai: Pony.ai is strategically focused on the commercialization of its Level 4 "Virtual Driver" technology across both Robotaxi and Robotruck segments. Unlike platform providers, Pony.ai emphasizes its vehicle-agnostic, full-stack autonomous driving technology, which integrates proprietary software, hardware, and services. As of August 2025, the company operates a fleet of over 500 Robotaxis and over 170 Robotrucks, demonstrating a dual commercialization path that targets both passenger and logistics mobility. Their recent joint initiative with Stellantis to develop L4 autonomous vehicles for the European market, highlights a strategic move to export their technology and scale their commercial model globally, leveraging their Chinese experience to penetrate new markets.
Huawei: Huawei's strategic positioning pivots on supplying the Intelligent Digital Foundation rather than producing its own vehicles or operating a direct ride-hailing service. The company leverages its core competencies in Information and Communications Technology (ICT), 5G, and Cloud Computing to offer comprehensive smart transportation solutions for infrastructure and commercial logistics. Their key products, such as the Intelligent Horizontal Transportation 2.0 and Port Operation AI Agent, both released in September 2025, are designed to address critical industry pain points like mixed traffic control and operational optimization in large-scale environments like ports (e.g., Tianjin Port). This strategy targets high-value enterprise and public-sector contracts, utilizing a vehicle-road-cloud synergy model that deeply integrates AI into the transport environment.
China AI in Transportation Market Recent Developments:
China AI in Transportation Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 6.338 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 13.944 billion |
| Growth Rate | 17.08% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Technology, Deployment, Application |
| Companies |
|
China AI in Transportation Market Segmentation:
- BY TECHNOLOGY
- Deep Learning
- Natural learning process
- Machine Learning
- Others
- BY DEPLOYMENT
- On-Premise
- Cloud
- BY APPLICATION
- Route optimization
- Shipping volume prediction
- Predictive Fleet Maintenance
- Real-time Vehicle tracking
- Others