Report Overview
Nanofibrillar Cellulose Market - Highlights
Nanofibrillar Cellulose Market Size:
The Nanofibrillar Cellulose Market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 18.08%, attaining USD 551.112 million in 2030 from USD 240.123 million in 2025.
The Nanofibrillar Cellulose (NFC) market is undergoing a rapid transition from a laboratory curiosity to a high-value industrial material. This material, derived from renewable sources like wood pulp, is distinguished by its high aspect ratio, excellent mechanical strength, and superior gas barrier properties. NFC's unique characteristics are positioning it as a critical next-generation platform material across multiple high-performance and sustainability-driven sectors. The market’s accelerated commercialization phase is driven by manufacturers successfully scaling production and optimizing cost structures, which, in turn, is enabling broader adoption in previously cost-prohibitive applications such as high-performance composites and flexible electronics. This momentum confirms NFC as an indispensable component in the global shift toward a circular, bio-based economy.
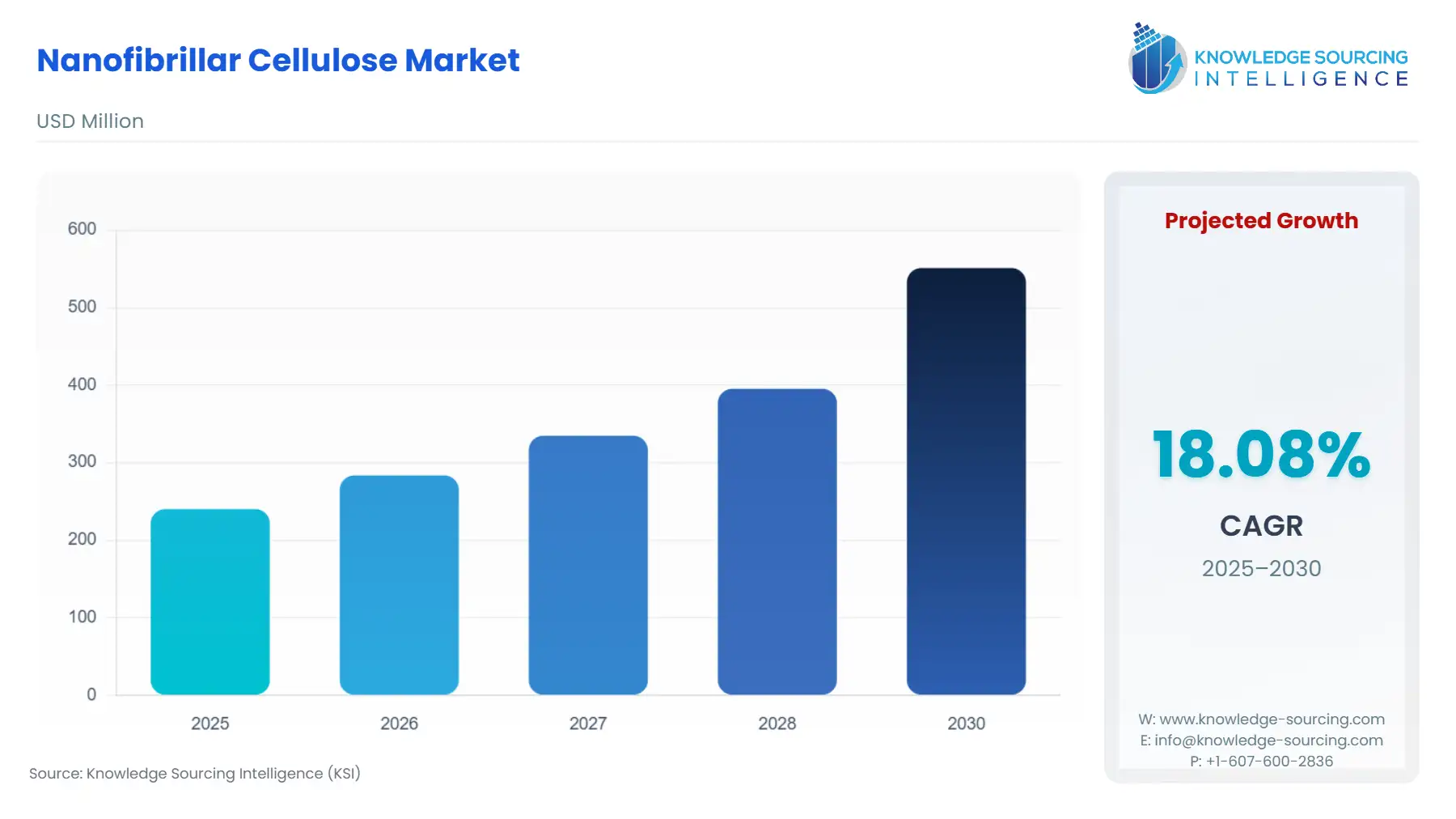
Nanofibrillar Cellulose Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers:
The primary factor propelling market expansion is the mandate for sustainable materials across industries, directly increasing demand for a renewable, biodegradable replacement for fossil-fuel derivatives. Legislative actions favoring bio-based products compel manufacturers to adopt NFC, which acts as a natural rheology modifier and a high-strength reinforcement agent. Automotive and aerospace lightweighting programs also directly spur demand; as Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) commercialize Nanofibrillar Cellulose-reinforced polyamide and polypropylene composites, the need for NFC as the core material escalates to achieve mandated fuel efficiency and performance standards. Furthermore, the imperative for improved food shelf-life creates specific demand for NFC in packaging, owing to its exceptional oxygen barrier properties.
- Challenges and Opportunities:
The key constraint facing the Nanofibrillar Cellulose market is the high initial capital expenditure required for large-scale, industrial-grade defibrillation and dewatering equipment, which raises the final product cost and hinders its competitive positioning against established commodity materials. This cost structure is a substantial barrier to high-volume application demand. Conversely, a significant opportunity lies in the burgeoning biomedical segment. The inherent biocompatibility and high surface area of NFC are creating a robust need for high-value applications, including injectable hydrogels, tissue engineering scaffolds, and advanced drug delivery systems, offering a premium market for specialized NFC grades. Moreover, global initiatives aimed at standardizing material grades will facilitate consistent product quality, further simplifying integration into manufacturing supply chains, thus boosting demand.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis:
Nanofibrillar Cellulose, a physical material, is predominantly sourced from wood pulp, which provides a stable and high-volume supply chain owing to the mature global pulp and paper industry. This dominance, accounting for approximately 58% of the market, is a function of both abundance and the developed processing infrastructure. Pricing dynamics are complex, influenced heavily by the high-energy consumption of the production process (e.g., homogenization, grinding). While raw cellulose is inexpensive, the cost of the final NFC product remains high due to the intensive processing required to achieve nanoscale fibrillation. However, commercialized process innovations, such as enzymatic hydrolysis, have begun to cut the high energy overhead—reducing it in some cases from over 15,000 kWh/ton to 5,000 kWh/ton—thereby introducing downward pressure on the final product price and improving market accessibility.
- Supply Chain Analysis:
The global Nanofibrillar Cellulose supply chain is currently concentrated at the production and innovation stage within key forest-rich regions, specifically Scandinavia, North America (Canada), and Japan. These regions are primary production hubs, leveraging local access to abundant wood pulp feedstock. Logistical complexities center on the material's form: NFC is often produced and shipped as a dilute aqueous gel to prevent irreversible aggregation (hornification), which results in high transportation costs for the water content. Consequently, the market is seeing a strategic shift toward establishing decentralized, regional manufacturing facilities near end-user industrial clusters to minimize high-volume shipping of dilute products and to secure resilient, low-carbon-footprint supply chains that meet localized demand for intermediate material forms.
Nanofibrillar Cellulose Market Government Regulations:
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Food and Drug Administration (FDA) / TSCA (Toxic Substances Control Act) | The FDA's ongoing, yet cautious, approach to approving NFC for direct food contact applications (as a stabilizing agent or thickener) for certain modified forms creates a regulatory bottleneck that slows immediate uptake in the high-volume Food & Beverage sector, thereby tempering demand. |
| European Union | REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) | REACH registration mandates for nanomaterials require extensive safety and toxicological data. This high-cost, time-intensive compliance requirement acts as a high barrier to entry for smaller manufacturers but simultaneously validates the safety of successfully registered materials, promoting confidence and eventual large-scale demand. |
| Japan | Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) / R&D Initiatives | METI’s substantial, sustained governmental funding and strategic national R&D programs for next-generation materials actively de-risk commercialization for domestic producers like Nippon Paper, accelerating technological maturity, production scaling, and thus, stimulating domestic and global demand. |
Nanofibrillar Cellulose Market Segment Analysis:
- By Application: Smart Coatings The Smart Coatings segment is critically driven by the necessity for advanced functionality on various surfaces without compromising sustainability. NFC-based coatings are seeing high demand in the electronics sector for creating transparent, flexible conductive films used in displays and sensors. This necessity is driven by NFC’s exceptional optical transparency coupled with its ability to act as a robust matrix for conductive elements like silver nanowires or carbon nanotubes. For instance, the need for flexible electronics requires a substrate that is both strong and transparent, which NFC uniquely provides as a bio-based alternative to glass or synthetic polymers. Furthermore, its ability to significantly enhance the scratch resistance and barrier properties of industrial and protective coatings creates specific demand in the high-end automotive and infrastructure sectors.
- By End-User Industry: Biomedical The Biomedical industry represents a high-growth, premium segment whose demand for Nanofibrillar Cellulose is directly driven by the material's unparalleled biocompatibility, non-toxicity, and highly tunable mechanical properties. NFC's hydrogel-forming capability is a key growth catalyst, enabling the development of advanced systems such as injectable scaffolds for tissue regeneration and as a protective matrix for live cells in 3D bioprinting. The material's structure closely mimics the natural extracellular matrix, making it ideal for encouraging cell proliferation and differentiation, which drives its uptake in regenerative medicine research. Moreover, its high surface area and modifiable chemistry spur demand for its use in advanced wound dressings as a high-capacity absorbent and in drug delivery systems as a carrier for targeted, controlled release of therapeutics.
Nanofibrillar Cellulose Market Geographical Analysis:
- US Market Analysis (North America)
The US market for Nanofibrillar Cellulose is characterized by robust, specialized demand, primarily within the high-performance composites and biomedical sectors. Local factors, specifically the increasing regulatory pressure for reducing vehicle weight to meet strict emission and fuel economy standards, are creating direct demand for NFC-reinforced polymer composites in the automotive supply chain. Additionally, substantial government and academic funding for advanced materials research, often channeled through agencies promoting sustainable technology, supports the demand for high-purity NFC grades required by the nation's leading medical device and tissue engineering companies.
- Brazil Market Analysis (South America)
The Brazilian Nanofibrillar Cellulose market is principally driven by its powerful Pulp & Paper industry and its vast agricultural base. Brazil, as a major global pulp producer, possesses an abundant and cost-effective supply of wood and non-wood cellulosic feedstocks, which is a major local factor supporting the establishment of domestic NFC production capacity. Market expansion is subsequently driven by utilizing NFC as an additive to enhance the strength and printability of paper and paperboard, directly improving the quality of locally produced packaging materials for its large domestic market and for export.
- Germany Market Analysis (Europe)
The German market's need for Nanofibrillar Cellulose is underpinned by its stringent environmental policies and its globally leading Automotive and Advanced Manufacturing sectors. Germany’s powerful push toward a circular economy and the EU's mandates favoring bio-based alternatives strongly propels the adoption of NFC. Specific local demand arises from Tier 1 automotive suppliers seeking to integrate NFC into interior and exterior components for both lightweighting and material sustainability, often driven by the competitive desire of major German car manufacturers to advertise a reduced carbon footprint in their flagship models.
- Saudi Arabia Market Analysis (Middle East & Africa)
The need for Nanofibrillar Cellulose in Saudi Arabia is an emerging market primarily driven by applications in the Oil & Gas sector and water treatment. Local demand centers on utilizing NFC’s unique rheological properties as an advanced additive in drilling fluids and cementing operations to enhance performance in extreme downhole conditions. Furthermore, the imperative for water security in the arid region creates focused demand for NFC-based filtration membranes and adsorbents, leveraging the material's high surface area for efficient separation and purification processes.
- China Market Analysis (Asia-Pacific)
The colossal and rapidly expanding Packaging, Textiles, and Construction sectors in China are the chief growth drivers for Nanofibrillar Cellulose. The rapid expansion of the domestic e-commerce market necessitates a massive volume of packaging, creating high demand for NFC as an additive to improve the mechanical strength and barrier properties of paper-based packaging, often replacing plastic films. The central government’s focus on industrial modernization and materials science research provides an institutional framework that supports local enterprises in scaling NFC production for high-volume, cost-sensitive industrial applications.
Nanofibrillar Cellulose Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The Nanofibrillar Cellulose market features a competitive landscape dominated by established players from the traditional forest products industry and specialized material science firms. Competition is bifurcated: high-volume capacity and cost optimization from former pulp and paper entities, versus high-purity, application-specific innovation from dedicated nanotech companies. Strategic positioning revolves around securing feedstock supply, optimizing energy-intensive production processes, and forming joint ventures with end-user industry players to accelerate commercial adoption.
- Nippon Paper Industries Co., Ltd.: Nippon Paper's strategy is one of vertical integration and product diversification, leveraging its core competency in wood pulp processing. The company’s positioning is solidified by its world-leading production scale in completely individualized TEMPO-oxidized CNF, with a significant facility dedicated to this product in Ishinomaki, Japan, possessing an annual capacity of 500 tons. A key product is their Carboxymethylated CNF (CM-CNF), which is specifically targeted as an additive for food and cosmetics, utilizing its unique characteristics like low temperature dependence of viscosity. The company announced the launch of a CNF mass production facility at the Gotsu Mill in September 2017 for food and cosmetics applications, demonstrating a strategic move into high-value additive markets.
- Alberta Innovates: This organization positions itself as an innovation catalyst and technology validator, focused on de-risking the material for industrial adoption in North America. Their strategic involvement included the launch of a pilot facility, the first in Canada, to produce Nanocrystalline Cellulose (NCC) from wood and straw pulp. This $5.5-million initiative was designed to supply researchers and commercial partners with up to 100 kg per week of NCC for testing in diverse applications, including automotive components, packaging, and building materials. Their objective is not volume production but rather to accelerate the development of a regional value-added bio-industrial sector by providing technical expertise and world-class facilities to validate commercial promise.
- UPM: UPM is strategically transforming into a material solutions company, positioning Nanofibrillar Cellulose as a key offering within its renewable fibers and advanced materials portfolio. The company leverages its deep expertise in forest management and eucalyptus pulp production to ensure a consistent, sustainable raw material supply. While specific, large-scale CNF production capacity announcements were not identified in the immediate recent period, UPM's broader strategy emphasizes value-enhancing growth in advanced materials, specialty papers, and flexible packaging. This commitment to renewable fibers positions them to capture increasing market share as packaging and labeling sectors escalate their demand for bio-based barrier and strength-enhancing additives.
Nanofibrillar Cellulose Market Recent Market Developments:
- May 2025: Nippon Paper Industries, through one of its consolidated subsidiaries, celebrated the completion of a new factory for Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) for use in Lithium-ion Battery (LiB) applications. While CMC is a chemically distinct cellulose derivative, this event signifies the company’s continuing strategic commitment and capacity expansion in high-performance, specialty cellulose-based functional materials for the Electronics sector, which directly underpins their strategic positioning for NFC-based battery and electronic component applications.
- 2024: Nippon Paper Industries commenced the supply of its nanocellulose product, "Cellenpia," for integration into resins in 2024, with a stated target of producing 100,000 automotive components annually. This product launch and subsequent commercial supply indicate a clear market shift, demonstrating the successful technical validation and industrial-scale integration of Nanofibrillar Cellulose as a reinforcing filler in plastic composites for the arduous, high-specification automotive end-user industry.
Nanofibrillar Cellulose Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 240.123 million |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 551.112 million |
| Growth Rate | 18.08% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Source, Application, End-User Industry, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Nanofibrillar Cellulose Market Segmentation:
- BY SOURCE
- Cotton
- Wood Pulp
- Others
- BY APPLICATION
- Smart Coatings
- Responsive Textiles
- Biosensors
- Shape-Memory Materials
- Others
- BY END-USER INDUSTRY
- Packaging
- Automotive
- Biomedical
- Paper & Pulp
- Electronics
- Textiles
- Others
- BY GEOGRAPHY
- North America
- USA
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- France
- Spain
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Taiwan
- Thailand
- Indonesia
- Others