Report Overview
Russia Probiotics Market - Highlights
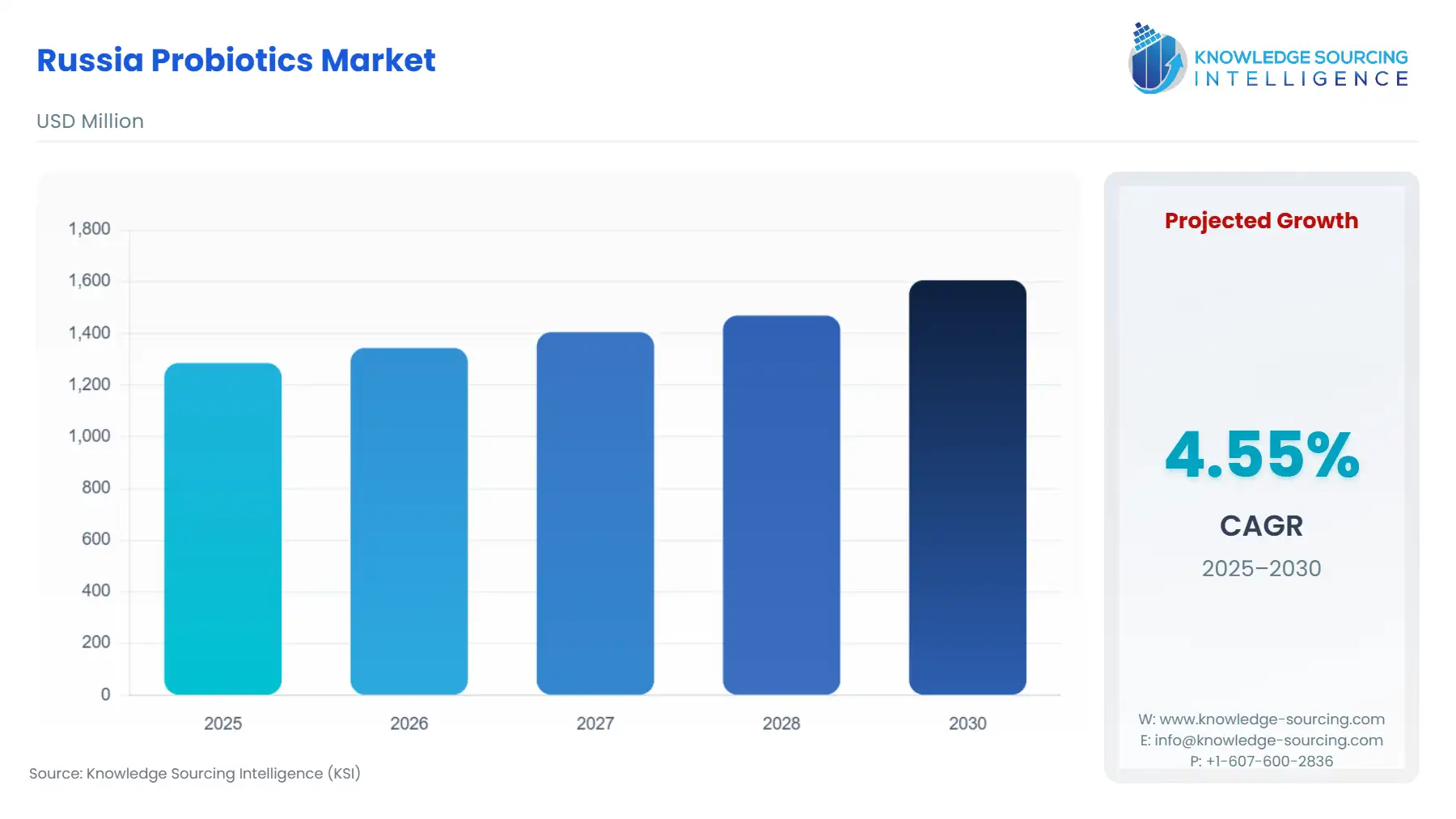
Russia Probiotics Market Size:
The Russian probiotics market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 4.55% over the forecast period to reach a market size of US$1,606.290 million in 2030, from US$1285.62 million in 2025.
Russia Probiotics Market Introduction:
The probiotic market in Russia is developing rapidly in both human and animal health. A policy was implemented on 1 March 2025 that limited the use of prophylactic antibiotics in animal husbandry. This attempt to replace antibiotics has stimulated faster development of domestic probiotic and synbiotic alternatives that could serve as sustainable and effective alternatives. The relationship between basic science and applied science has never been more important. For example, a collaborative project currently underway between scientists at Far Eastern Federal University (FEFU) and scientists at the Arnika R&D Centre is developing "next-generation" probiotics that utilize polysaccharides derived from marine resources with benign microbial therapeutics. The project has secured funding through the national program Priority 2030. It aims to produce next-generation probiotics for inclusion in livestock feeds as substitutes for antibiotics by 2026–27.
In a similar example, researchers from Kazan Federal University have developed synbiotic feed additives that use probiotics immobilised on mineral carriers, such as zeolite and bentonite. It is projected that these novel preparations will enhance gut health, improve nutrient efficiency, and boost survival rates in livestock. These synbiotics will address a market with increasingly higher production efficiencies; livestock mortality rates can be as high as 20%, so increased health and productivity may offer reductions up to this level. An increasingly large portion of the domestically produced pharmaceutical drug distribution is reflected in the analysis of the Russian drug register. Among all of the probiotic products recorded, 62.1% of these products, for example, maps associated with multistrain probiotic capsules, sachets, and lyophilised bacterial suspensions, are now manufactured by Russian firms. Compared to other years, domestic interactions with the yoghurt industry may suggest increased dosage forms for topical sprays and oral drops.
Lastly, in the agriculture aspect, the Russian feed sector is upgrading consistently; the government agencies are aiming to improve feed conversion efficiency by 10-12% by 2025, and saving costs of up to 15% (namely). Then, to support this partially state-funded initiative, nearly ?700 million is being allocated yearly to work on the design and development of your probiotics, prebiotics, and other sustainable interventions that will support the future of animal nutrition. There are multiple ways to segment the market, such as by form, type, end-user, function, and application.
Russia Probiotics Market Overview
Report Metric
Details
Study Period
2021 to 2031
Historical Data
2021 to 2024
Base Year
2025
Forecast Period
2026 – 2031
:
Historically, support to farmers was mostly provided by high-income countries, but in recent years, such support has also become widespread in several emerging countries, in some cases to support an objective of domestic self-sufficiency in certain products. This is the case in the Russian Federation, for instance, where the government sets production targets for several agricultural commodities, inclusive of but not limited to meat, among others, and provides various forms of financial support to farmers. Nevertheless, the meat import ban imposed by the Russian Federation until the end of 2019, combined with the depreciation of its currency, has resulted in increased domestic prices, which in turn will aid in stimulating the country’s meat production. By 2028, meat production in Russia is expected to reach 11218 ktcwe; meat consumption is expected to reach 11648 ktcwe; and fish and seafood production are estimated to attain levels of 5537 kt. To this extent, it should be noted that in early November 2019, the Russian Agricultural Ministry presented a new feed and feed additives development program, in which it was officially acknowledged that optimization of livestock production required the integration of modern feeding technologies, high-quality feed, and feed additives. This suggests that there is a proactive initiative from the Russian government that has the potential to expand the Russian probiotics market for animal feed use during the forecast period. Cellobacterinan Enzymatic Probiotic for Cattle was acquired by a Russian company, BIOTROF, which claims to have microorganisms that produce bacterial cellulases and has been introduced into the feed industry.
The probiotics industry in Russia is experiencing an extraordinary evolution due to a growing understanding of digestive health and immune support for consumers, coupled with changing regulations. Traditional fermented foods, such as kefir and sauerkraut, remain staples in the Russian diet, and modern probiotics in the form of functional foods, supplements, or animal feed are now gaining popularity. This cultural base fits well with public health objectives and agri?industrial goals.
Regulatory developments from Rospotrebnadzor, the Federal Service for the Oversight of Consumer Protection and Welfare, incorporate additional labelling requirements for probiotic products. Strain names, live culture counts, and shelf?life must be clearly stated on labels to enhance transparency and protect consumers. The Russian Federal Bureau of Technical Regulations and Metrology formally adopted "Probiotic Food Safety and Hygiene Requirements". The "Requirements" address hygiene compliance specific to probiotic?enriched foods.? Policy directed at agriculture is one of the few viable pathways for probiotic growth in livestock applications. The Ministry of Agriculture launched programs to modernize feed technology and additives to stimulate animal health and productivity.
Legislation set to start on September 1, 2024, broadens state aid for feed additive and enzyme producers by providing financial access to subsidised loans and investment reimbursements, an important step to ensure domestic manufacturing capabilities and reduce dependence on imports. In March 2025, Prime Minister Mishustin announced that producers who modernize or build food and feed additive facilities will be eligible for future cost reimbursements of up to 20%. This measure aims to promote regional development and enhance agricultural sovereignty.
In addition to this type of policy incentives, funding for specific areas of R&D is readily available. Research institutions in Russia, such as Kazan Federal University, are collaborating with firms in the biotechnology sector to develop next?generation synbiotics (probiotics and prebiotics) employing mineral carriers, enhancing delivery, and encouraging environmentally safe livestock practices These developments, taken together, indicate a vibrant and strong environment encouraging probiotics to enter the market for both humans and animals.
The government is involved in public health regulation, agricultural modernisation, research funding, and industrial subsidies for probiotics, combining public health improvements with dairy for agri?industrial goods. This collaborative effort will hasten the penetration of probiotics into functional foods, dietary supplements, and feed. This will allow time for innovative products and quality assurance to keep pace with consumer and grower demands. Overall, this restructuring creates a stronger and more resilient probiotics market in Russia that is capable of responding to wider health and agri?industrial objectives.
In comparing the 5 billion RUB in fermented feed and the 0.7 billion RUB in prebiotics and probiotics, it illustrates Russia's continuous, but cautious, transition to microbiome feed technology. Fermented feed is continuing to receive the vast majority of funding. The dedicated 700 million rubles for probiotics and prebiotics is a meaningful policy indicator of change and especially noteworthy because of an upcoming national ban on prophylactic antibiotics in livestock.. The funding shift suggests probiotics will no longer be mistaken for a niche additive. Rather, they are entering a more mainstream consideration as a functional component of Russia's agriculture reform initiative. The absolute spending leaves a smaller impression when compared to fermented feed, but this is an indication of building trust in science-based and targeted applications for microbial solutions that offer effective solutions on animal gut health, immunity, and feed efficiency without the additional risk of antibiotic residues.
This public funding in the Russian probiotic market today is creating an environment conducive to local innovation, commercialisation, and regulatory acceleration in feed-grade probiotics. It is also encouraging further alignment of biotech companies and feed companies with the government representation's priorities in addressing other opportunities to create faster conversion into practice, making optional subsidy support more enticing. As the industry evolves, there is a noticeable shift from traditional methods toward biologically advanced alternatives. This change positions the probiotics sector as a promising growth area within Russia's livestock and veterinary industries.
Russia Probiotics Market Drivers:
- Rising awareness about health and preventative care
Russia is witnessing a surge in innovation in a variety of food and beverage segments because of a myriad of factors, such as the growing awareness of consumers about various health benefits that are attributed to newer sources of nutrition than the traditional ones. Furthermore, the rising health consciousness coupled with allergies that consumers have developed towards dairy and meat products has steered the players in the food and beverage sector to fortify their products with probiotics to enable the consumers to maintain pristine gut health while simultaneously savouring their favourite snack and or food preparation. Furthermore, the emergence of a current pandemic, such as the recent outbreak of COVID-19, which has affected individuals in most of Eurasia and resulted in fatalities, has prompted consumers to prioritise their immune systems more than ever before, incorporating all viable measures to strengthen them. This change has placed significant emphasis on the role of probiotics in food.
Probiotics offer numerous health benefits, including improved digestive balance, enhanced immune function, better mental health, and healthier skin. Strains like Lactobacillus are known to help prevent acute diarrhoea, cardiovascular infections, cancer, cystic fibrosis, dental caries, and other diseases. Growing awareness of these preventive health benefits is driving increased consumer demand for probiotic products in Russia.
The Russian organic and healthy food market continues to exhibit robust growth, maintaining an annual expansion rate of approximately 10% in recent years. The primary catalyst behind this growth is the increasing health awareness among Russian consumers. Public opinion polls reveal that around 75-80% of Russians strive to lead a healthy lifestyle, with about 70% actively monitoring their health through regular check-ups and approximately 60% consciously choosing to eat healthily. Thus, the market is set to expand, especially among those with higher disposable incomes.
There is a notable growth in liquid probiotics in Russia, driven in part by the success of Bio-Vesta Group, a pioneer in this segment. Bio-Vesta was the first company in Russia to establish industrial production of liquid probiotics, offering products with high concentrations of live beneficial bacteria. (JSC-Russian Export Center)
This growth is further supported by global industry players providing a wide range of accessible products and government incentives promoting local production, such as support of the Export Support Center of the Novosibirsk Region and the Ministry of Industry, Trade and Entrepreneurship Development of the Novosibirsk Region, among others in export of probiotics Consumer acceptance and ongoing investment in research and development continue to fuel innovation, expanding the probiotics market in Russia.
As probiotics gain recognition as an effective preventive health option, their market in Russia is poised for continued growth.
Russia Probiotics Market Segmentation Analysis:
- Functional food and beverages are rising in popularity
By Application, the Russian Probiotics Market is segmented into functional food and beverages, dietary supplements, and animal feed. Functional foods are enriched with additional ingredients like probiotics, vitamins, minerals, fiber, or plant extracts that help in improving digestion, boosting immunity, and supporting overall health. As the Russian market is experiencing increasing health awareness and demand for healthy foods, as illustrated by various reports, it is also leading to expansion in functional foods and beverages such as Kefir, fortified juices, and others. As probiotics turn everyday foods and beverages into health-supporting products, their inclusion in the diet makes functional foods more effective, marketable, and desirable to health-conscious consumers, leading the Russian market to grow at a significant rate.
According to the Centre for Interdisciplinary Studies of Human Potential of RANEPA, dairy products constitute 13% of the total production of functional or health-related foods in Russia. Dairy products such as kefir and yogurt are well-known carriers of probiotics and form a critical segment of the Russian probiotics market. The substantial production of dairy and other beverages creates a strong foundation for the growth of probiotic-enriched functional foods and beverages. As consumer awareness of the health benefits of probiotics rises, the demand for probiotic-containing functional products will also increase significantly, driving market expansion in Russia.
Thus, the functional foods and beverages segment will grow rapidly. Continuous new product launches, innovation in probiotic formulations, and the rising penetration of modern retail and online distribution channels are making these products more accessible to consumers. Additionally, increasing investments by global players such as Yakult, Nestlé, and Danone are contributing significantly to the growth of the Russian probiotics market.
The Russia–Ukraine conflict and subsequent Western sanctions have significantly impacted the Russian market, particularly affecting global players in the functional foods sector such as Yakult and Nestlé. For example, Nestle, as per its press release, has drastically reduced its portfolio in Russia and implemented the actions.
However, despite these disruptions, some multinational companies have responded by localizing operations, rebranding products, or forming strategic partnerships to maintain their foothold in the growing Russian probiotics and functional foods market. For instance, in July 2023, Danone rebranded its popular probiotic dairy brand Activia to AktiBio in Russia. This move is part of a broader “localisation” strategy, allowing the French multinational to maintain market presence while adapting to shifting geopolitical and regulatory dynamics.
Russia Probiotics Market Recent Development and Expansions
- In 2025, Nestlé is expanded its reach with the new infant formula, which will be sold under Nestlé’s NAN brand.
- On July 20, 2022, A team of scientists from Russia's Kazan Federal University intends to combine probiotics with agricultural minerals to create a new class of feed additives known as synbiotics. The study's ultimate goal is to develop a new antibiotic alternative, as the Russian government's restrictions on the use of in-feed antibiotics beginning in January 2022 have forced livestock companies to adjust feed rationing.
Russia Probiotics Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
| Russia Probiotics Market Size in 2025 | US$1,285.62 million |
| Russia Probiotics Market Size in 2030 | US$1,606.290 million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 4.55% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Million |
| Segmentation |
|
| List of Major Companies in the Russia Probiotics Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Market Segmentation
- By Application
- Functional Food and Beverages
- Dietary Supplements
- Animal Feed
- By End-User
- Human
- Animal
- By Function
- Regular
- Preventative Healthcare
- Therapeutic
- By Type
- Lactobacillus
- Streptococcus
- Bifidobacterium
- Spore Formers
- Others
- By Form
- Liquid
- Dry