Report Overview
South Korea 5G Fuel Highlights
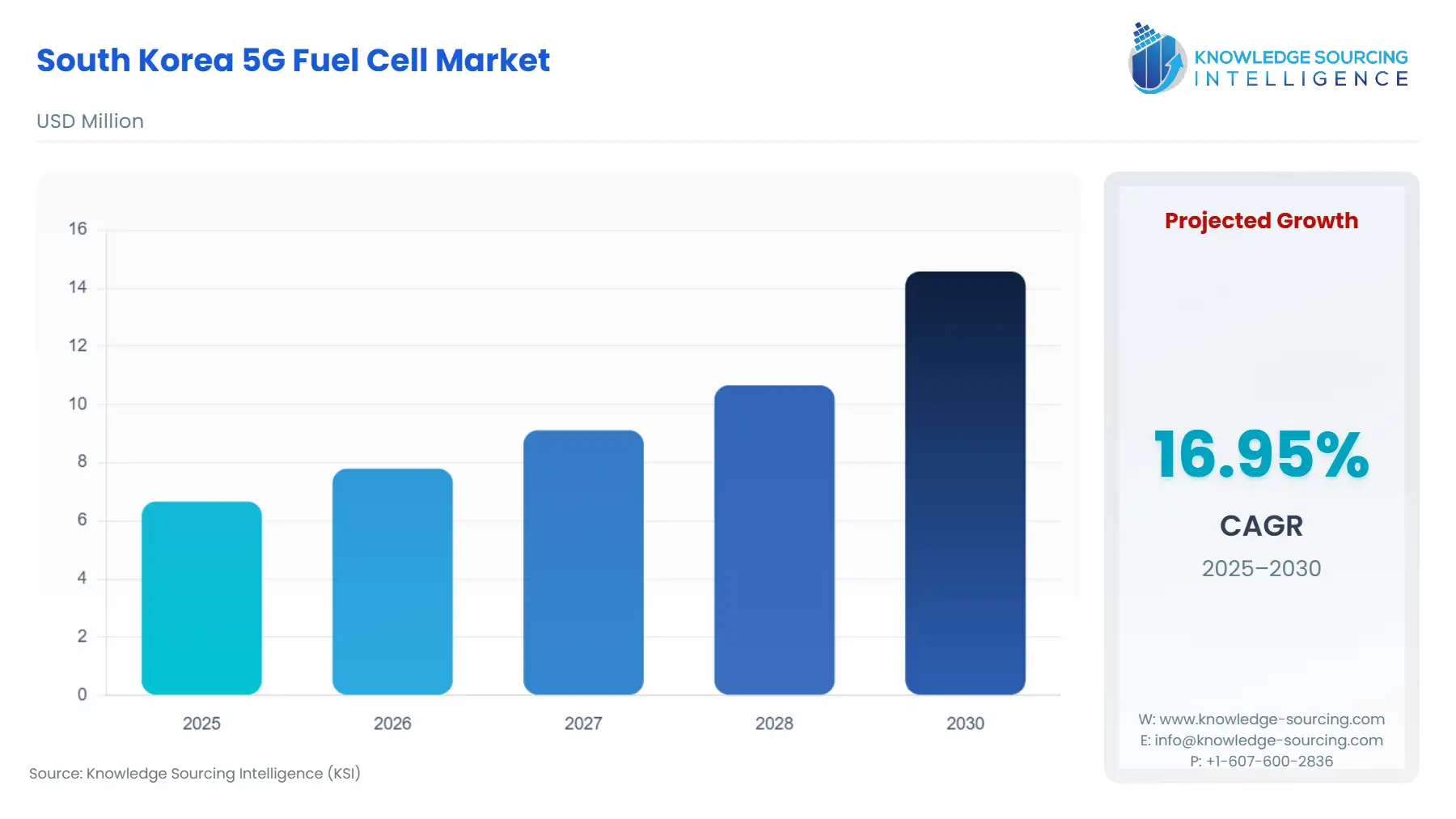
South Korea 5G Fuel Cell Market Size:
The South Korea 5G Fuel Cell Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 16.95%, reaching USD 14.582 million in 2030 from USD 6.664 million in 2025.
The South Korean 5G Fuel Cell market operates at the critical intersection of advanced telecommunications infrastructure and the nation's ambitious clean energy transition. Having been the first country globally to launch commercial 5G services, South Korea embarked on an intensive network densification drive, characterized by a proliferation of base stations, small cells, and radio units. This rapid rollout, while delivering world-leading connectivity, simultaneously created a severe energy consumption challenge, with 5G networks requiring substantially more power than previous generations. Fuel cells, particularly Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) and Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC), have emerged as an indispensable backup and potential primary power solution. The market is defined by a unique confluence of top-down government mandates promoting a hydrogen economy and bottom-up operational pressure on mobile operators (SK Telecom, KT, and LG Uplus) to mitigate rising energy costs and ensure network stability, thereby channeling significant capital investment into fuel cell technology specifically for telecommunication sites.
South Korea 5G Fuel Cell Market Analysis:
Growth Drivers
The imperative for network reliability directly propels demand, as 5G services—such as autonomous vehicles and industrial IoT—mandate ultra-low latency and uninterrupted operation, making traditional battery backup insufficient for extended outages. This high-availability requirement forces telecom operators and tower providers to invest in extended-run backup power systems, a core value proposition of fuel cells. Concurrently, the Hydrogen Economy Roadmap 2040 provides a critical regulatory push, creating a guaranteed domestic market and offering substantial incentives for hydrogen deployment across all energy sectors. This government support reduces market risk for fuel cell manufacturers and lowers the total cost of ownership for end-users, thereby increasing the commercial viability and adoption rate of fuel cell systems for 5G applications.
Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge constraining immediate widespread adoption is the high initial capital expenditure (CapEx) associated with fuel cell systems compared to incumbent battery technologies, which presents a significant barrier to entry, particularly for smaller tower and infrastructure providers. This cost structure suppresses initial demand volumes. However, a major opportunity lies in vertical integration and standardization. By localizing the manufacturing of key components, such as fuel cell stacks, and developing standardized, modular solutions for various 5G site configurations (macro, micro, and small cells), manufacturers can reduce unit costs through economies of scale. This transition from customized solutions to standardized products will directly stimulate demand by making the CapEx outlay more palatable to major MNOs.
Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The 5G fuel cell market, specifically for PEM technologies often favored for telecom backup power due to rapid startup, is critically reliant on Platinum Group Metals (PGMs), particularly platinum, which acts as the catalyst in the fuel cell stack. South Korea is almost entirely dependent on imports for PGMs, with the majority of global production and reserves concentrated in regions such as South Africa and Russia. This globalized, geopolitically sensitive supply chain creates inherent price volatility for a key Bill of Materials component, increasing the manufacturing cost and, consequently, the final product price. The World Platinum Investment Council notes that South Korea’s overall hydrogen plans could increase the demand for platinum significantly by 2030, putting upward pressure on material costs, forcing manufacturers to focus heavily on catalyst recycling and reducing platinum loading to stabilize pricing and sustain market growth in the price-sensitive telecom sector.
Supply Chain Analysis
The South Korean 5G fuel cell supply chain exhibits a dual nature: highly localized final assembly and system integration coupled with deeply globalized component sourcing. Key production hubs for the final product reside primarily in South Korea, involving major domestic players like Doosan Fuel Cell and S-Fuelcell. However, the supply chain for core components, such as the Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) stacks and high-pressure hydrogen tanks, often relies on specialized global manufacturers. This dependency introduces significant logistical complexities and geopolitical dependencies, particularly for PGMs and specialized membrane materials. The domestic manufacturing push, supported by the Hydrogen Economy Roadmap, aims to mitigate this risk by incentivizing local component production, thereby creating a more robust, domestically-controlled supply chain for the nation's critical communication infrastructure.
Government Regulations
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| South Korea | Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) | MSIT mandates and actively promotes rapid 5G network rollout, including spectrum allocation and shared rural network infrastructure. This densification creates thousands of new power nodes requiring reliable backup, directly increasing the addressable market and demand for fuel cells. |
| South Korea | Hydrogen Economy Roadmap (2019) | This national strategy sets ambitious targets for fuel cell power generation, offering financial incentives, subsidies, and R&D support. It de-risks investment for manufacturers and lowers CapEx for operators, acting as a powerful market catalyst that pushes the adoption curve forward. |
| South Korea | Telecommunications Business Act (Subordinate Regulations) | Regulations concerning network stability and power reliability ensure MNOs allocate sufficient resources for uninterruptible power supply (UPS) at base stations, establishing a foundational regulatory demand for resilient backup solutions like fuel cells. |
South Korea 5G Fuel Cell Market Segment Analysis:
By Application: Backup Power Solutions
Backup Power Solutions represent the most immediate and substantial demand segment in the South Korean 5G Fuel Cell Market. The massive densification of the 5G network—involving hundreds of thousands of base stations, particularly in high-frequency bands like 3.5 GHz—necessitates a robust, long-duration backup solution. Traditional battery systems are bulky, require constant maintenance, and offer limited run-times, which becomes critically insufficient for extended power outages that could disrupt essential 5G services like remote healthcare or emergency response systems. Fuel cells directly address this demand gap by providing hours to days of uninterruptible power at a consistent voltage. The growth driver is rooted in the high service availability mandate for 5G, where downtime is financially punitive and operationally unacceptable. MNOs are increasingly replacing or augmenting existing lead-acid or lithium-ion batteries with fuel cell systems to meet heightened reliability requirements imposed by the network's mission-critical nature.
By End-User: Telecom Operators
Telecom Operators (SK Telecom, KT, and LG Uplus) are the primary growth factor, driving the market through large-scale capital investments in their network infrastructure. Their specific growth driver is a strategic focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) reduction and compliance with national decarbonization goals. While 5G networks offer high throughput, they also consume approximately three times the energy of 4G, making energy costs a rapidly escalating component of operational expenditure (OPEX). Fuel cells, which offer high efficiency and a pathway to cleaner energy consumption when running on hydrogen, provide a strategic advantage by mitigating fluctuating electricity prices and supporting corporate sustainability mandates. The operators procure fuel cells not just as a power source, but as a component of their overall energy strategy, seeking to deploy high-capacity solutions (50 kW and above for major hub sites) to stabilize the core network and ensure competitive service quality.
South Korea 5G Fuel Cell Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The competitive landscape is defined by the strategic maneuvering of domestic industrial powerhouses capitalizing on national hydrogen policy, alongside international specialists penetrating the market through local partnerships. The market sees direct competition among domestic fuel cell system integrators and specialized technology providers.
Doosan Fuel Cell Co. Ltd.
A major domestic leader, Doosan specializes in Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (PAFC) and Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) technologies, traditionally focused on large-scale power generation. Their strategic positioning leverages the vast resources and industrial footprint of the Doosan Group. The company has explicitly pursued expansion into mobile and distributed power, aiming to localize the manufacturing of SOFC stacks by 2024 to reduce costs and secure the domestic supply chain. Their focus is on supplying high-capacity fuel cell systems, often exceeding 50 kW, for centralized 5G network nodes and larger infrastructure projects, aligning their offerings with the long-term, high-power targets of the Hydrogen Roadmap.
S-Fuelcell Co., Ltd.
This company focuses on decentralized and residential fuel cell solutions, but is a key competitor in the smaller-capacity segment, which is highly relevant for 5G small cell and remote applications. Their strategy centers on providing compact, highly modular PEM fuel cell systems. By specializing in systems below 5 kW, they target the rapidly proliferating number of remote and difficult-to-access 5G repeater sites, where the small footprint and zero-emission profile of PEM fuel cells offer a distinct logistical advantage over diesel generators or large battery arrays.
South Korea 5G Fuel Cell Market Recent Developments:
- July 2025: Doosan Fuel Cell started full-scale mass production of solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) systems, leveraging licensed UK technology from Ceres, at its new 50 MW facility in South Korea. This initiative aims to supply clean power systems for commercial, industrial, and AI data centers, significantly boosting domestic SOFC market capabilities and reducing import reliance.
- March 2025: Hyundai Motor reached an agreement with its labor union to build a new, large-scale hydrogen fuel cell plant at its Ulsan manufacturing complex. This is a key step to centralize production and accelerate the development of its hydrogen fuel cell value chain, supporting its goal of expanding hydrogen usage.
South Korea 5G Fuel Cell Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 6.664 million |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 14.582 million |
| Growth Rate | 16.95% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Product Type, Deployment, Power Output Range, End-User |
| Companies |
|
South Korea 5G Fuel Cell Market Segmentation:
- BY PRODUCT TYPE
- Fuel Cell Systems
- Fuel Cell Stacks & Components
- Fuel Supply Solutions
- BY DEPLOYMENT
- Backup Power Solutions
- Off-grid / Remote Power Solutions
- Hybrid Energy Systems
- High-capacity Solutions
- BY POWER OUTPUT RANGE
- <5 kW
- 5–50 kW
- 50 kW
- BY END USER
- Telecom Operators
- Tower & Infrastructure Providers
- Government & Defense Communication Networks
- Enterprise 5G Networks