Report Overview
Japan 5G Fuel Cell Highlights
Japan 5G Fuel Cell Market Size:
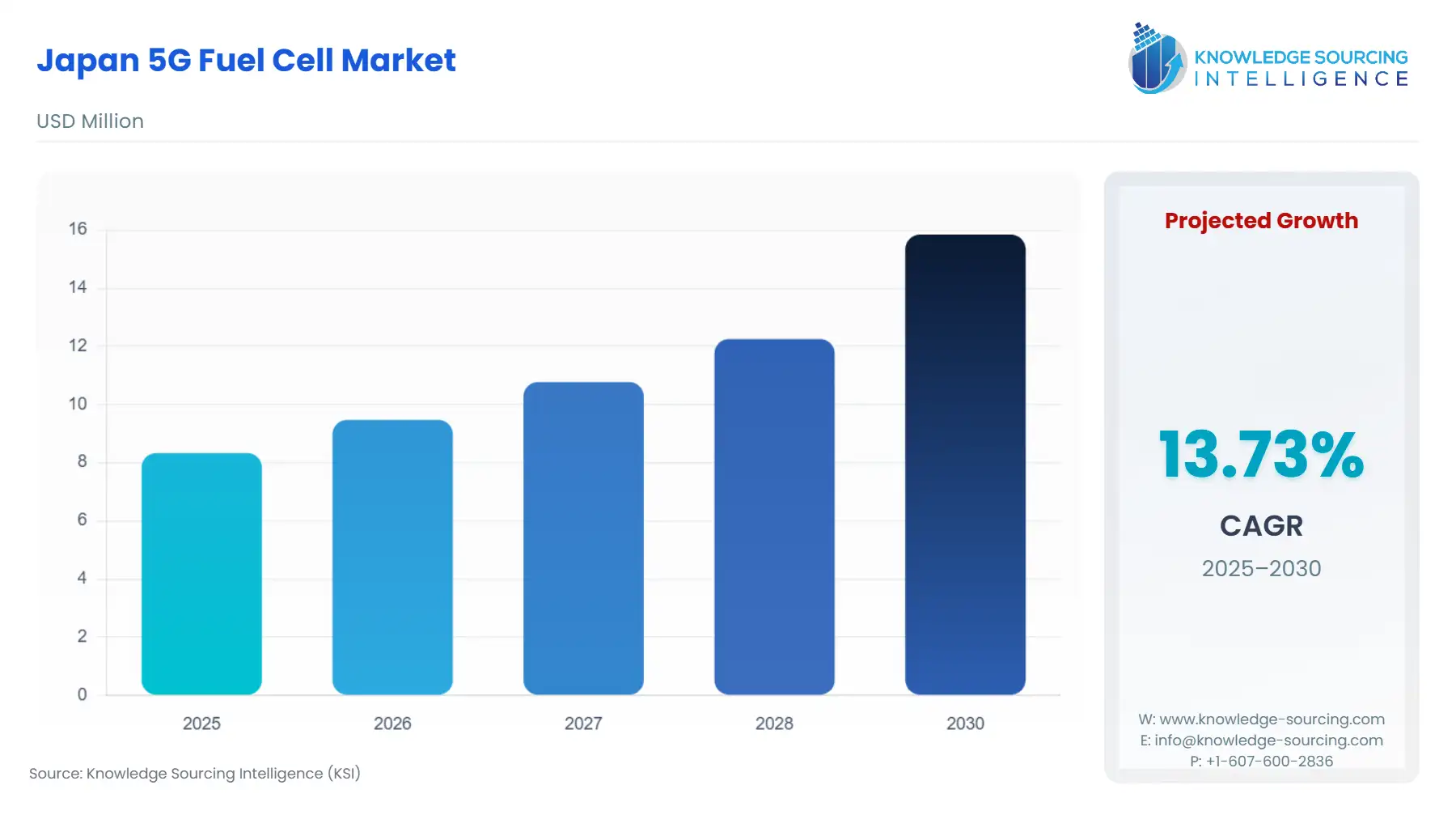
The Japan 5G Fuel Cell Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 13.73%, reaching USD 15.850 million in 2030 from USD 8.330 million in 2025.
The convergence of Japan's 5th Generation mobile network rollout and its aggressive commitment to a hydrogen-based society has created a discrete, high-value market for fuel cell power solutions. This market is defined by a rigorous set of technical requirements centered on reliability, high power-density, and minimal operational noise—features that conventional diesel and battery backup systems often fail to satisfy in dense urban environments. The transition from 4G to 5G infrastructure mandates a significantly denser network of base stations and corresponding edge data centers, which drastically increases the total energy load and the associated need for highly available, resilient power solutions. Fuel cell technology, offering extended runtime capacity over traditional battery banks with zero on-site emissions, represents a decisive strategic advantage for telecom operators and infrastructure providers committed to a green energy transition.
Japan 5G Fuel Cell Market Analysis:
Growth Drivers
National energy policy, spearheaded by the Hydrogen Basic Strategy, acts as the foundational catalyst, creating direct demand by subsidizing hydrogen-related technologies. This government support reduces the initial capital expenditure for telecom operators seeking to adopt zero-emission backup power, accelerating the displacement of fossil-fuel generators. The 5G network density imperative drives market scale; the physical requirement for a greater number of base stations necessitates a proportional increase in resilient power sources. Critically, the need for enhanced business continuity and disaster resilience, particularly for maintaining communication networks during seismic events, creates demand for fuel cells’ long-duration, high-availability power output, a capability superior to most conventional battery-only systems.
Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge constraining immediate, widespread market adoption is the existing high cost of hydrogen infrastructure, including storage and transportation, which directly impacts the total cost of ownership (TCO) for End-Users. This TCO imbalance limits demand, particularly for smaller, low-power (<5 kW) off-grid deployments. Conversely, significant opportunity resides in the Enterprise 5G Networks segment, where private networks in industrial complexes, factories, and ports require ultra-reliable power for mission-critical applications. These high-value use cases possess a higher tolerance for initial capital expenditure, thus creating specific, inelastic demand for superior power uptime assurance provided by fuel cell systems over conventional alternatives.
Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The Japanese 5G Fuel Cell Market fundamentally relies on Platinum Group Metals (PGMs), primarily platinum, for the catalysts within Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) fuel cells, the dominant technology for stationary backup power. Platinum’s price volatility directly influences the manufacturing cost of the Fuel Cell Stacks segment, introducing a material risk to system manufacturers. Japan’s domestic supply chain depends heavily on imports for both PGMs and membrane components. This import dependency subjects local producers to global supply chain fluctuations, making cost reduction via catalyst-free alternatives and domestically produced membrane electrode assemblies (MEAs) a critical corporate and national strategy to stabilize and reduce the final product price, thereby stimulating long-term demand.
Supply Chain Analysis
The global supply chain is bifurcated into highly specialized component manufacturing and localized system integration. Key production hubs for the critical Fuel Cell Stacks & Components exist across Japan, North America, and parts of Europe (notably for PEM membranes and carbon paper gas diffusion layers). Logistical complexities arise from the necessity of transporting high-precision, fragile components and the compressed or liquefied hydrogen (for initial system commissioning and subsequent refueling). Japanese domestic integrators, such as Kyocera and Fuji Electric, focus on packaging imported stacks and domestic components into turnkey Backup Power Solutions that meet strict Japanese regulatory compliance for 5G infrastructure, creating a significant dependency on a smooth, tariff-free flow of specialized core components.
Government Regulations
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Japan | Strategic Road Map for Hydrogen and Fuel Cells (METI) | Directly stimulates market expansion through public-private partnerships, R&D funding, and subsidies that significantly lower the capital cost for adopting stationary fuel cell systems in the energy sector, which includes telecom power. |
| Japan | High Pressure Gas Safety Act (HPGSA) | Imposes stringent safety and siting restrictions on high-pressure hydrogen storage tanks near 5G base stations and data centers. This constraint directly impacts the deployment and design of Fuel Supply Solutions, increasing engineering complexity and installation costs, which limits demand for high-capacity, on-site storage systems. |
| Japan | Disaster Prevention and Resilience Measures (Cabinet Office) | Creates an inelastic demand for ultra-reliable backup power by mandating that communication infrastructure maintain operational capability for extended periods during emergencies. This requirement strongly favors fuel cell solutions over limited-duration battery-only systems for core 5G nodes. |
Japan 5G Fuel Cell Market Segment Analysis:
By Application: Backup Power Solutions
The Backup Power Solutions segment constitutes the overwhelming majority of current demand, driven almost exclusively by the imperative for network reliability within the 5G ecosystem. Unlike 4G, which could tolerate brief outages, the massive data throughput and mission-critical applications (e.g., remote surgery, autonomous driving) enabled by 5G demand a near-zero downtime environment. Fuel cells address the fatal flaw of traditional lithium-ion battery banks, which are limited to runtimes of a few hours. A base station outage lasting longer than the battery life is a guaranteed service failure; fuel cells, however, are restricted only by the availability of fuel. This unique long-duration capability creates specific demand from major Telecom Operators seeking to align their power systems with the revised Business Continuity Plans (BCP) required by government and industry standards. This segment is characterized by a high purchasing volume and a primary growth driver focused on Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) rates and minimal maintenance cycles.
By End User: Telecom Operators
Telecom Operators represent the most influential end-user segment, as they directly control the procurement standards, technology evaluation, and large-scale deployment schedules for the entire 5G network. Their core growth driver is the strategic goal of achieving decarbonization coupled with superior network reliability. Operators are leveraging the public relations and regulatory benefits of transitioning from carbon-intensive diesel generators to zero-emission fuel cells. Furthermore, as network traffic continues its exponential climb, the resultant increase in power consumption across all base station sites makes the operational efficiency of the power source a major competitive differentiator. Operators are currently driving demand for 5G fuel cell systems that can provide 10 kW to 50 kW of output for at least 72 hours, shifting the market focus toward standardized, easily integrated Fuel Cell Systems that can be rapidly deployed across thousands of existing and new tower sites.
Japan 5G Fuel Cell Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The competitive landscape is dominated by large, diversified Japanese industrial conglomerates and select international pure-play fuel cell manufacturers. Japanese firms possess the critical advantage of domestic integration expertise and deep relationships with key end-users—Telecom Operators and Tower Providers. Foreign competitors, such as Ballard Power Systems, primarily focus on supplying high-performance Fuel Cell Stacks & Components, relying on domestic partners for final system integration. The competition is not solely based on price but increasingly on the verified system reliability, ease of maintenance, and the total lifetime ownership cost, particularly in relation to hydrogen refueling logistics.
Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions Corporation
Toshiba’s strategic positioning in the market leverages its long-standing expertise in energy systems and power electronics, offering its proprietary H2Rex™ pure hydrogen fuel cell systems for stationary applications. The company’s core strategy is to be an integrated solution provider, offering not only the fuel cell unit but also the associated hydrogen supply chain management and power control systems. A key verifiable development supporting its stationary power push was the November 21, 2024, announcement of a joint development agreement with Nimbus Power Systems to create a next-generation pure hydrogen fuel cell stack specifically for large mobility and stationary power. This investment in foundational stack technology confirms a commitment to the >50 kW segment required for 5G data center backup.
Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
Honda is strategically entering the stationary fuel cell market by repurposing its proven automotive fuel cell technology from its mobility division. This approach provides an immediate cost advantage and a high level of operational maturity. Honda's focus is on utilizing these high-volume, high-reliability fuel cell power units for commercial Backup Power Solutions. A key example of this strategy is the joint demonstration project announced in December 2023 with Tokuyama and Mitsubishi Corp., focusing on a Stationary Fuel Cell Power Station that reuses fuel cell systems originally designed for Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs). This initiative directly targets the backup power needs of data centers and is a pivotal move to penetrate the highly reliable power segment essential for 5G core networks.
Japan 5G Fuel Cell Market Recent Developments:
- December 2024: Fuji Electric announced capital investment to significantly increase the production capacity for its switchgear and power supply systems, including at its Kobe Factory. The official rationale for this expansion explicitly cited the surge in demand from data centers and large-scale projects, confirming a tangible capacity addition to the core electrical infrastructure that directly consumes and integrates fuel cell backup power solutions within the 5G ecosystem.
- November 2024: Toshiba announced a joint development agreement with Nimbus Power Systems to develop a next-generation pure hydrogen fuel cell stack. This joint effort is specifically designed for high-power, large-scale applications, including stationary power. This strategic collaboration is a foundational product development that establishes a clear path for future high-power fuel cell systems targeting the 5G tower and core infrastructure market.
- December 2023: Honda, in partnership with Tokuyama and Mitsubishi Corp., announced a joint demonstration project utilizing a Stationary Fuel Cell Power Station designed to repurpose fuel cell systems from FCEVs. This project focuses on verifying the utility and reliability of these repurposed units as a backup and primary power source for data centers, representing a direct, verifiable product launch focused on a key end-user segment for 5G network resilience.
Japan 5G Fuel Cell Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 8.330 million |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 15.850 million |
| Growth Rate | 13.73% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Product Type, Deployment, Power Output Range, End-User |
| Companies |
|
Japan 5G Fuel Cell Market Segmentation:
- BY PRODUCT TYPE
- Fuel Cell Systems
- Fuel Cell Stacks & Components
- Fuel Supply Solutions
- BY DEPLOYMENT
- Backup Power Solutions
- Off-grid / Remote Power Solutions
- Hybrid Energy Systems
- High-capacity Solutions
- BY POWER OUTPUT RANGE
- <5 kW
- 5–50 kW
- 50 kW
- BY END USER
- Telecom Operators
- Tower & Infrastructure Providers
- Government & Defense Communication Networks
- Enterprise 5G Networks