Report Overview
Space-Based Solar Power Market Highlights
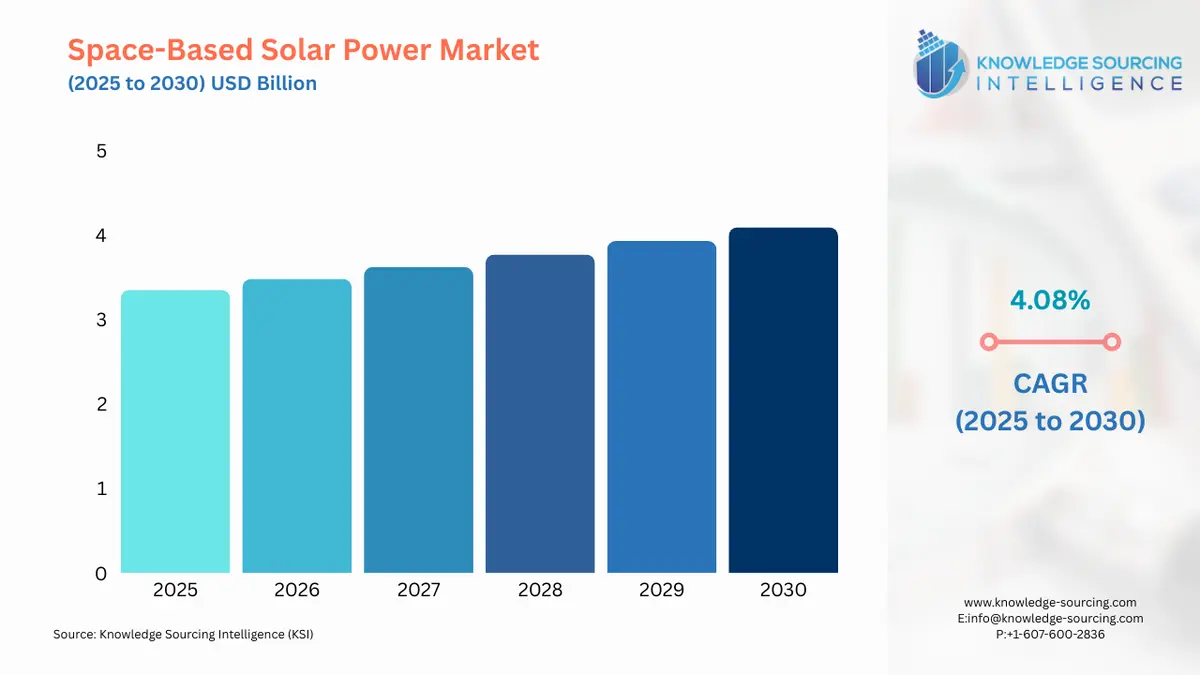
Space-Based Solar Power Market Size:
Space-Based Solar Power Market, growing at a 3.96% CAGR, is anticipated to reach USD 4.222 billion in 2031 from USD 3.345 billion in 2025.
Space-Based Solar Power Market Trends:
The space-based solar power market is projected to grow at a constant rate during the forecast period. Space-based solar power is a groundbreaking approach to harnessing solar energy from space and transmitting it to earth, thereby effectively eliminating the intermittency issues faced by traditional terrestrial renewable energy sources. This innovative concept offers numerous advantages, including the generation of clean, uninterrupted base-load energy, all while requiring significantly less land compared to conventional renewable energy solutions. The space-based solar power industry growth is being fuelled by an increase in electricity demand, and a reduction in the costs associated with space launches followed by favorable initiatives and investments.
Space-Based Solar Power Market Segmentation Analysis:
Rise in electricity demand bolster the space-based solar power market growth.
Space-based solar power provides an innovative solution by offering constant, uninterrupted energy production, unlike traditional renewable sources that are subject to fluctuations due to day-night cycles and weather conditions. This constant energy provision aligns with the continuously growing demand for electricity which is spurred by population growth, industrialization, and the rapid proliferation of digital technologies, all of which require reliable and continuous power supply. According to the Central Electricity Authority, India anticipates annual growth of 7.2% in its electricity demand, projecting it to escalate from 1,320 billion units in the fiscal year 2021/22 to 1,874 billion units by March 2027.
Declining cost of space launches drives the space-based solar power market.
The decreasing cost of space launches is a significant enabler for the growth of the space-based solar power industry. In the past, one of the main hurdles for space-based solar power was the prohibitive expense associated with launching and installing infrastructure in space. However, with advancements in space technology and the advent of private space companies investing in reusable rockets and more efficient launch systems, these costs are gradually diminishing. Lower launch costs make it economically feasible to place the necessary solar power collection and transmission equipment in orbit. For instance, according to the NASA Technical Reports, the launch cost to Low Earth Orbit (LEO) from NASA's space shuttle amounts to $54,500 per kilogram whereas SpaceX’s Falcon’s launch cost amount to $2,720 per kilogram.
Favorable initiatives and investments drive space-based solar power market growth.
Space-Based Solar Power is being pursued as an innovative solution to harness solar energy directly from space, offering a continuous and virtually inexhaustible source of clean power. The growth of space-based solar power is significantly influenced by government initiatives and global support thereby ultimately contributing to its growing prominence in the global energy landscape. For instance, in June 2023, UK innovators had been granted £4.3 million in funding to advance the development of space-based solar power. Also, in 2022, Japan initiated the launch of solar panels for space-based solar power systems, The government is focused on resolving technical challenges, including the development of larger panels, and cost management. The goal is to achieve the practical application of this system by 2050.
Space-Based Solar Power Market Geographical Outlook:
Europe is predicted to dominate the space-based solar power market.
Europe will hold a significant market share of the space-based solar power market as the governments in the region are actively supporting the development of space-based solar power through funding, regulatory support, and the fostering of public-private collaborations. For instance, in 2021, 50 leading British technology organizations, aligned under the UK Space Energy Initiative which seeks to explore the potential of developing a space-based solar power plant in the U.K. Also, in 2022, the European Space Agency unveiled an innovative program named Solaris whose primary objective was to determine the technological and economic viability of deploying solar structures into orbit. These structures would be designed to capture solar energy and transmit the harvested power back to Earth.
Space-Based Solar Power Market Growth Drivers:
Increasing space debris may restrain the space-based solar power market.
The surge in launches of satellites and other necessary infrastructure to establish space-based solar power systems might inadvertently exacerbate an already growing space debris. This accumulation presents a multi-faceted risk. On one hand, it could jeopardize the functionality and operational longevity of the space-based solar power systems themselves, as collisions with debris could damage or destroy these costly and complex facilities. On the other hand, the proliferation of space debris could also threaten other satellites, both those related to space-based solar power and unrelated ones.
Space-Based Solar Power Market Company Products
Solar Power Satellites: Solaren's Solar Power Satellites, stationed in geostationary earth orbit (GEO), harness the Sun's energy. This energy is converted into electricity by high-efficiency solar cells. The electricity is then transformed into a radio frequency (RF) energy beam by the solid-state power amplifier array. This RF energy beam is aligned and directed towards Earth by the RF antenna, aiming specifically at Solaren's ground receive station. Here, the energy is received and can be used for various applications.
Space Solar Cells: CESI S.p.A provides state-of-the-art Space Solar Cells that boast a typical efficiency of 30%. These cells are designed and qualified to operate in diverse space environments, specifically for satellites in both Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and Geostationary Orbit (GEO), in compliance with the standard ECSS E ST20-08C.
List of Top Space-Based Solar Power Companies:
Solaren Corporation
Northrop Grumman Corporation
AZUR SPACE Solar Power GmbH (5N Plus Inc)
CESI S.p.A
SPACETECH GmbH
Space-Based Solar Power Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Companies |
|
Report Metric | Details |
Space-Based Solar Power Market Size in 2025 | USD 3.345 billion |
Space-Based Solar Power Market Size in 2030 | USD 4.085 billion |
Growth Rate | CAGR of 4.08% |
Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
Base Year | 2024 |
Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
Segmentation |
|
Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
List of Major Companies in the Space-Based Solar Power Market |
|
Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Space-Based Solar Power Market Segmentation
By Technology
Microwave Transmitting Satellite
Laser Transmitting Satellite
By Material
Silicon
Gallium Arsenide
Others
By End-User
Residential
Commercial
Industrial
By Geography
Americas
United States
Others
Europe, the Middle East, and Africa
Germany
United Kingdom
Netherlands
Others
Asia Pacific
China
Japan
South Korea
India
Others