Report Overview
UAE Additive Manufacturing Market Highlights
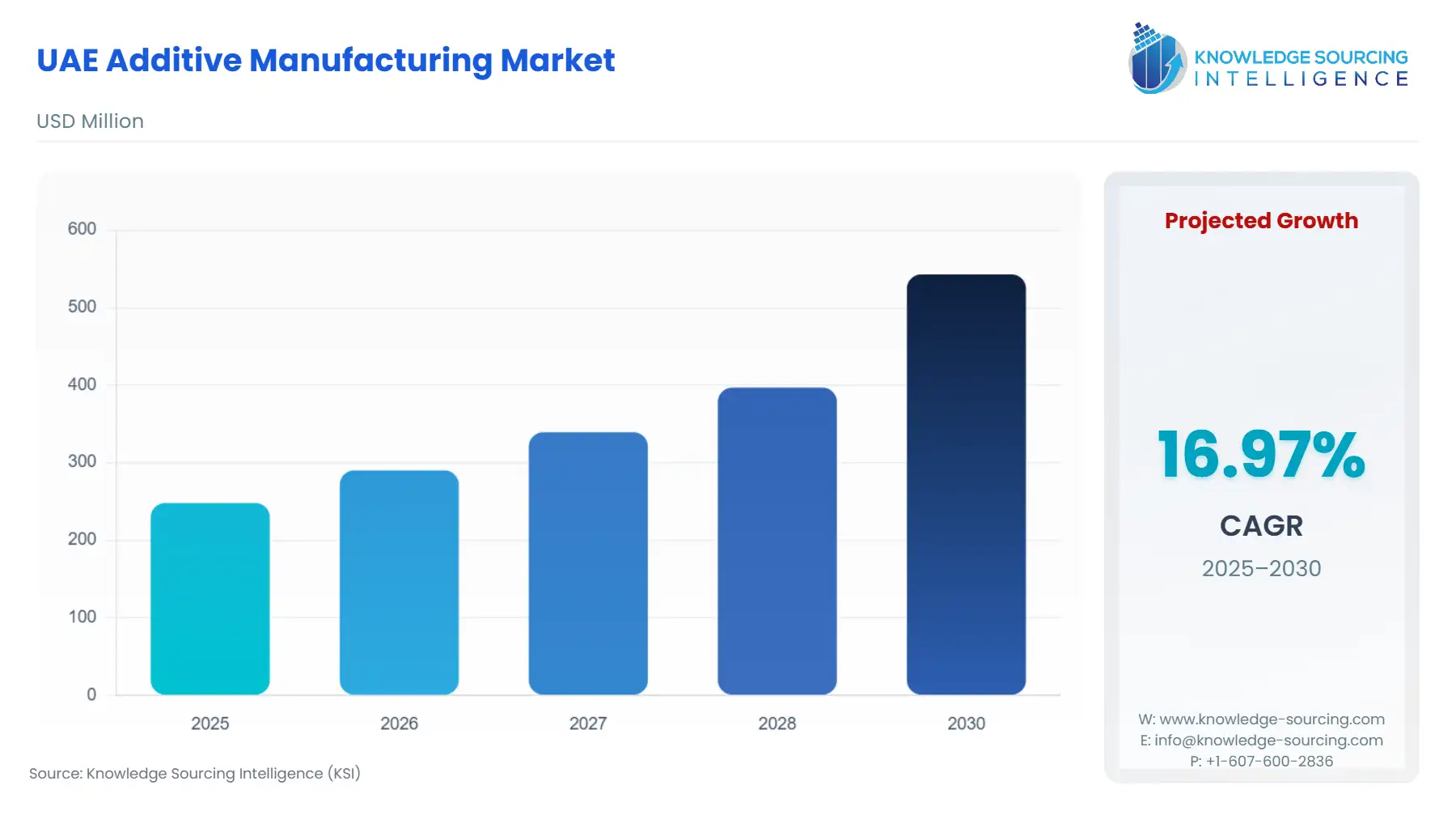
UAE Additive Manufacturing Market Size:
The UAE Additive Manufacturing Market is expected to increase at a CAGR of 16.97%, climbing to USD 0.543 billion in 2030 from USD 0.248 billion in 2025.
The UAE's Additive Manufacturing (AM) market is rapidly transitioning from a niche prototyping tool to a strategic pillar of its industrial future, largely driven by top-down government policy. This paradigm shift, framed within the national drive for economic diversification and advanced technology adoption, fundamentally redefines regional manufacturing processes. The market’s current trajectory emphasizes application in high-value, high-complexity sectors, where AM’s core benefits—design freedom, part consolidation, and mass customization—offer compelling economic and performance advantages over traditional subtractive methods. The deployment of advanced manufacturing capabilities in the Emirates is now an integral component of the national industrial strategy, setting the stage for significant capital and technological investment.
UAE Additive Manufacturing Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Government mandates act as the primary catalyst, explicitly generating demand for AM solutions. The Dubai 3D Printing Strategy requires that a quarter of all new building components be 3D printed by 2030, a directive that creates guaranteed, large-volume demand for construction-focused AM technologies like robotic extrusion systems and Powder Bed solutions. Concurrently, Operation 300bn, the national industrial strategy, compels manufacturers to adopt Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies to raise the industrial sector's contribution to GDP. This strategy directly increases demand for AM hardware, software, and services by incentivizing enterprises to integrate digital manufacturing for enhanced productivity and local value creation (In-Country Value, or ICV). The necessity for lightweighting in the aerospace sector further drives specialized demand for metal AM (e.g., Selective Laser Melting), as Emirates and Etihad Engineering explore printed aircraft components to improve fuel efficiency and performance.
- Challenges and Opportunities
A significant constraint is the talent and knowledge gap, where the limited domestic pool of engineers skilled in Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM) restricts the ability of local companies to transition from basic prototyping to full-scale, high-complexity production. This supply-side friction limits the immediate demand for advanced AM services. Conversely, the opportunity for localized material development presents a key growth avenue. Currently, access to a wide range of high-performance materials (e.g., aerospace-grade titanium and high-performance thermoplastics) is limited and reliant on costly imports. Developing local production capabilities for AM-specific powders and filaments would substantially reduce raw material costs and import dependencies, directly increasing the profitability and therefore the demand for domestic AM capacity.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The UAE Additive Manufacturing Market fundamentally revolves around physical products (hardware, materials), necessitating a raw material analysis. The market is primarily reliant on imported feedstocks, namely metal powders and specialized polymers. The cost of these materials—particularly aerospace-grade Titanium and Nickel Alloys—is significantly higher than conventional manufacturing feedstocks due to energy-intensive plasma processing and limited global atomizer capacity. This high material cost structure translates to a premium on the final printed component, creating a pricing headwind that constrains demand for high-volume AM applications. Consequently, the necessity is concentrated in high-value, low-volume applications like aerospace parts and medical implants where performance justifies the premium, rather than in mass-market consumer or automotive production.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global AM supply chain is concentrated in key production hubs across North America, Europe, and Asia, which serve as the primary source for advanced AM systems (hardware), proprietary software, and certified raw materials. The UAE market's reliance on these international hubs introduces significant logistical complexities, high shipping costs, and extended lead times for capital equipment and specialized powders. Local dependencies are heavily focused on the service layer—local 3D printing bureaus and on-demand manufacturers—which utilize the imported systems. A critical vulnerability is the dependency on foreign Intellectual Property (IP) and design files, making the secure management of digital assets, such as through platforms like Assembrix's Virtual Manufacturing Space, a key enabler for distributed manufacturing within the region.
UAE Additive Manufacturing Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
Dubai |
Dubai 3D Printing Strategy |
Mandates 25% of new buildings' components to be 3D printed by 2030, creating a protected and guaranteed market for construction AM services, thereby driving hardware and material requirements. |
|
UAE (Federal) |
Operation 300bn (MoIAT) |
Incentivizes the adoption of 4IR technologies, including AM, to boost industrial GDP contribution, leading to increased corporate investment in AM solutions and an accelerated demand for industrial AM services. |
|
Dubai Health Authority (DHA) |
Point-of-Care AM Partnerships |
Established regulatory support for 3D-printed medical devices and anatomical models, directly stimulating demand for medical-grade AM systems and bio-compatible materials for patient-specific applications. |
UAE Additive Manufacturing Market Segment Analysis:
- By Technology: Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a key technology segment experiencing high growth, primarily driven by its capacity for batch production and the elimination of support structures. This technology is crucial in meeting the demands of the consumer and industrial goods sectors for complex, interlocking parts and rapid tooling. The ability of SLS to produce parts from robust nylon-based materials with excellent mechanical properties drives growth from the automotive sector for jigs, fixtures, and internal components that require moderate volumes without the cost or lead time of injection molding. The intrinsic efficiency of the process, particularly its material recycling capability, aligns with the UAE's sustainability and waste-reduction goals, further cementing its market profile over other polymer-based AM technologies. Its suitability for functional prototyping significantly accelerates product development cycles for local manufacturing firms, acting as a direct market growth lever.
- By End-User: Aerospace & Defense
The Aerospace & Defense end-user segment demonstrates a high-priority, high-value demand for Additive Manufacturing. This necessity is intrinsically linked to government objectives for sovereign manufacturing capabilities, reducing reliance on global OEM supply chains, and achieving platform lightweighting. The creation of the Emirati 3D Printing Centre of Excellence, with its focus on aerospace and defense, institutionalizes demand for high-strength metal AM processes (e.g., Electron Beam Melting and Laser Sintering) to produce flight-qualified fuel nozzles, turbine blades, and satellite components. The imperative for on-demand production of spare parts for legacy aircraft reduces inventory costs and aircraft downtime, translating into a direct, non-negotiable need for AM services that offer certified, rapid-turnaround production of mission-critical components.
UAE Additive Manufacturing Market Competitive Analysis:
The UAE AM competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of local service bureaus, international system vendors, and a growing number of corporate in-house facilities. Competition is shifting from price-based service provision to a focus on application expertise and material certification, particularly in the highly regulated aerospace and healthcare verticals.
- EOS GmbH: As a leading global supplier of industrial metal and polymer AM systems, EOS positions itself as a core technology enabler. Their strategy involves providing high-performance, validated platforms (e.g., the EOS M 290) and a comprehensive portfolio of materials, enabling local partners to enter the high-end production market. Their focus on the Aerospace, Automotive, and Medical industries aligns directly with the UAE’s strategic demand centers.
- Assembrix Ltd: As a pure-play software provider, Assembrix partners with local entities like EVAP Investment LLC. Their core strategy is to provide the secure, cloud-based Virtual Manufacturing Space (VMS) platform, enabling international manufacturers (especially in Aerospace and Defense) to utilize local UAE AM service providers for secure, on-demand production, thus acting as a digital bridge that generates and protects regional requirements for AM.
UAE Additive Manufacturing Market Developments:
- September 2025: Phillips Machine Tools, a major advanced manufacturing equipment supplier, announced plans to showcase its cutting-edge additive and hybrid manufacturing solutions at the AM Conclave Middle East in Abu Dhabi. This move highlights their strategic partnership with EOS, a global leader in high-end AM technologies, focusing on both polymer and metal 3D printing systems, including Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS). The unveiling emphasizes integrated hybrid manufacturing that combines traditional CNC machining with AM to boost efficiency, cut costs, and improve part quality, directly supporting the UAE’s 'Operation 300bn' initiative to increase the manufacturing sector's GDP.
- October 2024: ADNOC Gas, a division of the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company, partnered with Immensa Technology Labs, a prominent regional AM company, to develop a comprehensive digital file catalogue for thousands of critical spare parts. This collaboration focuses on cultivating an extensive digital inventory that enables on-demand 3D printing of spare parts for their vast operations. The initiative is a significant step towards localizing the supply chain for the energy sector, reducing lead times, minimizing inventory reliance, and ensuring operational resilience by shifting to efficient additive manufacturing for maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO).
UAE Additive Manufacturing Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 0.248 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 0.543 billion |
| Growth Rate | 16.97% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Technology, End-User Industry |
| Companies |
|
UAE Additive Manufacturing Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
- Material
- BY TECHNOLOGY
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Laser Sintering (LS)
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
- Fused Disposition Modelling
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- BY END-USER INDUSTRY
- Aerospace & Defense
- Healthcare
- Automotive
- Construction
- Consumer
- Others