Report Overview
Taiwan Additive Manufacturing Market Highlights
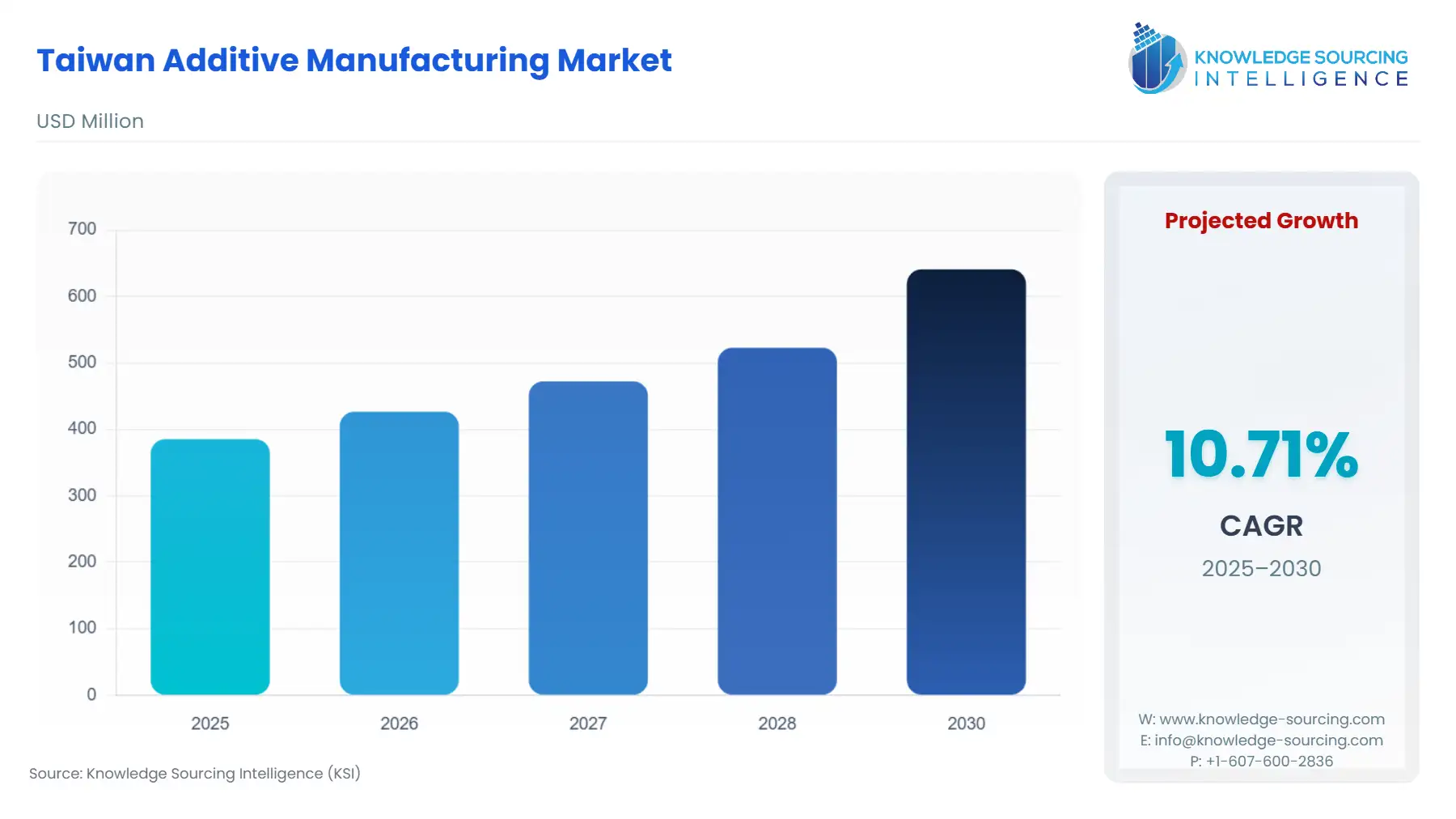
Taiwan Additive Manufacturing Market Size:
The Taiwan Additive Manufacturing Market is projected to increase at a CAGR of 10.71%, reaching USD 641.023 million in 2030 from USD 385.409 million in 2025.
The Taiwanese Additive Manufacturing (AM) market is transitioning from a prototyping-centric industry to a key enabler of advanced domestic manufacturing, directly supporting the island's globally critical electronics and high-tech ecosystems. This evolution is strategically aligning AM capabilities—including metal laser sintering and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)—with the national imperative for high-mix, low-volume, and customized production. The market's trajectory is fundamentally interwoven with the demand for supply chain resilience and component optimization in high-stakes sectors like aerospace, automotive, and, critically, semiconductor equipment manufacturing, where AM facilitates precision tooling and rapid part iteration.
Taiwan Additive Manufacturing Market Growth Drivers:
The foundational growth driver for AM is Taiwan's undisputed leadership in the global semiconductor industry. This ecosystem requires high-precision, customized components and jigs for wafer handling and testing equipment, which conventional methods struggle to produce quickly or economically. AM, particularly metal laser technologies, meets this demand by delivering intricate geometries, custom tooling, and spare parts rapidly, thereby minimizing expensive semiconductor production line downtime. Furthermore, the push for lighter and more complex components in the burgeoning domestic electric vehicle (EV) supply chain, driven by the shift towards next-generation mobility, directly increases the demand for AM services and high-performance polymer/metal materials for part consolidation and weight optimization. The need for rapid product iteration in consumer electronics also necessitates AM for functional prototyping, accelerating time-to-market.
- Challenges and Opportunities:
A primary constraint on market expansion is the significant initial capital outlay associated with industrial-grade AM systems, support equipment (e.g., inert gas chambers, post-processing units), and highly specialized materials. This high entry barrier suppresses demand, particularly from Taiwan’s vast base of small and medium-sized manufacturers who operate on tighter margins. However, a parallel opportunity exists in the medical device sector. The Guidance for the Management of Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) Medical Devices provides a clear regulatory pathway for customized, patient-specific implants and surgical guides. This clarity reduces certification risk for manufacturers, directly stimulating demand for both metal and bio-compatible polymer AM technologies and the accompanying design and service bureaus, particularly in Southern Taiwan's medical device industry cluster.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis:
Additive Manufacturing equipment, software, services, and materials constitute the market; therefore, a raw material and pricing analysis is critical. The market's reliance on metal powders (e.g., titanium, specialty alloys) and high-performance photopolymers creates supply chain complexity. Pricing for these materials remains a significant cost factor, often dictated by non-Taiwanese international suppliers and subject to global commodity and logistics volatility. Domestic players are responding by focusing research, often in collaboration with ITRI and academia, on developing proprietary materials and recycling/re-purposing metal powders to secure the supply chain and mitigate foreign pricing pressures. The cost-per-part reduction imperative for AM’s broader adoption hinges on lowering the effective price of high-purity metal and polymer feedstocks.
- Supply Chain Analysis:
The Taiwanese AM supply chain is characterized by a "hub-and-spoke" model. The high-value, R&D-intensive component (hardware and materials) is largely dependent on global production hubs in Europe and North America. Taiwan’s strength lies in the downstream application and services sector, driven by its sophisticated manufacturing base. Key domestic production is centered around high-speed 3D printing research and application, particularly in central and southern science parks. The core logistical complexity involves the import of specialized metal powders and industrial equipment, which are subject to stringent regulations and international trade dynamics. This dependence contrasts with Taiwan's self-sufficiency in many other high-tech supply chains.
Taiwan Additive Manufacturing Market Government Regulations:
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Taiwan | Ministry of Health and Welfare / Food and Drug Administration (TFDA) | The Guidance for the Management of Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) Medical Devices (2018) provides a transparent, principles-based framework for 3D-printed medical devices. This clarifies regulatory risk and is a direct growth catalyst for AM in the high-value Healthcare End-User segment. |
| Taiwan | Industrial Technology Research Institute (ITRI) | ITRI's sustained government support, beginning with the formation of laser AM clusters and metal AM laboratories (since 2012), promotes technology transfer and talent development. This initiative validates and subsidizes the technology, increasing commercial demand for domestically developed AM solutions. |
Taiwan Additive Manufacturing Market Segment Analysis:
- By Technology: Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) The Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) technology segment in Taiwan is uniquely propelled by the need for complex, lightweight nylon and polymer parts for the Consumer and Automotive end-user segments. SLS creates strong, highly detailed, and temperature-resistant components without the need for support structures, making it exceptionally efficient for batch production of functional parts and sophisticated prototypes. The transition in the domestic consumer electronics industry towards customized product casings, optimized internal components, and specialized jigs for assembly lines directly drives the adoption of SLS. Furthermore, the automotive sector utilizes SLS for producing interior components, ducting, and end-of-arm tooling in automation, demanding this technology’s high throughput and material versatility. The efficiency of SLS in using powder feedstock, which is critical for reducing material waste in high-cost manufacturing environments, provides a compelling economic justification, thereby sustaining demand.
- By End-User Industry: Healthcare The Healthcare segment is experiencing accelerated need for AM, fueled by the imperative for patient-specific solutions in orthopedics, dentistry, and oncology. The regulatory clarity provided by the Ministry of Health and Welfare has de-risked the commercialization pathway for customized medical devices. This enables surgeons to demand anatomically matched implants and cutting guides, which is geometrically impossible or prohibitively expensive to produce with traditional subtractive methods. The establishment of dedicated 3D-printed medical device smart manufacturing demonstration sites directly links clinical needs with production capabilities, creating a localized demand chain. This focus on bio-compatible metal and polymer AM materials and the associated sterilization and validation services is repositioning AM from a general manufacturing tool to a high-value medical-precision technology within Taiwan.
Taiwan Additive Manufacturing Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The Taiwan Additive Manufacturing competitive landscape features a mix of global hardware giants and specialized domestic players focusing on material and service innovation. Competition is primarily concentrated in the high-end industrial systems segment, while domestic firms excel in application development and specialized material R&D.
- Kinpo Group (Taiwan): As a major Electronic Manufacturing Service (EMS) and Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) firm, Kinpo Group has strategically leveraged its mass manufacturing expertise to enter the desktop and professional Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Stereolithography (SLA) market through its subsidiary, XYZprinting. Kinpo’s strategic positioning focuses on democratizing the technology, aiming for broad market adoption through accessible, consumer-grade and professional-entry printers. This volume-driven approach seeks to cultivate a wider installed base that will, in turn, drive long-term demand for materials and services.
- Phrozen Tech Co., Ltd. (Taiwan): Phrozen specializes in high-resolution Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 3D printers, which fall under the Vat Photopolymerization (VP) technology category. Their strategic focus is on delivering fine detail and accuracy at a competitive cost, positioning them strongly in the Dental and Jewelry professional segments. Their official product releases emphasize large build volumes and high printing speed, directly addressing the demand from labs and small-batch manufacturers for increased throughput without sacrificing resolution.
Taiwan Additive Manufacturing Market Developments:
- September 2025: FUJIFILM Corporation, a global materials giant with substantial operations in Hsinchu and Tainan, Taiwan, launched an advanced packaging Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP) slurry that has significant implications for Taiwan's core semiconductor industry. Although not a 3D printer, this specialized slurry is crucial for the planarization of hybrid bonding surfaces in advanced packaging, a key step in manufacturing high-performance AI semiconductors. The local production sites and focus on cutting-edge packaging underscore the deep integration of advanced materials manufacturing into Taiwan's high-tech production ecosystem, impacting future applications for 3D printed components in electronics.
- August 2025: The Taiwan-based 3D scanning and inspection solution provider, 3DeVOK, garnered significant attention at the Taiwan 3D Printing & Additive Manufacturing Show by showcasing its high-precision MT Handheld 3D Scanner. The demonstration highlighted its industrial capabilities, including a 34-line blue laser mode achieving 0.04mm accuracy and 0.10mm resolution on metallic components. This product launch and prominent exhibition focused on industrial applications like reverse engineering and quality inspection, reinforcing Taiwan's role in the precision metrology segment of the additive manufacturing workflow.
Taiwan Additive Manufacturing Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 385.409 million |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 641.023 million |
| Growth Rate | 10.71% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Technology, End-User |
| Companies |
|
Taiwan Additive Manufacturing Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
- Material
- BY TECHNOLOGY
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Laser Sintering (LS)
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
- Fused Disposition Modelling
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- BY END-USER INDUSTRY
- Aerospace & Defense
- Healthcare
- Automotive
- Construction
- Consumer
- Others