Report Overview
Argentina Application-Specific Integrated Circuits Highlights
Argentina Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Size:
The Argentina Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 9.04%, attaining USD 115.888 million in 2030 from USD 75.192 million in 2025.
The Argentine market for Application-Specific Integrated Circuits operates as a crucial, albeit supply-constrained, node within the global semiconductor ecosystem. It is defined not by local manufacturing capacity—which is minimal—but by the accelerating domestic demand for highly specialized processing power across its burgeoning information and communications technology (ICT) and industrial sectors. The shift toward advanced digital infrastructure, primarily accelerated by telecommunications deregulation and state-sponsored data infrastructure projects, creates an environment where ASICs are an essential imported component for performance and energy efficiency.
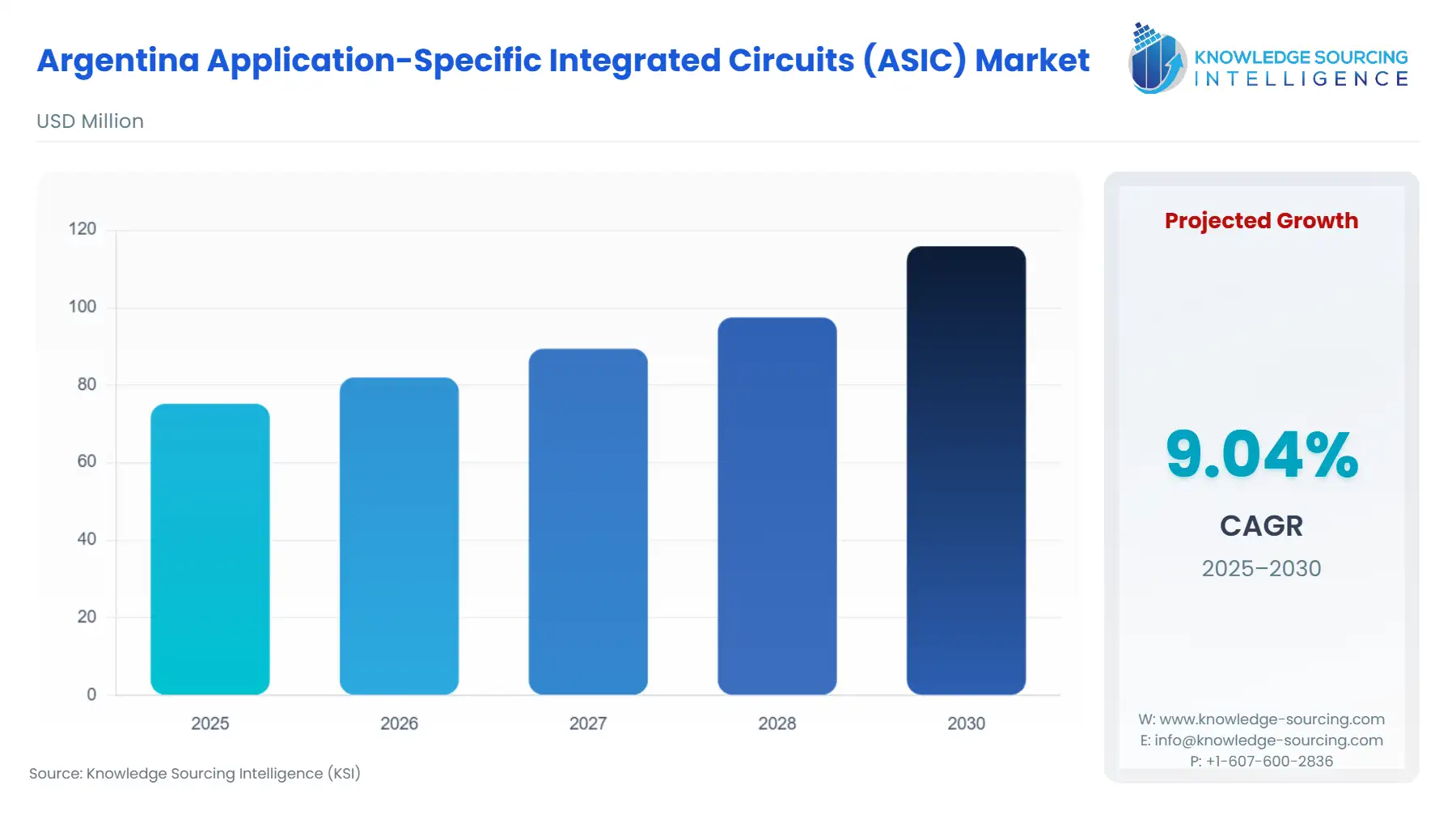
Argentina Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
The primary factors propelling the Argentine ASIC market are rooted in national infrastructure modernization and sector-specific performance mandates, which create a direct, unyielding demand for specialized silicon.
The 5G Network Deployment is the single most significant catalyst. Following the October 2023 spectrum auctions, the major telecom operators (Claro, Telecom, Telefónica) began the critical build-out phase. This infrastructure requires massive multiple-input multiple-output (mMIMO) systems and high-capacity beamforming, which general-purpose processors cannot efficiently handle. The necessity for high-speed, low-latency data processing and superior power-per-watt performance in 5G base stations directly translates to a surge in demand for specialized ASICs optimized for digital front-end (DFE), baseband processing, and network protocol acceleration. Without these ASICs, the promised performance gains of 5G remain unattainable, making their procurement a capital expenditure imperative.
The National Push for Digital Economy and Cloud Services further drives demand. Government support for a “cloud first” policy, including the development of a national data center by ARSAT, requires infrastructure capable of supporting advanced computation. Data centers utilize custom ASICs—often designed by hyperscalers or major vendors—to accelerate machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), and cryptography. These specialized chips provide superior performance-per-watt compared to traditional CPUs/GPUs for specific workloads, which is paramount for operational cost management in high-density computing environments. The commitment to a robust national data center creates a direct, long-term requirement for these specialized, high-end ASICs.
- Challenges and Opportunities
A significant market challenge is the Dependency on Foreign Currency and Import Logistics. Argentina's historical economic instability and regulatory frameworks often result in constraints on foreign currency access and protracted import processes. Since the nation relies heavily on importing fully manufactured ASICs and related components, these financial and logistical bottlenecks directly increase the cost and delay the deployment of essential electronic systems, thereby suppressing the overall volume of demand and extending product lifecycles.
A key opportunity lies in the Incentive Regime for Large Investments (RIGI), authorized by Decree 749/2024. This regime offers tax, customs, and foreign currency benefits to targeted industrial sectors, including nanotechnology and defense manufacturing. While the focus is not on ASIC fabrication, this policy framework creates a more stable and attractive environment for large-scale, ASIC-consuming projects—such as in defense or electric vehicle components—to be established, directly encouraging the high-volume, predictable demand necessary for international suppliers to prioritize the Argentine market.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis:
ASICs are physical products. Their upstream supply chain is a global construct, and Argentina is not a hub for semiconductor raw material mining or wafer fabrication. The critical raw material is the silicon wafer, which is converted into an integrated circuit via fabrication plants (foundries) predominantly located in East Asia. Local pricing for ASICs is a function of three primary components: the global commodity price of the chip, the cost premium associated with complex, highly advanced process nodes (e.g., 5nm and below), and the significant import tariff/currency risk premium imposed by the Argentine economic structure. Global need for cutting-edge nodes, particularly from hyperscalers developing in-house AI accelerators, keeps the price floor high. In Argentina, the currency restrictions and high logistics costs introduce a high-volatility layer to the final landed cost, making long-term pricing and procurement planning a considerable hurdle for local entities.
- Supply Chain Analysis:
The Argentina ASIC supply chain is characterized by its final-mile positioning, operating at the end of a long, intricate global network. The supply chain originates in key production hubs in East Asia (Taiwan, South Korea) for fabrication and continues through international packaging and testing facilities. Logistical complexities are immense due to the high-value, low-volume nature of ASICs and the highly regulated import environment of Argentina. The country is dependent on large, multinational distributors and logistics firms to navigate customs and tariff complexities. This dependency creates a vulnerability, as any global supply shock—such as those experienced during the post-pandemic recovery—disproportionately impacts delivery schedules and costs for Argentine buyers. The lack of a local foundry or advanced packaging hub dictates that the market operates entirely on global dependencies.
Argentina Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Government Regulations:
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Argentina (Federal) | National Semiconductor Law (Ley Nacional de Semiconductores) | Argentina's National Semiconductor Law, enacted in 2023, aims to incentivize the local semiconductor industry through tax exemptions, subsidies, and research funding. The law encourages local production of semiconductors, including ASICs, and offers benefits to manufacturers involved in R&D. As a result, there is a significant push for the development of ASICs tailored for Argentina's key industries, such as telecommunications, automotive, and consumer electronics. This regulation will reduce costs for local manufacturers and stimulate innovation, potentially leading to an increased supply of ASICs in these sectors. |
| Argentina (Environmental Protection) | Law 25,675 – General Environmental Law | Law 25,675 regulates the environmental impact of industrial activities, including the disposal of electronic waste (e-waste) and chemical substances used in semiconductor manufacturing. ASIC manufacturers in Argentina must adhere to these environmental standards to ensure sustainable operations. Compliance with these regulations could lead to higher manufacturing costs due to the need for environmentally safe disposal of hazardous materials. However, it may also drive demand for eco-friendly ASICs that meet global sustainability standards. |
| Argentina (Telecommunications) | Ente Nacional de Comunicaciones (ENACOM) Regulation | ENACOM regulates Argentina's telecommunications infrastructure, including radio frequency management and the certification of telecommunications equipment. ASICs used in communication systems (such as those supporting 5G or broadband technologies) must comply with ENACOM's standards for frequency management and network optimization. This regulation increases demand for ASICs designed for next-generation communication technologies, creating a growth opportunity for specialized semiconductor products. |
| Argentina (Customs & Trade) | Customs Law (Ley de Aduanas) | Argentina's Customs Law controls imports and exports, particularly in high-tech goods like semiconductors. Import duties and tariffs on foreign semiconductors, including ASICs, can make it more expensive for companies to source components not produced locally. This regulation incentivizes local production of ASICs, thus promoting the growth of local manufacturers or foreign companies setting up production facilities in Argentina. However, high tariffs on imported goods may increase costs for businesses that rely on international suppliers. |
| Argentina (Energy Efficiency) | Energy Efficiency Law (Ley de Eficiencia Energética) | The Energy Efficiency Law promotes the use of energy-efficient technologies in various industries, including electronics. ASICs, particularly those used in data centers, telecommunications, and industrial applications, are subject to this law's requirements for energy consumption and power efficiency. As a result, ASIC manufacturers must focus on creating power-efficient designs to comply with the law, driving the demand for low-power, high-performance ASICs. |
Argentina Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Segment Analysis:
- By Application – Data Centers & Cloud Computing: The Data Centers & Cloud Computing segment is a primary growth vector for high-performance ASICs in Argentina, driven by the structural requirement for computational efficiency in hyperscale and national cloud environments. The shift to a digital economy, accelerated by the growth in e-commerce and online government services, requires significant investment in fixed infrastructure. ASICs, especially those engineered for AI/ML inference (e.g., proprietary accelerators for computer vision and natural language processing) and specialized networking functions, offer an undeniable performance-per-watt advantage over general-purpose CPUs. This advantage directly lowers the total cost of ownership (TCO) for data center operators, making the investment in custom silicon a performance-critical and economically sensible decision for scaling operations, particularly in an energy-cost-sensitive environment. The government's explicit investment in the national data center through ARSAT mandates the procurement of these highly efficient, specialized chips.
- By Application – Industrial & IoT: The Industrial & IoT segment in Argentina exhibits strong demand for mature and mid-range node ASICs, prioritizing durability, low power consumption, and long product lifecycles over bleeding-edge performance. The growing adoption of industrial automation (Industry 4.0) and smart city projects drives the need for embedded systems requiring predictable, reliable processing. ASICs designed for sensor fusion, low-power connectivity (e.g., LoRaWAN, NB-IoT), and motor control are essential for these applications. In manufacturing, the consolidation of multiple functions into a single ASIC increases system reliability, reduces component count, and minimizes power draw, directly addressing the local industrial need for robust, long-term operational stability in remote or challenging environments. The shift towards electric mobility and renewable energy systems further propels the demand for specialized power management and control ASICs within this end-user segment.
Argentina Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The Argentine ASIC market is characterized by a competitive landscape dominated by global semiconductor giants, as local fabrication capacity is absent. Competition focuses on design win support, supply chain reliability, and the performance metrics of the imported silicon. Key players leverage their international scale and advanced technology portfolio to secure high-volume demand from major telecommunications and industrial customers.
- STMicroelectronics: STMicroelectronics maintains a strategic position in the Argentine market through its focus on Industrial, Automotive, and Microcontroller ASICs. The company's strength lies in its comprehensive portfolio of mixed-signal, power management, and microcontrollers, which are essential components for the local assembly of industrial and consumer electronics. STMicroelectronics' value proposition centers on providing robust, specialized chips for high-reliability applications, such as power supplies, smart grid infrastructure, and vehicle control units. Their official publications frequently detail new products in power management and smart mobility, which directly align with Argentina's growing electric vehicle and industrial automation sectors, thereby securing design-in opportunities with local original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and assemblers.
- Microchip Technology: Microchip Technology strategically targets the Argentine Industrial and Embedded Systems segment with its broad offering of microcontroller and analog ASICs. The company's positioning is built on providing highly customizable, easily integrated solutions with a focus on long-term product availability, which is crucial for customers whose end products have extended lifecycles (e.g., defense, industrial control). Key offerings, such as their specialized field-programmable gate array (FPGA) and microcontroller units (MCUs), act as foundational components for local developers. By emphasizing comprehensive technical support and development ecosystems, Microchip aims to reduce the design friction for Argentine engineers, thus securing high-volume ASIC demand through strategic partnerships and local technical seminars.
Argentina Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Developments:
- September 2025: STMicroelectronics announced new details regarding the development of the next generations of Panel-Level Packaging (PLP) technology through a new pilot line in Tours, France. This advanced, automated chip packaging and test process aims to increase manufacturing efficiency and flexibility, allowing for the creation of smaller, more cost-effective electronic devices. This strategic investment in manufacturing technology, which extends ST's PLP use across automotive, industrial, and consumer applications, will result in higher-density, lower-cost ASICs that eventually service the demand from Argentina's local assembly sector.
Argentina Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 75.192 million |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 115.888 million |
| Growth Rate | 9.04% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Process Technology, Product Type, Application |
| Companies |
|
Argentina Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Segmentation:
- BY PROCESS TECHNOLOGY
- Advanced Nodes
- 3 nm and below
- Leading-Edge Nodes
- 5 nm
- 7 nm
- Mid-Range Nodes
- 10 nm
- 12 nm
- 14 nm
- 16 nm
- Mature Nodes
- 22 nm and above
- Advanced Nodes
- BY PRODUCT TYPE
- Full-Custom ASIC
- Semi-Custom ASIC
- Standard Cell-Based ASIC
- Gate-Array Based ASIC
- Programmable ASIC
- Others
- BY APPLICATION
- Consumer Electronics
- Automotive
- Networking & Telecommunications
- Data Centers & Cloud Computing
- Healthcare
- Industrial & IoT
- Defense & Aerospace
- Others