Report Overview
Automotive Tire Market Size, Highlights
Automotive Tire Market Size:
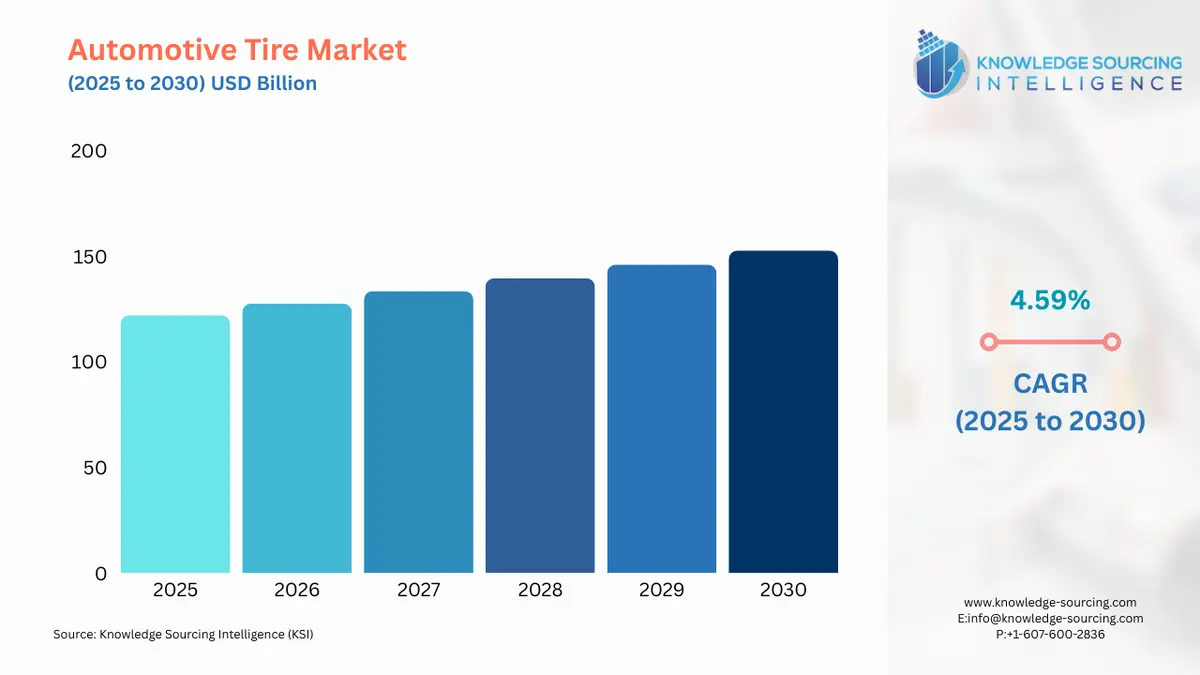
The Automotive Tire Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.59%, reaching USD 152.668 billion in 2030 from USD 121.979 billion in 2025.
The automotive tire market is a foundational component of the broader automotive industry, underpinned by the ongoing global expansion of vehicle fleets and the continuous need for replacement products. This market's dynamics are a direct reflection of macroeconomic trends, technological shifts in vehicle design, and the evolving regulatory landscape.
Automotive Tire Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
The primary drivers of demand in the automotive tire market are directly linked to the expansion and utilization of the global vehicle fleet. A fundamental catalyst is the continuous increase in new vehicle production and sales. As vehicle manufacturing, particularly in the passenger car and light commercial vehicle segments, sees robust expansion, it creates a direct and immediate demand for tires for original equipment (OE) fitment. According to the European Automobile Manufacturers Association (ACEA), over 68 million passenger cars were manufactured globally in 2022, a 7.9% increase from the previous year. This metric illustrates a direct correlation between vehicle production volumes and OE tire demand.
Beyond new vehicle sales, the aftermarket segment, driven by tire replacement, is a significant and stable demand driver. The average lifespan of a vehicle has increased due to enhancements in technology and manufacturing, which, in turn, has created a larger and more mature installed base of vehicles on the road. This growing fleet requires a consistent and predictable supply of replacement tires, a cycle influenced by factors such as average annual mileage and tire durability. The growth of e-commerce and logistics has further propelled demand in the commercial vehicle segment, as a surge in online shopping necessitates a corresponding expansion of delivery and freight fleets, each requiring durable, high-performance tires to withstand demanding operational conditions.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The automotive tire market faces significant challenges, primarily centered on fluctuating raw material costs and intense competition from emerging manufacturers. The supply chain for tire production is heavily reliant on commodities such as natural rubber and carbon black, and price volatility in these markets can compress profit margins for manufacturers. Such cost pressures can lead to reduced investment in research and development and may hinder a company's ability to maintain a competitive price point. Furthermore, the market is characterized by a high degree of competition, with companies from emerging economies increasingly improving product quality and technology, thereby challenging the market share of established premium brands.
Despite these challenges, opportunities for growth are emerging from technological and regulatory shifts. The proliferation of electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant opportunity. EVs present unique demands on tires due to their heavier battery packs and instant torque delivery, which cause increased tire wear. This has created a new segment for specialized EV tires designed for low rolling resistance to maximize range, enhanced durability to handle higher loads, and acoustic damping to mitigate interior noise. The demand for these purpose-built tires creates a new revenue stream for manufacturers. Similarly, increasing consumer and regulatory emphasis on fuel efficiency and sustainability drives demand for "green tires" with low rolling resistance, offering an opportunity for innovation and market differentiation.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The production of automotive tires is dependent on a complex supply chain of physical raw materials, making pricing dynamics a critical factor. The key components include synthetic rubber, natural rubber, carbon black, and steel cord. Natural rubber is an agricultural commodity, and its supply and price are subject to geopolitical factors, weather patterns, and plant diseases in major producing regions like Southeast Asia. Synthetic rubber, a petroleum-derived product, is influenced by the volatility of crude oil prices. Carbon black, another critical reinforcing filler, is also derived from petroleum feedstock. The prices of these materials are a primary determinant of a manufacturer's production costs and, consequently, its final product pricing. When material costs rise, tire companies often face the decision of either absorbing the increased expense, which erodes margins, or passing the cost on to consumers, which can impact demand. This dynamic necessitates sophisticated supply chain management and forward-looking procurement strategies to mitigate risk and maintain profitability.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global automotive tire supply chain is a highly integrated network. The primary production hubs for natural rubber are concentrated in Southeast Asia, with countries like Thailand, Indonesia, and Vietnam dominating global output. The manufacturing of finished tires is more geographically diversified but maintains a strong presence in Asia-Pacific, particularly in China and India, which serve as major production and consumption centers. Key logistical complexities include the transportation of heavy, bulky finished products from manufacturing plants to regional distribution centers and, subsequently, to OEMs and aftermarket retailers. The just-in-time inventory models of many automotive manufacturers create a dependency on efficient logistics, as delays in tire delivery can halt vehicle production lines. The supply chain also has dependencies on the upstream chemical industry for synthetic rubber and carbon black and on the steel industry for steel cord, making it susceptible to disruptions in these sectors.
- Government Regulations
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| European Union | EU Tyre Labelling Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2020/740) | This regulation requires tires to be labeled with information on fuel efficiency (rolling resistance), wet grip, and external rolling noise. This transparency directly influences consumer purchasing decisions, as buyers can compare products based on performance metrics. It has spurred manufacturers to invest in R&D to improve ratings, particularly for rolling resistance, thereby driving demand for more technologically advanced and efficient tires. |
| United States | U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) | The NHTSA sets minimum safety standards for tires, including the Tire Safety Standard (FMVSS 139), which mandates performance requirements for new pneumatic tires. These regulations ensure a baseline level of quality and safety for all tires sold in the U.S. and influence product design to meet specific durability, endurance, and high-speed performance criteria. |
| China | China Quality Certification Center (CQC) / GB Standards | China's Compulsory Product Certification (CCC) system mandates that all motor vehicle tires must be certified to national GB standards. The GB 9743-2024 and GB 9744-2024 standards, effective from May 1, 2025, outline specific performance and safety requirements. This regulatory framework creates a high barrier to entry for international manufacturers and ensures that all products in the market conform to a single set of national performance benchmarks. |
Automotive Tire Market Segment Analysis:
- Passenger Cars
The passenger car segment represents a foundational and dominant force in the automotive tire market. Its demand is a function of multiple factors, most notably the sheer volume of passenger vehicles on the road, which necessitates a continuous cycle of tire replacement. The demand for passenger car tires is bifurcated into original equipment (OE) for new vehicle assembly and the much larger, more stable aftermarket. The increasing need for OE is directly tied to the annual production figures of global automotive manufacturers. In the aftermarket, market growth is driven by the number of registered vehicles and the average miles driven. As the average lifespan of a vehicle increases, the number of opportunities for tire replacement over that vehicle's life cycle also grows. Furthermore, consumer preferences for SUVs and crossovers have led to an increase in demand for larger rim-size tires, which are typically more profitable for manufacturers. The shift towards electric vehicles is also a significant demand catalyst within this segment, as EVs require purpose-built tires with low rolling resistance to maximize battery range and a more robust construction to handle the vehicle's additional weight and instant torque. These technological imperatives create a new demand profile, moving consumers toward premium, specialized products.
- Aftermarket
The aftermarket segment, which includes replacement and retread tires, is the most substantial and structurally stable component of the automotive tire market. Unlike the volatile original equipment market, which is susceptible to the cyclical nature of new vehicle sales, the aftermarket is driven by the maintenance and usage of the existing vehicle fleet. The growth is directly correlated with the number of vehicles in operation, average vehicle mileage, and the physical wear and tear on tires. Factors such as improved road infrastructure and longer vehicle lifespans have created a larger installed base of vehicles that require periodic tire replacement. The aftermarket is highly sensitive to consumer behavior and economic conditions; consumers often prioritize durable and cost-effective solutions. The retread market, particularly for commercial vehicles, is a key sub-segment, driven by fleet operators' imperative to reduce operating costs and extend the life of their assets. Innovations in tire compounds that extend tread life and the advent of smart tires that monitor wear are reshaping this segment, creating new demand for higher-performance, longer-lasting products. The market's stability makes it a critical focus area for manufacturers seeking consistent revenue streams.
Automotive Tire Market Geographical Analysis:
- US Market Analysis
The US automotive tire market is characterized by a mature vehicle fleet and a strong aftermarket segment. The market is primarily driven by replacement demand, which accounts for the majority of total tire sales. A key demand driver is the consumer preference for larger vehicles, particularly light trucks, SUVs, and crossovers. This trend has shifted demand toward larger rim-size tires with higher load ratings. Furthermore, the US market is segmented by regional weather patterns, which create distinct demand for all-season, summer, and winter tires. The proliferation of electric vehicles, particularly from US-based manufacturers, is creating a growing need for specialized, low-rolling-resistance tires to maximize range. The regulatory environment, overseen by the NHTSA, ensures a high baseline for product quality and safety, reinforcing demand for high-performance products that meet or exceed these standards. - Brazil Market Analysis
The Brazilian tire market is heavily influenced by the country's economic cycles and its significant agricultural and logistics sectors. This market is propelled by the growing vehicle fleet and government-led infrastructure projects that increase the need for commercial vehicles and, consequently, their tires. The aftermarket for passenger cars is a consistent demand source, though it can be sensitive to consumer disposable income. A notable demand driver is the country's reliance on road transportation for freight, which fuels a strong market for truck and bus tires, including a robust retreading segment. The market also sees demand from the agricultural sector, where specialty off-the-road (OTR) tires are required for farming machinery. Economic stability and industrial activity are direct determinants of tire demand in this region. - German Market Analysis
The German market is a key hub in the European tire industry, defined by a focus on premium and high-performance products. This growth is driven by the country's extensive network of high-speed roads (Autobahn) and a culture of performance-oriented vehicle ownership. This environment creates a consistent demand for Ultra-High Performance (UHP) tires for passenger cars. The market is also heavily influenced by regulatory mandates for winter tires, which are legally required in certain weather conditions. This regulation creates a predictable and recurring seasonal demand cycle, with consumers often owning and swapping between two sets of tires (summer and winter). The increasing number of electric vehicles on German roads is also an emerging demand factor, as German consumers seek out tires that align with their vehicle's performance capabilities and efficiency requirements. - South African Market Analysis
The South African automotive tire market faces unique challenges and demand drivers. The country's vast and diverse road conditions, ranging from paved urban centers to rugged rural areas, necessitate a wide range of tire types, from standard passenger car tires to robust all-terrain and off-road tires. The market’s expansion is also influenced by the large number of imported used vehicles, which contribute to the aftermarket. The logistics and mining sectors are significant consumers of commercial and OTR tires, as they are crucial to the country's economy. The market is highly sensitive to economic growth and consumer purchasing power. Regulatory frameworks and standards for tire quality are also shaping consumer choice, albeit with a different emphasis than in developed economies. - Chinese Market Analysis
China is the world's largest automotive market and a major hub for tire production and consumption. This growth is primarily driven by the country's massive and rapidly expanding vehicle fleet and its position as the world's leading automotive manufacturing base. The market is characterized by a high volume of new vehicle sales, which fuels significant OE tire demand. The aftermarket is also experiencing explosive growth as the number of registered vehicles matures and requires replacement tires. Government policies promoting electric vehicle adoption have created a surge in demand for specialized EV tires. The market also features a highly competitive landscape with both international and domestic manufacturers vying for market share. The Chinese government's implementation of national standards and certifications, such as the CCC system, directly impacts the types of tires available and ensures a minimum level of product quality.
List of Top Automotive Tire Companies:
The automotive tire market is dominated by a few global players who have established formidable brand recognition, extensive distribution networks, and a focus on premium product segments. The competitive landscape is also marked by an increasing presence of manufacturers from emerging economies, who compete on price and are rapidly improving their technology and product quality. Companies maintain their competitive edge through a combination of strategic acquisitions, continuous innovation, and diversification across different market segments.
- Michelin Group
Michelin, a French multinational company, maintains its position through a robust focus on innovation and a premium-pricing strategy. The company's business model is centered on creating high-performance, long-lasting products that command a higher price point. Michelin's strategic positioning is evident in its emphasis on sustainable mobility, with R&D efforts aimed at developing more fuel-efficient and eco-friendly tires. The company's product portfolio includes the MICHELIN Pilot Sport line, which targets the performance car segment, and the MICHELIN CrossClimate series, which addresses the growing demand for versatile all-season tires. Michelin also leverages its B2B relationships, supplying tires to major automotive manufacturers for OE fitment and expanding its service offerings to fleet customers. - The Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company
Goodyear operates as a global leader with a diversified portfolio spanning passenger, commercial, and specialty tire segments. The company's strategy is built on operational excellence, brand value, and a commitment to advanced mobility solutions. Goodyear's acquisition of Cooper Tire & Rubber Company, completed in June 2021, was a strategic move to broaden its brand portfolio, increase its scale, and strengthen its distribution network in North America. This merger allowed Goodyear to expand its market presence and capture additional value in the replacement and original equipment segments. The company's product lines, such as the Assurance and Wrangler series, are well-established, targeting mainstream consumers and light truck markets, respectively. - Bridgestone Corporation
Bridgestone is a Japanese multinational tire manufacturer with a global footprint and a strong presence in the Asia-Pacific region. The company's strategy is centered on its "Dan-Totsu" (clear and absolute leader) business plan, focusing on creating high-quality, high-value products and reinforcing its premium-mass strategy. Bridgestone's key product lines include the Turanza for passenger cars and the Ecopia line, which is designed for fuel efficiency. The company's strategic investments, such as the US$85 million investment in its Indian plants, underscore its commitment to reinforcing production and development in key growth markets. These initiatives are designed to improve its capability to produce premium tires and align with the growing demand for High Rim Diameter (HRD) tires in regions like India.
Automotive Tire Market Developments:
- December 2025: Hankook Tire unveiled the "Sustainable Concept Tyre" at its Design Innovation Day, featuring an organic design realized through advanced 3D printing and recycled materials.
- September 2025: Continental showcased the Conti Urban HA 5 NXT city bus tire at Busworld Europe 2025, featuring up to 60 % renewable and recycled materials and reduced rolling resistance for electric bus efficiency.
- September 2025: Hankook Tire unveiled future mobility innovations at its Design Innovation Day 2025, showcasing sustainable concept tire designs using 3D printing and recycled materials for future automotive applications.
- May 2025: Goodyear completed the sale of the Dunlop tire brand rights to Sumitomo Rubber Industries, receiving $735 million to support its Goodyear Forward strategy and focus on core automotive tire products.
- February 2025: Pirelli launched the new Cinturato summer tire, utilizing patented "SmartNet Silica" to improve mileage by 20% and achieve Class A wet grip ratings across the range.
Automotive Tire Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Automotive Tire Market Size in 2025 | USD 121.979 billion |
| Automotive Tire Market Size in 2030 | USD 152.668 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 0.0459 |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in the Automotive Tire Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Automotive Tire Market Segmentation:
- By Vehicle Type
- Passenger Cars
- Light Commercial Vehicles
- Heavy Commercial Vehicles
- Two-Wheelers
- Off-the-Road Vehicles
- By Tire Type
- Radial
- Bias
- By End-User
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
- Aftermarket
- By Rim Size
- <18 Inches
- 18-20 Inches
- 20 Inches
- By Geography
- North America
- South America
- Europe
- Middle East and Africa
- Asia Pacific