Report Overview
Brazil Application-Specific Integrated Circuits Highlights
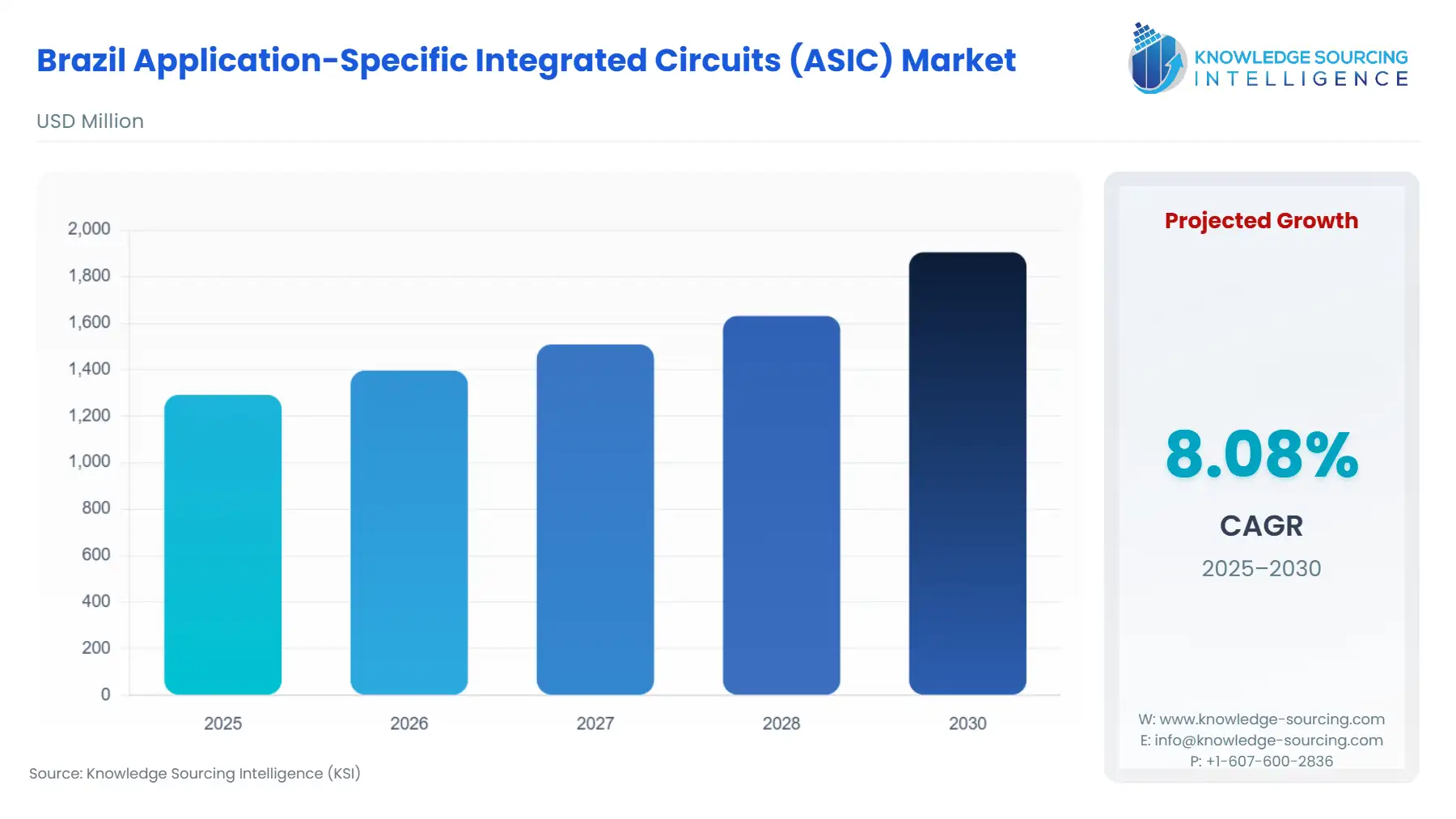
Brazil Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Size:
The Brazil Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 8.08%, reaching USD 1.905 billion in 2030 from USD 1.292 billion in 2025.
The Brazilian Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) market is undergoing a structural transformation, shifting from a primarily import-reliant consumer electronics ecosystem to one increasingly defined by strategic national priorities in digital infrastructure and sustainable mobility. This transition is not organic; rather, it is a deliberate, policy-driven response to global supply chain concentration and the domestic imperative for technological sovereignty.
The market is unique in that its value chain is heavily weighted toward the consumption and assembly end, while advanced semiconductor fabrication remains outsourced globally. However, the government's extended fiscal incentives for R&D and design activities are fundamentally changing the market profile, moving it away from general-purpose chips toward customized, high-value, and energy-efficient solutions necessary for next-generation telecommunications and data center buildouts. The confluence of these public-sector initiatives and targeted private-sector investments in Artificial Intelligence (AI) compute power, especially within the Data Centers & Cloud Computing segment, underscores the market's evolving complexity and its increasing strategic importance in the Latin American digital economy.
Brazil Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
The most significant factors propelling the demand for ASICs in Brazil stem directly from government-backed infrastructure mandates and sectoral industrial policy. The national 5G rollout, managed by the National Telecommunications Agency (ANATEL), is a core driver. As mobile network operators (MNOs) expand coverage across municipalities and transition to Standalone (SA) 5G, the requirement for highly optimized, power-efficient chips for base stations, beam-forming, and radio access network (RAN) equipment increases. This technical requirement translates into a non-negotiable demand for specialized ASICs over commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) processors, as only custom silicon can achieve the necessary latency and throughput targets for the 3.5 GHz band operation.
A secondary, yet equally powerful, driver is the mandated technological upgrade within the automotive industry. The Rota 2030 program, which provides R&D expenditure refunds, has incentivized multinational automotive OEMs and their Tier-1 suppliers to localize assembly and manufacturing for electric and hybrid vehicles. This localization directly increases the demand for Full-Custom and Semi-Custom ASICs, notably high-voltage power devices based on Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN), crucial for traction inverters and battery management systems (BMS). These components require automotive-grade reliability and temperature tolerance that only purpose-built ASICs can deliver. Furthermore, the push for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) in newer vehicle models necessitates specialized vision processing and sensor fusion ASICs designed to handle real-time data from gyroscopes and environmental sensors, creating a new, high-value segment of demand.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary structural challenge facing the Brazilian ASIC market is the entrenched dependence on international fabrication capacity. The domestic process technology ceiling for logic remains at mature nodes (e.g., 65nm or 90nm), compelling all advanced-node designs (e.g., 7nm and below) to rely on Asian foundries. This dependency exposes local design houses and end-users to global export control risks, extended logistics lead times, and the volatility of international freight rates. This constraint inflates the total cost of ownership for cutting-edge Brazilian products and slows time-to-market.
However, this challenge simultaneously creates a distinct opportunity in the realm of design and packaging. The government's focus, formalized by the Brasil Semicon program (signed into law in September 2024), shifts the national competitive strategy toward cultivating a world-class fabless design ecosystem. The opportunity lies in accelerating this design-first approach through partnerships, concentrating R&D funds on intellectual property (IP) blocks and System-on-Chip (SoC) architectures for high-growth domestic applications (AI, 5G, automotive). Furthermore, Brazil's established position as the second-largest Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) hub outside of Asia presents a tangible opportunity to build a regional competence center for advanced packaging and testing, mitigating some of the back-end supply chain risks associated with overseas final production.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis:
As a physical product, the ASIC's material supply chain directly impacts its pricing and domestic industrial viability. The pricing dynamic of the final ASIC is largely determined by the cost of the silicon wafer, specialized materials (e.g., photoresists, process gases), and the raw input for advanced packaging components, most of which are imported. The cost of these inputs is subject to global commodity pricing and exchange rate volatility, which is particularly acute for local companies operating with the Brazilian Real (BRL).
A key factor for future resilience is Brazil's positioning in the critical materials value chain. The country possesses the world's third-largest reserves of rare earth elements (REE), which are essential for high-performance magnets used in electric motors, specialized sensors, and advanced semiconductor manufacturing equipment. The Brazilian Development Bank (BNDES) and the government's innovation agency (Finep) have allocated financial backing to mineral projects, aiming to structure an integrated domestic industrial chain for REE mining and local processing. If successful, this national effort could partially de-risk the end-to-end supply chain for high-performance components, stabilizing the cost structure for locally designed ASICs and providing a strategic hedge against global material price fluctuations.
- Supply Chain Analysis:
The Brazilian ASIC supply chain is characterized by a globally distributed, Asia-centric front-end (wafer fabrication) feeding a growing domestic back-end (Assembly, Test, and Packaging).
The primary production hubs for the logic and memory components that feed into Brazilian-designed ASICs remain heavily concentrated in Asia-Pacific (Taiwan, South Korea, China) for advanced nodes. This logistical complexity involves extended lead times for the most advanced wafers, necessitating rigorous inventory planning by local Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and design houses.
Brazil's strategic role is concentrated in two areas:
- Fabless Design: A small but expanding ecosystem of companies focuses on designing specialized ICs and IP blocks.
- Assembly, Test, and Packaging (ATP): Brazil maintains a globally competitive footprint in OSAT services, notably in the Manaus Free Trade Zone (ZFM), which benefits from fiscal incentives. This domestic packaging and testing capability provides a final assembly point closer to the domestic consumer electronics and automotive end-markets, reducing the last-mile logistics risk for final integration. Key dependencies remain on the import of high-value manufacturing equipment and specialized process materials, reinforcing the 'Brazil Cost' challenge regarding complex tax and customs regimes.
Brazil Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Government Regulations:
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Brazil (Federal) | Law No. 14,968 / PADIS & Brasil Semicon Programme | Enacted 11 September 2024, Law?14,968 modifies Brazil's semiconductor industrial policy, including the PADIS programme (Support Programme to the Technological Development of the Semiconductor Industry). It extends incentives (tax relief, tariff exemptions) for semiconductor manufacturing until December 2029 and establishes the Brasil Semicon Programme. These incentives lower the cost base for ASIC development and production in Brazil—reducing import duties, tax burdens on goods and machinery, and increasing competitiveness for local ASIC firms. |
| Brazil (Telecommunications/Certification) | ANATEL – Resolution No. 780/2025 | Resolution 780 (effective 1 August 2025) strengthens product certification and conformity assessment for telecommunications products. It expands enforcement (e.g., marketplaces are held liable for non-compliant goods), includes data centers within the scope of certification, and tightens labeling and approval requirements. For ASICs used in networking, telecom infrastructure, or devices that interface with regulated wireless/telecom equipment, this increases the complexity and cost of bringing devices to market unless the ASICs are designed and certified in compliance. |
| Brazil (Telecommunications / Spectrum & Standards) | ANATEL – Act No. 2105 and Resolution 772 of 2025 | Act No.?2105 updates technical requirements for devices (including 5G NB NTN, RedCap, LTE Cat 1bis), and Resolution 772 revises the allocation and emission limits for frequency bands used by wireless devices. ASIC designers targeting wireless communication applications must now design to newer testing regimes and stricter emission standards. This raises R&D and compliance costs but also creates demand for higher-spec ASICs that satisfy these new technical/regulatory thresholds. |
| Brazil (Environment / Chemical Regulation) | Law No. 15.022/2024 – National Inventory of Chemical Substances | Law No. 15.022 (13 November 2024) requires production or import of chemical substances above certain volumes to be registered, with hazard classification, usage, risk assessment. ASIC production involves certain chemical materials (etchants, dopants, photoresists, solvents). This regulation increases regulatory oversight on chemical inputs, potentially increasing costs of raw materials, documentation, safety compliance. ASIC manufacturers must ensure supply of registered chemicals, which may reduce flexibility in sourcing from foreign suppliers not compliant with Brazilian inventory standards. |
Brazil Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Segment Analysis:
- By Application – Data Centers & Cloud Computing: The Data Centers & Cloud Computing segment constitutes a major structural growth pillar for high-performance Application-Specific Integrated Circuits. The sector's expansion is fueled by the rapid domestic adoption of hyperscale cloud services, a dramatic increase in local data generation, and the burgeoning need for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) processing capabilities. This necessity is intrinsically linked to ASICs because general-purpose CPUs cannot efficiently handle the massive computational loads required for AI model training and real-time inference at scale. Hyperscale providers and large enterprise users actively seek custom silicon—such as proprietary Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) or specialized ASIC accelerators—to gain a competitive edge in performance-per-watt metrics. The requirement here focuses on 7nm and 5nm process nodes for maximum transistor density and energy efficiency. Verifiable strategic statements from global silicon providers targeting Brazil as a future AI infrastructure hub (e.g., NVIDIA) underscore the immediate and high-volume demand for Data Center ASICs designed for accelerated compute. This segment acts as a key vertical for introducing the most advanced ASIC technology into the Brazilian market.
- By Application – Automotive: The Automotive segment is defined by a non-negotiable shift toward electrification and automation, fundamentally transforming its silicon demand profile from microcontrollers to sophisticated ASICs. The market driver is the domestic localization trend, incentivized by programs like Rota 2030, which pushes vehicle manufacturers to integrate more advanced technology locally. This segment's growth is concentrated in three critical ASIC sub-categories: Power Management ASICs (SiC and GaN) for high-efficiency charging and motor control in electric vehicles; Sensor Fusion ASICs for processing data streams from Lidar, Radar, and camera systems in ADAS features; and Robust Microcontrollers/ASICs capable of operating reliably in extreme vehicle environments (e.g., -40°C to 150°C). The requirement is highly specific, favoring Full-Custom and Semi-Custom ASICs with rigorous quality and functional safety certifications (e.g., ISO 26262). The move by international OEMs to establish local assembly of power electronics directly drives a new, persistent need for locally-sourced or localized ASIC components certified for this resource-intensive application.
Brazil Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The competitive landscape in Brazil is dominated by multinational fabless and Integrated Device Manufacturer (IDM) companies whose global product portfolios address the critical domestic demand verticals: Data Center, Telecommunications, and Automotive. Direct local competition in advanced-node fabrication is negligible, placing the competition squarely in the design and ecosystem support arena.
- Intel: Intel's strategic positioning in Brazil centers on its dominance in the central processing unit (CPU) segment for corporate and data center infrastructure, increasingly utilizing its advanced processes to build semi-custom server-grade ASICs. While the company's official news releases in 2024-2025 focus on its global push toward its 20A and 18A foundry roadmap and major US-centric capacity additions, its leverage in the Brazilian market is its established enterprise sales channels and localized technical support network. Intel's competitive advantage for ASICs lies in its ability to offer System-on-Chip (SoC) solutions that integrate custom accelerators alongside its core Xeon processors, targeting hybrid workloads in large-scale Brazilian cloud and telecommunications data centers. The company also employs a strategic focus on its Altera (now Intel FPGA) portfolio, offering programmable ASICs (FPGAs) as an alternative for clients requiring rapid, flexible deployment before committing to a full-custom design tape-out.
- NVIDIA: NVIDIA's strategic focus in the Brazilian market is laser-sharp: establishing the core compute infrastructure for Artificial Intelligence. The company's competitive differentiation is its proprietary GPU and specialized data center ASIC architecture (e.g., the Blackwell platform), which has become the de facto standard for AI model training. NVIDIA explicitly stated in August 2025 that it views Brazil as a future hub for AI infrastructure development in Latin America, signifying a direct investment and long-term commitment. The firm actively engages with the Brazilian government on the "Brazilian AI Plan," which is intended to attract investment through tax incentives. This positioning bypasses competition in traditional consumer ASICs and focuses on the high-value Data Centers & Cloud Computing segment, where its custom silicon is a non-substitutable asset for large-scale, accelerated computing projects.
- Infineon Technologies: Infineon's strategic positioning targets the high-growth, high-reliability Application-Specific Integrated Circuits required by the domestic automotive and industrial sectors. The company is a key supplier of power semiconductors, a market segment directly benefiting from Brazil's electric vehicle localization trend and the Rota 2030 program. Infineon's product strategy emphasizes ASICs built on specialized materials, specifically Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN) power MOSFETs and gate drivers. These components are Full-Custom or Semi-Custom ASICs critical for maximizing the efficiency and thermal performance of electric vehicle battery management and charging systems. This specialization makes Infineon a deeply embedded strategic partner in the domestic supply chains of automotive Tier-1s and power infrastructure providers, insulating it from the cyclicality of the general-purpose semiconductor market.
Brazil Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Developments:
- August 2025: NVIDIA publicly outlined a strategic expansion into Latin America, explicitly identifying Brazil as a future hub for AI infrastructure development. The company cited a collaboration with the Brazilian government on the "Brazilian AI Plan," a program involving tax incentives to attract technology infrastructure investment. This announcement directly signals a major investment pipeline for high-performance, custom data center ASICs, such as the company's Blackwell chip platform, into the Brazilian market for AI training and inference.
- April 2025: Brazil's National Development Bank (BNDES) and Finep (the government's innovation agency) accelerated funding for strategic mineral projects, many of which focus on rare earth elements (REE). This governmental financial backing is aimed at structuring an integrated domestic industrial chain for REE mining and local processing. Since REEs are critical for high-performance magnets and specialized semiconductor components, this move is a direct, pre-emptive measure to de-risk the future supply chain and stabilize the material cost base for domestic electronic manufacturing.
- August 2024: The Brazilian Senate passed legislation creating the Brasil Semicon Programme, an initiative to promote the entire national production chain by encouraging investment in research, innovation, and value-added chip production. The legislation authorized the extension of the Semiconductor Development Support Programme (PADIS) through 2073, incorporating service activities, including software design for virtual environments, as eligible for tax relief. This regulatory action is a long-term catalyst for ASIC design houses, lowering the financial barrier for domestic R&D projects.
Brazil Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 1.292 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 1.905 billion |
| Growth Rate | 8.08% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Process Technology, Product Type, Application |
| Companies |
|
Brazil Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Market Segmentation:
- BY PROCESS TECHNOLOGY
- Advanced Nodes
- 3 nm and below
- Leading-Edge Nodes
- 5 nm
- 7 nm
- Mid-Range Nodes
- 10 nm
- 12 nm
- 14 nm
- 16 nm
- Mature Nodes
- 22 nm and above
- Advanced Nodes
- BY PRODUCT TYPE
- Full-Custom ASIC
- Semi-Custom ASIC
- Standard Cell-Based ASIC
- Gate-Array Based ASIC
- Programmable ASIC
- Others
- BY APPLICATION
- Consumer Electronics
- Automotive
- Networking & Telecommunications
- Data Centers & Cloud Computing
- Healthcare
- Industrial & IoT
- Defense & Aerospace
- Others