Report Overview
Canada Electric Commercial Vehicles Highlights
Canada Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Size:
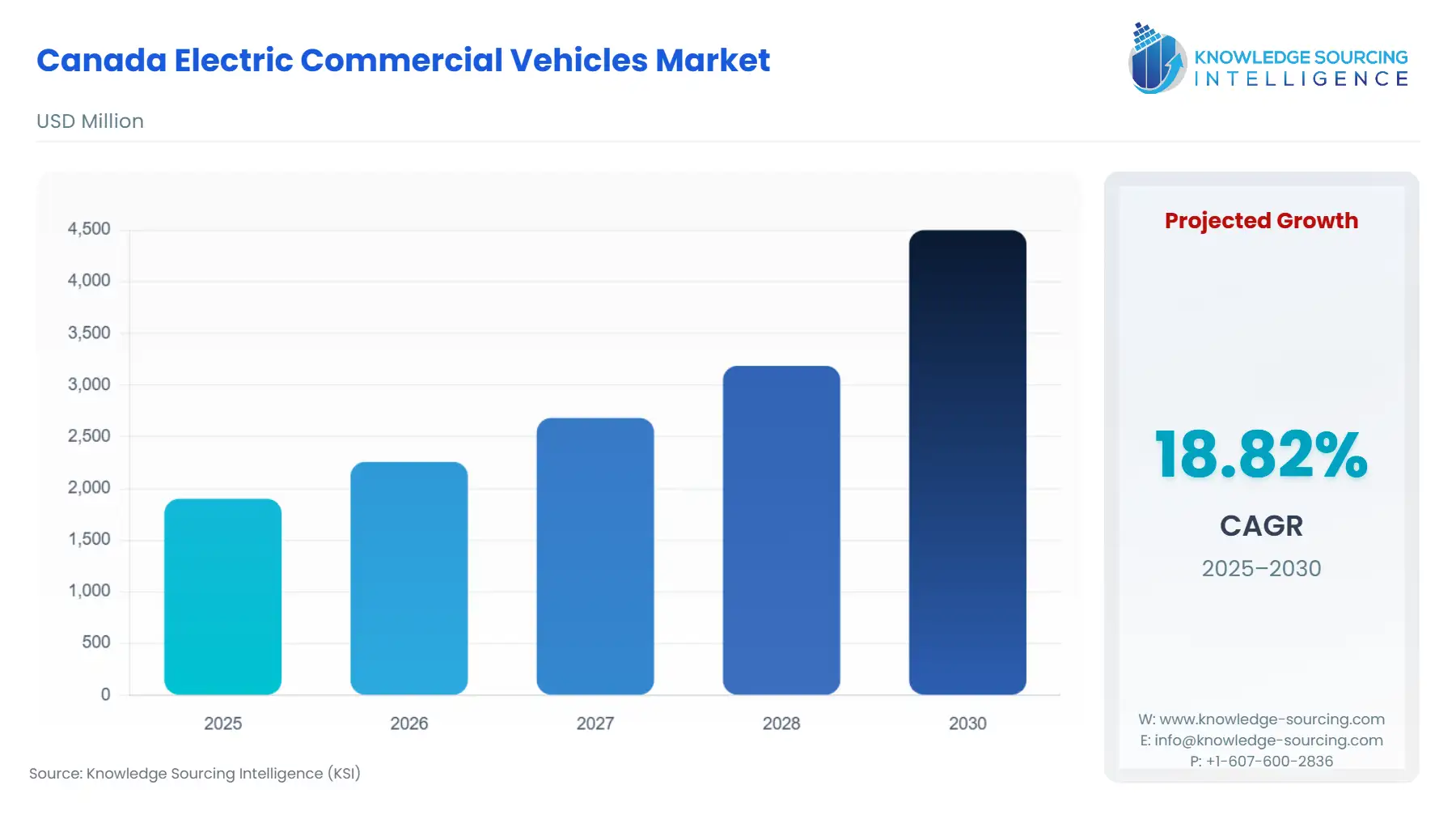
The Canada Electric Commercial Vehicles Market is expected to advance at a CAGR of 18.82%, reaching USD 4.5 billion in 2030 from USD 1.9 billion in 2025.
The Canadian electric commercial vehicle (eCV) market is transitioning from an early-adopter environment to a mandate-driven procurement model, principally steered by federal decarbonization commitments. The sector includes all vehicle classes from light-duty vans to heavy-duty trucks and public transit buses. Regulatory pressure, combined with substantial point-of-sale incentives, is forcing fleet conversion across all major industries. This systemic shift creates immediate demand for battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) and associated charging infrastructure, moving the market away from internal combustion engine (ICE) models for urban and regional operational cycles.
Canada Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Government financial support is the most effective growth driver in the nascent eCV market. The iMHZEV program, offering up to $200,000 at the point-of-sale for eligible medium- and heavy-duty zero-emission vehicles (MHDVs), directly lowers the total cost of acquisition for fleet operators. This reduction in the initial capital expenditure accelerates the business case for adoption, translating directly into a greater volume of purchase orders from logistics, public transit, and municipal fleets. Furthermore, corporate sustainability goals and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) mandates compel major Canadian corporations with large logistics operations to procure electric fleets, which is a non-negotiable factor increasing demand irrespective of fluctuating fuel prices.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary constraint on market expansion is the inadequate deployment of robust, high-power charging infrastructure, particularly for medium- and heavy-duty applications. Complex application processes for charging funding and protracted utility timelines for grid upgrades directly create friction in fleet electrification timelines, dampening the potential demand from operators needing high-utilization vehicles. An additional financial constraint is the high upfront vehicle cost, exacerbated by elevated interest rates, which steers some cost-sensitive commercial buyers towards hybrid alternatives, diverting sales from pure ZEVs. Conversely, the opportunity lies in the burgeoning market for integrated "Charging-as-a-Service" and fleet management software solutions. The need to optimize charging times, manage load profiles, and integrate vehicle diagnostics presents a substantial demand opportunity for Canadian technology providers to close operational gaps.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
Electric commercial vehicles are physical products, making them susceptible to raw material supply chain dynamics, particularly for lithium-ion battery packs. Battery prices constitute a considerable portion of the final vehicle cost. Global price volatility for key battery components—lithium, cobalt, and nickel—creates pricing uncertainty for Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), who must manage these costs to keep the final vehicle purchase price within the reach of government incentives. The long-term demand curve remains heavily dependent on sustained reductions in battery pack costs, which lowers the overall vehicle MSRP and enhances the competitiveness of electric models against diesel counterparts.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global supply chain for eCVs is characterized by significant dependence on Asia-Pacific regions for battery cell manufacturing. This dependency creates logistical complexities and potential vulnerability to geopolitical disruptions, affecting vehicle production timelines for Canadian OEMs. Vehicle final assembly hubs are emerging in North America, often leveraging existing manufacturing footprints, but key components such as e-axles, power electronics, and battery modules are sourced globally. Logistical challenges are compounded by the necessity of transporting heavy, high-voltage battery packs, arduous specialized handling and transportation protocols throughout the North American distribution network.
Canada Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Government Regulations:
Key federal and provincial regulations exert a direct influence on eCV demand by establishing compliance requirements and providing financial mechanisms to mitigate cost barriers.
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
Federal (Canada) |
Incentives for Medium- and Heavy-duty Zero-Emission Vehicles (iMHZEV) |
The point-of-sale rebate directly reduces capital expenditure, making BEV procurement financially viable and immediately stimulating fleet purchase orders. |
|
Federal (Canada) |
Proposed Regulated Sales Targets for ZEVs (Model Year 2026 onwards) |
Establishes a compliance-based push for manufacturers, guaranteeing a continuous supply of diverse ZEV models in the Canadian market, thereby increasing fleet options. |
|
Federal (Canada) |
Zero Emission Vehicle Infrastructure Program (ZEVIP) / Energy Innovation Program (EIP) |
Provides financial support for charging infrastructure, which is crucial for reducing range/utilization anxiety and directly enabling the demand generated by vehicle purchases. |
Canada Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segment Analysis:
- By Vehicle Type: Heavy-Duty Trucks
The long-term imperative to decarbonize regional haulage and drayage operations primarily drives the need for heavy-duty electric trucks (Class 8). Unlike long-haul transport, which is constrained by range and charging time, regional fleets operate on predictable, back-to-base routes. This operational profile aligns perfectly with current battery technology limitations and the depot-charging model. Large logistics companies in Canada, facing increasing pressure from shareholders and municipal partners to reduce their carbon footprint in urban areas, create a strong, verifiable demand for electric Class 8 tractors for short- and medium-mileage routes where the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) advantage begins to mature. The availability of high-power charging corridors (megawatt charging systems) along key trade routes will be the single most critical enabler for expanding demand beyond the current drayage applications.
- By Application: Public Transportation
The public transportation segment, dominated by electric buses and coaches, exhibits a high and sustained demand because it is largely shielded from consumer affordability concerns and is mandated by publicly funded procurement. In 2023, electric buses constituted more than 20% of bus sales in Canada. This growth is fueled by the federal government's Zero Emission Transit Fund (ZETF), which offers significant investment for transit authorities to purchase electric buses and install necessary charging infrastructure. Public transit buses operate on fixed routes with centrally managed depots, simplifying charging logistics and maximizing vehicle uptime. The successful deployment of pilot fleets and the resulting reduction in operational costs (lower fuel and maintenance expenses) provide a compelling, proven business case that continuously increases purchase volumes from municipalities across the country.
Canada Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Competitive Analysis:
The competitive landscape is bifurcated between established global OEMs and aggressive domestic start-ups focused exclusively on electric platforms. Competition centers on vehicle availability, demonstrable real-world performance in Canadian weather conditions, and comprehensive charging/service support.
- The Lion Electric Company
Lion Electric, a Canadian manufacturer, maintains a strategic position focusing on all-electric medium- and heavy-duty urban vehicles, notably school buses and trucks. Their strategy is based on vertically integrated manufacturing and a local-for-local supply chain strategy. Lion's commitment to the electric school bus segment, which leverages public sector procurement and predictable duty cycles, provides a robust, anchor-client base. Key products include the LionC all-electric school bus and the Lion8 heavy-duty truck, which provides a dedicated option for regional distribution and vocational fleets.
- Daimler Truck AG (RIZON Brand)
Daimler Truck leveraged its new RIZON brand to enter the Canadian market with battery-electric Class 4-5 trucks. This launch strategy focuses on established OEM reliability and a global manufacturing backbone to capture the medium-duty urban delivery and vocational segment. RIZON's positioning capitalizes on its eligibility for the iMHZEV program, targeting fleet operators who require a proven, dependable commercial platform backed by an extensive dealer and service network, directly challenging regional start-ups.
Canada Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Developments:
- August 2025: The Canadian government, through Natural Resources Canada's (NRCan) Energy Innovation Program (EIP), announced over $8 million in funding for six projects targeting the medium- and heavy-duty commercial vehicle sectors. This funding supports technological development, including high-voltage lithium-ion battery pack prototypes for MHDVs.
- November 2024: The Lion Electric Company announced in its Q3 2024 results the delivery of 89 vehicles, consisting of 71 school buses and 18 trucks, with 45 vehicles delivered in Canada. This operational data confirms the ongoing commercialization and delivery of their core product lines, despite a lower volume compared to the previous year.
- April 2024: Daimler Truck's new brand, RIZON, announced the Canadian launch of its battery-electric Class 4-5 trucks, including the e16L, e16M, e18L, and e18M variants. This product introduction expands the available verified OEM options for medium-duty fleet operators.
Canada Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 1.9 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 4.5 billion |
| Growth Rate | 18.82% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Vehicle Type, Propulsion Type, Power Output, Application |
| Companies |
|
Canada Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segmentation:
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Buses and Coaches
- Trucks
- Light-Duty Trucks
- Medium-Duty Trucks
- Heavy-Duty Trucks
- Vans
- BY PROPULSION TYPE
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEV)
- BY POWER OUTPUT
- Up to 150 kW
- 150-250 kW
- Above 250 kW
- BY APPLICATION
- Logistics and Transportation
- Public Transportation
- Construction (Excavators, Loaders, Others)
- Mining
- Agriculture (Tractors, Harvesters, Others)
- Others