Report Overview
China 5G Fuel Cell Highlights
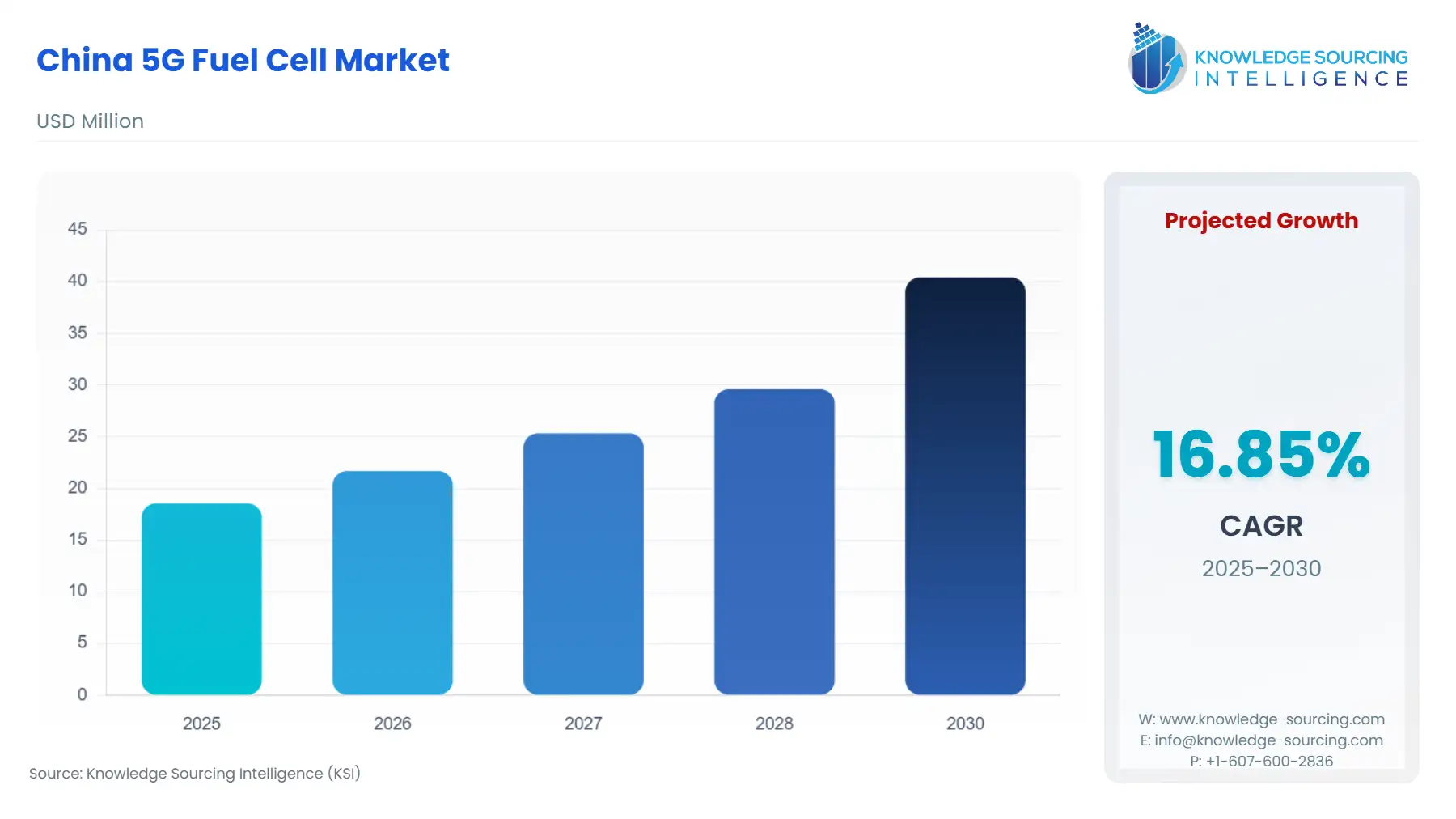
China 5G Fuel Cell Market Size:
The China 5G Fuel Cell Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 16.85%, reaching USD 40.430 million in 2030 from USD 18.560 million in 2025.
The rapid, large-scale deployment of 5G infrastructure across China establishes a significant, enduring demand opportunity for high-capacity, zero-emission stationary power solutions. The market represents a convergence of national digitalization strategy—the "New Infrastructure" initiative—and a sweeping, state-driven commitment to decarbonization. This dual imperative positions Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs) as an essential technology for ensuring the operational continuity and sustainability of one of the world’s largest and most energy-intensive communication networks. The transition from legacy diesel generators and limited-duration battery systems to hydrogen-fueled solutions is a key operational pivot for network operators, shifting capital investment toward long-term operational efficiency and regulatory compliance.
China 5G Fuel Cell Market Analysis:
Growth Drivers
The primary growth catalyst is the mandated, rapid rollout of 5G infrastructure, requiring hundreds of thousands of base stations. Each 5G site’s significantly increased power draw, often exceeding 10 kW, renders legacy battery and low-capacity backup systems functionally inadequate for extended outages. This performance gap creates an explicit and immediate demand for high-energy-density fuel cell solutions capable of providing long-duration backup power, particularly in remote or underserved areas. Concurrently, the state’s aggressive carbon neutrality pledges by 2060 make zero-emission power a procurement necessity, effectively pricing out diesel generators and thereby directing operator capital expenditure toward fuel cells. The need to reduce operational expenditure (OpEx) for site maintenance also propels demand, as fuel cells promise fewer replacement cycles and reduced maintenance visits compared to battery banks, delivering a superior total cost of ownership (TCO) in long-term operations.
Challenges and Opportunities
The chief challenge confronting the market is the underdeveloped hydrogen refueling infrastructure, specifically its geographical alignment with remote 5G tower sites. A lack of accessible, cost-effective hydrogen supply creates a logistical constraint that can diminish the TCO advantage of fuel cells, thereby suppressing demand, particularly in decentralized, rural deployments. However, this infrastructure gap simultaneously presents a monumental opportunity for vertically integrated players. The opportunity lies in the ability of manufacturers to transition toward a localized, decentralized hydrogen supply model, utilizing small-scale, on-site electrolyzers powered by renewable energy. This strategic shift not only resolves the refueling constraint but also converts the 5G sites into distributed energy nodes, accelerating technology adoption and directly boosting the demand for integrated fuel cell and hydrogen production packages, especially in off-grid or remote power segment applications.
Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The pricing dynamics within the Chinese 5G Fuel Cell market are fundamentally influenced by the cost and supply chain efficiency of two core components: the Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) and the platinum group metal (PGM) catalysts. While China is aggressively pursuing domestic R&D to reduce PGM loading in catalysts, the current cost of the fuel cell stack remains substantially tied to global PGM prices, creating a pricing volatility constraint. The substantial domestic control over the manufacturing of PEMs and components like bipolar plates, largely concentrated in hubs such as Jiangsu and Shanghai, acts as a downward pricing pressure, stabilizing the supply chain. Successful government-backed initiatives focused on domestic technological breakthroughs, particularly in PEM and Gas Diffusion Layer (GDL) technology, are the singular determinant for meeting the target of significant stack cost reduction, which is imperative for achieving long-term demand growth outside of heavily subsidized pilots.
Supply Chain Analysis
The Chinese 5G Fuel Cell supply chain exhibits a significant degree of vertical integration, particularly in the manufacturing of balance-of-plant (BOP) components and the critical Proton Exchange Membrane. Key production and assembly hubs are consolidated in the Greater Shanghai region, Guangdong Province, and select parts of the Yangtze River Delta, leveraging existing chemical and advanced manufacturing bases. The primary logistical complexity arises not from component supply, but from the dependency on a nascent hydrogen distribution network. The current supply chain model relies on established, centralized hydrogen production facilities (often from industrial by-products) and road transport for delivery, making fuel delivery to scattered 5G tower sites a high-cost and efficiency-constraining factor. Future demand hinges on establishing localized hydrogen production and storage dependencies that decouple the power-generation equipment from the industrial hydrogen supply chain.
Government Regulations
Key government policies have fundamentally reshaped the market landscape by explicitly prioritizing hydrogen and green energy.
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Central Government (State Council) | Medium- and Long-Term Plan for the Development of the Hydrogen Energy Industry (2021–2035) | Mandates the development and commercialization of the entire hydrogen industry chain. Creates a clear political imperative for telecom operators to adopt hydrogen solutions to meet state-level industrial goals, directly generating demand for pilot and large-scale fuel cell procurement. |
| Central Government (NDRC, MIIT) | 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025) for the Digital Economy | Accelerates the large-scale rollout of 5G infrastructure, particularly in rural and remote areas. The corresponding pressure for resilient, long-duration backup power in these new, often grid-insecure sites establishes a non-negotiable demand floor for the superior operational profile of fuel cells over traditional batteries. |
| Provincial Governments (e.g., Guangdong, Shanghai) | Local Hydrogen Industry Development Policies and Subsidy Programs | Provides direct financial subsidies and preferential treatment for the deployment of hydrogen-related projects, including stationary fuel cell systems. This localized support lowers the initial capital expenditure barrier for telecom operators, acting as a critical short-term catalyst for demand adoption in specific provincial clusters. |
China 5G Fuel Cell Market Segment Analysis:
By Application: Backup Power Solutions
The backup power solutions segment forms the definitive demand anchor for the China 5G Fuel Cell Market. The operational necessity for ensuring uninterrupted network service across a sprawling 5G footprint drives this segment's growth. Traditional lead-acid batteries offer insufficient run-time for extended grid outages, a common issue in remote or peripheral network areas, creating a structural demand vacuum that fuel cells are uniquely equipped to fill. PEMFC backup systems offer significantly longer autonomy (days versus hours) with minimal footprint compared to the equivalent energy capacity in battery banks, directly increasing the perceived value proposition for tower operators. The high-power density of fuel cells allows them to efficiently support the substantial power requirements of multiple co-located radios and cooling equipment on a 5G site. Furthermore, the inherent longevity of fuel cells—operating efficiently over thousands of hours without major degradation—substantially lowers the OpEx associated with frequent battery replacement and disposal, making TCO a pivotal growth driver. The initial capital expenditure remains high, but the verifiable decrease in lifecycle costs propels operators to scale their fuel cell pilot programs into sustained procurement strategies, solidifying this as the core revenue segment.
By End-User: Telecom Operators
Telecom Operators represent the largest and most strategically important end-user segment, driven by both regulatory compliance and the critical need for network reliability as a core competitive differentiator. The increasing 5G coverage expansion, particularly to meet national connectivity mandates, forces operators to deploy infrastructure in challenging locations where grid stability is compromised. This exposure to outage risk translates directly into demand for the high-resilience attributes of fuel cells. Operators such as China Mobile and China Unicom are compelled by both the national decarbonization agenda and internal sustainability targets to integrate cleaner power solutions. Their procurement decisions are therefore fundamentally shaped by system reliability metrics (e.g., Mean Time Between Failures, or MTBF) and the solution’s ability to operate autonomously for prolonged periods. The deployment of fuel cells on remote sites not only assures network uptime but also reduces the costly logistical burden of dispatching maintenance crews with portable generators. Ultimately, the imperative to manage the exponential energy costs of 5G networks, where fuel cells offer a path to cheaper, potentially green hydrogen in the long term, makes Operators the primary market driver in this segment.
China 5G Fuel Cell Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of highly capitalized domestic energy conglomerates, specialized Chinese fuel cell system providers, and international firms with advanced technology transfer arrangements. The market competition revolves around system integration capabilities, stack durability, and the ability to reduce TCO through hydrogen supply partnerships. Domestic leaders leverage deep government ties and established manufacturing infrastructure, while international players offer validated high-performance stack technology.
Weichai Power Co., Ltd.
Weichai Power, primarily a global powerhouse in the commercial vehicle and engine sector, strategically positions itself as a dominant force in the broader new energy ecosystem, extending its traditional engine manufacturing base into hydrogen and fuel cell solutions. Its strategy is one of comprehensive vertical integration and technological partnership, notably through its investment and collaboration with Ballard Power Systems for stack technology and Ceres Power for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) technology, complementing its core PEM focus. This positioning allows Weichai to control critical component supply and rapidly scale production. The company's competitive advantage in the 5G market stems from its immense financial resources and its capability to mass-produce and industrialize power generation solutions, enabling it to offer systems with superior reliability and cost efficiency that appeal to large-scale telecom infrastructure providers.
Beijing SinoHytec Co., Ltd.
Beijing SinoHytec (SinoHytec) is a dedicated fuel cell system integrator and manufacturer, with a strong focus on the Chinese market and government-backed projects. The company's strategic positioning is predicated on its localized R&D expertise and crucial joint venture (JV) with Toyota Motor Corporation, a globally recognized leader in fuel cell technology. This partnership provides SinoHytec with access to proven, high-durability fuel cell stack technology, which is essential for the challenging, high-uptime requirements of 5G backup power. SinoHytec differentiates itself by focusing on complete system integration, tailoring its product offerings for specific regional and application requirements within the domestic market. Its direct ties to major state-owned enterprises and government R&D programs ensure its products are aligned with national technical standards and subsidy eligibility criteria, making it a preferred domestic supplier for pilot and commercial deployments.
China 5G Fuel Cell Market Recent Developments:
- June 2025 - Robert Bosch GmbH acquired extended intellectual property rights from PowerCell Group to further adapt and localize PowerCell's S3 fuel cell stack, specifically targeting the rapidly growing Chinese automotive market. The agreement, valued at approximately €6 million, allows Bosch to intensify local stack adaptation for high-performance hydrogen solutions in China's mobility sector. Crucially, the partners also agreed to jointly explore the potential of using PowerCell's technology for non-automotive applications in China, including stationary power and industrial mobility, which directly impacts the 5G base station power sector.
- August 2024 - The Toyota SinoHytec Fuel Cell R&D and Production Center, a joint venture between SinoHytec and Toyota Motor Corporation, commenced operations. The facility was established with a significant initial capacity, estimated at 10,000 units of fuel cell systems per year, with a focus on commercial vehicle applications but representing a critical, large-scale addition to the national fuel cell manufacturing ecosystem. This capacity provides the necessary production volume and technology transfer to efficiently scale up stack and system manufacturing for stationary applications like 5G power in the near term.
China 5G Fuel Cell Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 18.560 million |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 40.430 million |
| Growth Rate | 16.85% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Product Type, Deployment, Power Output Range, End-User |
| Companies |
|
China 5G Fuel Cell Market Segmentation:
- BY PRODUCT TYPE
- Fuel Cell Systems
- Fuel Cell Stacks & Components
- Fuel Supply Solutions
- BY DEPLOYMENT
- Backup Power Solutions
- Off-grid / Remote Power Solutions
- Hybrid Energy Systems
- High-capacity Solutions
- BY POWER OUTPUT RANGE
- <5 kW
- 5–50 kW
- 50 kW
- BY END USER
- Telecom Operators
- Tower & Infrastructure Providers
- Government & Defense Communication Networks
- Enterprise 5G Networks