Report Overview
China Electric Vehicle Components Highlights
China Electric Vehicle Components Market Size:
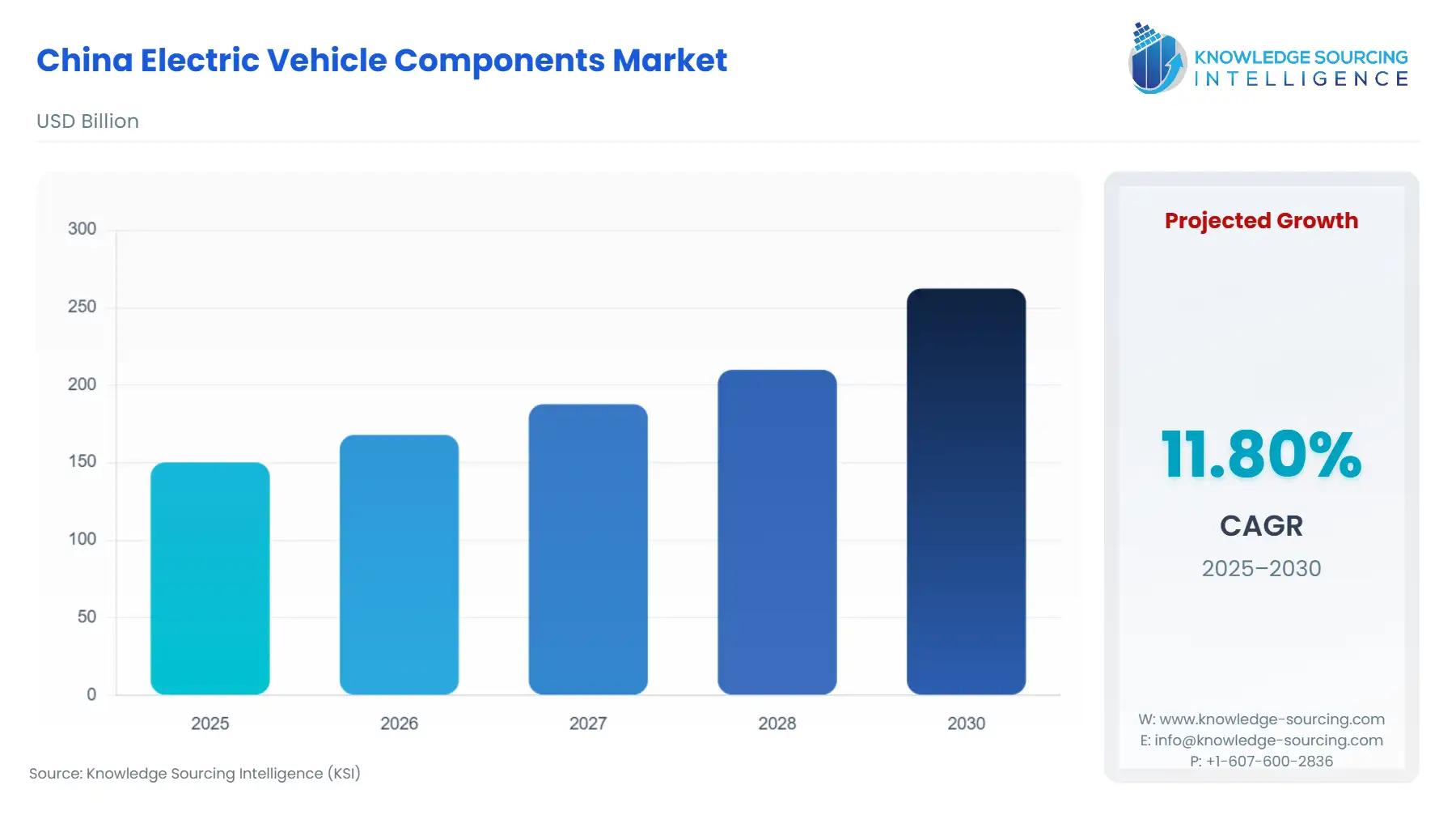
The China Electric Vehicle Components Market is set to rise at a CAGR of 11.80%, attaining USD 262.344 billion in 2030 from USD 150.212 billion in 2025.
The Chinese Electric Vehicle Components Market is fundamentally shaped by the nation's strategic industrial policy and its dominant global manufacturing scale. With plug-in electric vehicle sales reaching nearly 50% of the overall automotive sales in 2024, the market has transitioned from a subsidized growth model to one driven by sheer volume and technological sophistication. This rapid rate of EV adoption translates directly into sustained, high-volume demand for critical EV components, including battery packs, electric motors, and power electronics, establishing China as the undisputed center of the global EV supply chain. The scale of domestic production, coupled with an increasing focus on exports, mandates continuous component innovation and supply chain efficiency to maintain the competitive advantage.
China Electric Vehicle Components Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The primary factor propelling market growth is the sheer scale of domestic New Energy Vehicle (NEV) production and sales, which accounted for over 11 million electric car sales in 2024. This volume creates an immense, recurring baseline demand for full component sets, from high-voltage battery modules to inverters and converters. Furthermore, the Chinese government's national strategy, outlined in the "New Energy Vehicle Industry Development Plan (2021-2035)," actively encourages the development of e-powertrain advancements. This policy directly increases demand for higher-specification, technologically advanced components, such as more efficient electric motors and wide-bandgap (SiC/GaN) power electronics, as OEMs strive to meet evolving performance benchmarks. The expansion of Chinese OEM exports, which saw significant year-over-year growth in the first half of 2024, also translates domestic component manufacturing capacity directly into global demand.
- Challenges and Opportunities
A core challenge facing the market is the sustained volatility in raw material pricing for critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can account for up to 40% of the final battery pack cost. This instability presents a pricing constraint for component manufacturers, potentially diminishing margins and necessitating flexible sourcing strategies. However, this same pressure creates a significant opportunity: an accelerated demand shift towards lower-cost chemistries, such as Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP), and the accompanying components optimized for these chemistries. Another challenge is the intensifying competitive landscape, which has triggered price wars among vehicle OEMs, forcing component suppliers to continually reduce costs and enhance efficiency. The corresponding opportunity lies in the demand for integrated component solutions, like the "cell-to-body" architecture, which simplify assembly and reduce overall manufacturing cost for the OEM end-users.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The components market, particularly the battery segment, is characterized by China’s profound control over the processing of key raw materials. China processes a controlling share of the world’s refined lithium, cobalt, and graphite. This processing dominance provides Chinese component manufacturers with a structural cost advantage and significant leverage in the global supply chain, directly impacting the final component pricing. For example, China's implementation of export restrictions on graphite products in 2023 introduced a degree of uncertainty, driving demand for localized, secure sourcing and alternative anode material development. The component market must navigate the tension between maintaining cost competitiveness and investing in new materials and designs to mitigate geopolitical risks and raw material price fluctuations.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The Chinese EV components supply chain is highly centralized and vertically integrated, a distinct advantage over fragmented global competitors. Production hubs are concentrated in provinces that benefit from clustered industrial ecosystems, efficient logistics networks, and established infrastructure for refining and manufacturing. This structure facilitates a "flatter" supply chain, enabling Tier-2 and Tier-3 component manufacturers to supply innovative products directly to emerging NEV OEMs, bypassing traditional Tier-1 bottlenecks. Key dependencies remain in the import of raw battery minerals from countries like Australia (lithium) and the Democratic Republic of Congo (cobalt), yet the domestic refining capacity acts as a crucial buffer against global supply shocks, ensuring continuous material flow to battery cell production lines.
China Electric Vehicle Components Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
China (State Council) |
New Energy Vehicle Industry Development Plan (2021-2035) |
Mandates technological advancement, creating direct demand for higher-performance, high-efficiency core components (motors, batteries) to meet national targets for energy consumption and range. |
|
China (Ministry of Finance) |
Purchase Tax Exemption for NEVs (Extended 2024-2027) |
Directly stimulates consumer demand for NEVs, providing an immediate and significant requirement for all EV components utilized by the vehicle manufacturers (OEMs). |
|
China (Various) |
Dual-Credit Policy (CAFC and NEV Credits) |
Compels traditional vehicle manufacturers to increase NEV production volumes, guaranteeing a minimum level of component demand by establishing a quota system for electric vehicle output. |
China Electric Vehicle Components Market Segment Analysis:
- By Component Type: Battery Pack
The Battery Pack segment is the most strategically vital component, accounting for a substantial portion of an EV’s cost and defining its performance metrics. The segment is primarily driven by three critical OEM imperatives: extended range, faster charging, and lower cost. The continuous push for greater driving range—evidenced by the launch of batteries exceeding 1,000 km—translates directly into demand for higher energy density cell chemistries and more advanced battery management systems (BMS) capable of handling increased voltage and thermal loads. The simultaneous emphasis on "super-fast charging" drives a parallel need for specialized cell structures and sophisticated thermal management components designed to safely and efficiently manage high C-rates. Furthermore, the structural market shift towards LFP chemistry—due to its lower cost—creates a massive demand for optimized LFP-based packs and their specific, required ancillaries.
- By End-User: OEMs
The OEM end-user segment represents the overwhelming majority of the demand for EV components, as nearly all components are integrated into the initial vehicle assembly. The need from OEMs is characterized by high volume, stringent specifications, and intense pressure on unit cost reduction. The key driver is the explosive growth of domestic Chinese OEMs and their increasing market share, both domestically and internationally. This surge in OEM production mandates a corresponding scale-up in component supply chain capacity. Furthermore, the OEM segment drives demand for highly customized, integrated components, moving away from standardized parts. This is exemplified by the need for components that support platform-based manufacturing (e.g., BYD’s e-Platform), requiring suppliers to engage in deeper co-development and integrate components directly into the vehicle's structural design.
China Electric Vehicle Components Market Competitive Analysis:
The Chinese EV components market features a highly concentrated and globally dominant competitive landscape, particularly within the battery segment. Competition is centered on economies of scale, vertical integration, and aggressive technological road-mapping. Major players are strategically expanding their global footprint and deepening integration with vehicle OEMs.
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Limited (CATL)
CATL maintains its strategic position through its sheer scale and technological diversification, focusing on high-density and fast-charging technologies. The company's core strategy involves securing key material supply, massive capacity build-out, and deep joint ventures with major automakers (e.g., SAIC, GAC). Its key products, like the Shenxing PLUS battery, which offers over 1,000 km range and a 600 km recharge in 10 minutes, set new performance benchmarks, forcing competitors and OEMs to continually upgrade their component specifications.
- BYD Company Limited (BYD)
BYD employs a distinct strategy of radical vertical integration, controlling every aspect of the EV component supply chain from battery cell production (FinDreams Battery) to electric motor manufacturing and final vehicle assembly. This unparalleled integration provides a significant cost advantage and a rapid development cycle. The company's Blade Battery technology, a proprietary LFP-based cell-to-pack design, underpins its competitive positioning by optimizing space utilization and safety, driving internal demand for its own component manufacturing divisions.
China Electric Vehicle Components Market Developments:
- June 2024: The groundbreaking ceremony for the Beijing Times Battery Base Project was held, a joint investment by CATL, BAIC Group, Jingneng Group, and Xiaomi Group. This strategic capacity addition, including the planned construction of battery production facilities, directly addresses the surging OEM demand resulting from new vehicle launches by partners like Xiaomi.
- April 2024: CATL launched the Shenxing PLUS lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery at the Beijing International Auto Show. The new battery delivers a claimed cruising range exceeding 1,000 km and an ultra-fast charging capability of 600 km in 10 minutes, raising the technological bar for the LFP cell and pack component segment.
China Electric Vehicle Components Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 150.212 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 262.344 billion |
| Growth Rate | 11.80% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component Type, Vehicle Type, Technology, End User |
| Companies |
|
China Electric Vehicle Components Market Segmentation
- BY COMPONENT TYPE
- Battery Pack
- Electric Motor
- Power Electronics
- Inverter
- Converter (DC-DC)
- On-Board Charger
- Thermal Management System
- Body & Chassis
- Other Components
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Passenger Cars
- Commercial Vehicles
- Two-Wheelers & Three-Wheelers
- BY TECHNOLOGY
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
- BY END-USER
- OEMS
- Aftermarket