Report Overview
France Electric Vehicle Market Highlights
France Electric Vehicle Market Size:
The France Electric Vehicle Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.76%, reaching a market size of USD 35.945 billion in 2030 from USD 21.564 billion in 2025.
The French electric vehicle market has matured from a niche segment into a central pillar of the nation's mobility transition. This evolution is predicated on a confluence of supportive policy frameworks, advancing technological capabilities, and a shifting consumer mindset toward sustainable transportation. The market's trajectory is directly linked to the efficacy of government incentives and the continuous expansion of charging infrastructure, which together address the primary barriers to mass adoption: cost and range anxiety. While the market demonstrates a clear and sustained growth pattern, driven by both private and commercial demand, it must navigate underlying challenges related to the global supply chain and the competitive influx of international players.
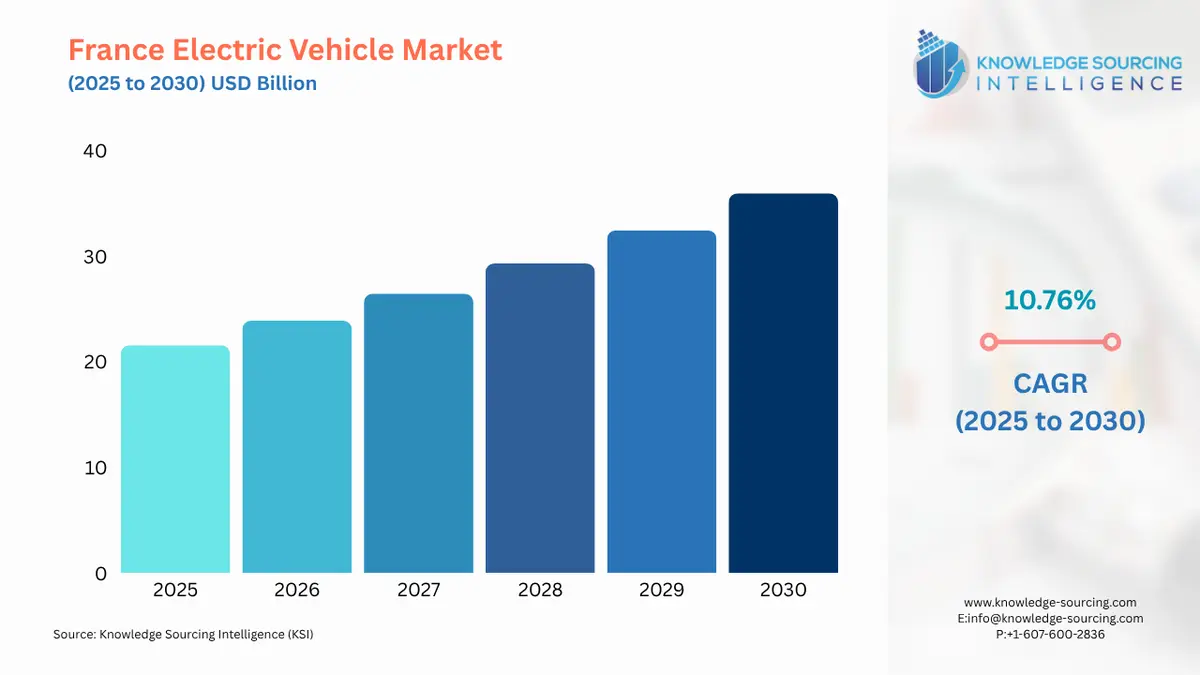
France Electric Vehicle Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
A combination of strategic governmental policies, infrastructure development, and corporate initiatives directly propels the electric vehicle market in France. The French government's "bonus écologique" (environmental bonus) and other financial incentives directly lower the total cost of ownership, making EVs more accessible and competitive with internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. A new extra subsidy for electric cars made in Europe, announced in September 2025, provides an additional €1,000 bonus for buyers, directly stimulating demand for locally-sourced vehicles and bolstering the domestic and European supply chain. This tiered approach, which links subsidies to both income and an "environmental score," effectively channels consumer demand towards more efficient and sustainably-produced models.
Furthermore, the expansion of the charging infrastructure network is a critical growth catalyst. The French government's goal of reaching 100,000 public charging points by the end of 2021 (a target that was reached and surpassed) and the subsequent Mobility Orientation Law (LOM) mandate for new and renovated parking lots directly alleviates consumer range anxiety. This infrastructure proliferation, particularly at retail, hotel, and parking operator locations, makes EV ownership more practical for daily use, thereby converting hesitant consumers into buyers. Finally, the rise of corporate fleet electrification, spurred by sustainability targets and regulatory compliance, creates a substantial and predictable source of demand. Businesses are increasingly adopting EVs to reduce long-term operating costs and align with France's decarbonization goals, creating a sustained market pull.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The French EV market faces significant headwinds, primarily a high initial purchase cost and a dependence on foreign supply chains. Despite government incentives, the upfront price of many EVs remains a barrier for a broad segment of the population, which can constrain the pace of mass-market adoption. This challenge creates an opportunity for manufacturers to introduce more affordable models, as evidenced by the success of mid-priced and entry-level EVs. The increasing competition from international brands, particularly from Asia, presents a dual challenge and opportunity. While it intensifies competition for domestic players, it also drives down prices and expands the range of available models, which in turn can stimulate overall demand.
A critical opportunity lies in leveraging France's existing industrial and technological base to address supply chain vulnerabilities. As a key growth driver, the demand for EV batteries presents a strategic imperative for domestic production. The EMILI project, launched by Imerys to mine lithium in central France, represents a direct effort to reduce import dependency and secure the supply of a crucial raw material. This strategic investment in a localized battery value chain could mitigate future supply shocks and establish France as a more resilient and self-sufficient player in the global EV market.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The electric vehicle market, as a physical product sector, is intrinsically linked to the supply and pricing dynamics of key raw materials, particularly those for battery production. The lithium-ion battery, a core component of most EVs, depends on a supply chain that includes lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite. The pricing of these materials is subject to global market volatility and geopolitical factors, which can directly influence the final cost of an electric vehicle. For instance, the demand for lithium has surged with the widespread adoption of EVs, prompting a strategic response within France. The Imerys project to produce lithium hydroxide from 2028 is a direct response to this market dynamic, aiming to stabilize the supply chain and insulate domestic production from external price fluctuations. This initiative, with a targeted output of 34,000 metric tons per year, directly impacts the pricing stability of domestically manufactured EVs. The high cost of these raw materials, coupled with a supply chain dominated by a few key players, creates a pricing challenge that manufacturers must manage to maintain consumer affordability.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global supply chain for the French electric vehicle market is complex and characterized by significant dependencies. While vehicle assembly largely takes place within Europe, the critical components, especially battery cells and packs, often originate from a limited number of production hubs, primarily in Asia. This geographical concentration introduces logistical complexities and creates a strategic vulnerability. The reliance on a single source for a key component, such as semiconductors, has already proven to be a significant constraint on production volumes, directly impacting the supply of finished vehicles to the market. This dependency has necessitated a strategic shift toward onshoring and nearshoring production. The French government and European Union have initiated programs to foster a domestic battery production ecosystem, aiming to create a more resilient and integrated value chain. This shift, while a long-term endeavor, is vital for mitigating risks and ensuring the consistent supply needed to meet growing domestic demand.
France Electric Vehicle Market Segment Government Regulations:
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
| France | "Bonus écologique" & "Prime à la conversion" | These direct purchase incentives have significantly lowered the effective cost of EVs, thereby increasing consumer demand. The tiered structure, which favors lower-income households and more environmentally-friendly vehicles, directs demand towards specific models. |
| France | Mobility Orientation Law (LOM) | This law mandates a minimum percentage of EV charging points in new and renovated parking lots. The regulation directly promotes the expansion of charging infrastructure, which is a key driver for consumer adoption by reducing range anxiety. |
| France | Ban on fossil-fuel vehicle sales by 2040 | This long-term regulatory signal provides market clarity and a clear deadline for the transition. It accelerates the strategic planning of automakers and encourages consumers to consider EVs, creating a sustained demand pull over the next two decades. |
France Electric Vehicle Market Segment Analysis:
- Passenger Vehicle
The passenger vehicle segment is the primary growth factor within the French electric vehicle market. Several demand-specific factors drive this segment’s growth. Government purchase incentives, such as the "bonus écologique," directly lower the financial barrier to entry, making EVs a more viable option for individual consumers. Concurrently, increasing environmental awareness and the implementation of low-emission zones in major urban centers like Paris and Lyon create a regulatory push. These zones restrict access for older, high-polluting vehicles, compelling private citizens to transition to electric alternatives for daily commuting. Technological advancements, particularly in battery range and charging speed, have also directly influenced consumer choice within this segment. As battery ranges extend to meet or exceed the needs of most daily trips, range anxiety diminishes, further stimulating demand. The introduction of a wider variety of electric models, from compact city cars to family-friendly SUVs, by both domestic and international manufacturers, also caters to diverse consumer preferences, expanding the total addressable market.
- By Propulsion Type: Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
The Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) segment has established itself as the dominant propulsion type within the French market. The demand for BEVs is directly influenced by their zero-emission status, which aligns with both consumer environmental consciousness and stringent government regulations. The "bonus écologique" heavily favors BEVs, providing a more substantial financial incentive compared to other propulsion types, which directly influences consumer purchasing decisions. Moreover, the expanding network of public charging infrastructure is particularly crucial for BEV demand. The increasing density of fast-charging points on highways and in urban areas makes long-distance travel and daily use more practical for BEV owners. This infrastructure development, coupled with continuous improvements in battery technology, which increases range and reduce charging times, directly addresses the primary operational concerns of potential buyers. The simplification of the ownership experience—requiring only electricity—makes BEVs a compelling and direct alternative to traditional gasoline and diesel cars, propelling their market leadership.
France Electric Vehicle Market Competitive Analysis:
The French electric vehicle market is shaped by a competitive landscape that includes both long-established domestic players and a growing number of international entrants. Key players are strategically positioning themselves to capitalize on the shift to electric mobility by leveraging their brand recognition and expanding their electric product portfolios.
- Renault Group
As a long-standing domestic champion, Renault Group maintains a strong position in the French EV market. The company has focused its strategy on developing a wide range of electric vehicles, from the compact Renault Twingo E-Tech electric to the larger Renault Megane E-Tech electric. This diversification caters to different end-user segments, from private urban commuters to families. Renault's strategic positioning is also built on its historical expertise in small, efficient vehicles, a trait that translates well to the electric segment. The company has consistently invested in its electric product line, which has helped it maintain a strong market presence.
- Stellantis
Stellantis, a multinational automotive giant, has a significant footprint in France through its brands such as Peugeot and Citroën. The company's strategy is centered on a multi-brand, multi-platform approach, allowing it to offer a diverse range of electric vehicles on shared platforms to achieve economies of scale. The Peugeot E-208 and Citroën e-C4 are key products that have driven demand in the passenger vehicle segment. Stellantis has also been proactive in its electrification strategy for commercial vehicles, with products like the Ram ProMaster EV. This dual-pronged strategy, targeting both passenger and commercial end-users, positions the company as a comprehensive provider of electric mobility solutions in France.
France Electric Vehicle Market Recent Developments:
- September 2025: The French government announced a new bonus of €1,000 for buyers of electric cars whose batteries and assembly are located within Europe. This new incentive is an addition to the existing "bonus écologique" and is designed to promote the relocation of the EV value chain and support industrial employment within the continent.
- September 2025: TSG, a European technical services leader for mobility solutions, announced its acquisition of Taverne Montage Industriel (TMI) in France as part of a triple acquisition across Europe. TMI specializes in the assembly of industrial electrical panels. This strategic move is significant because it directly strengthens TSG's integrated electrical infrastructure offering in France. The acquisition allows TSG to improve competitiveness in cost and lead time for electrical cabinet assembly, a critical component for EV charging and multi-energy solutions, supporting the build-out of a robust national charging network.
- January 2025: The French Mobility Orientation Law (LOM) went into effect on January 1, 2025, mandating that parking lots with more than 20 spaces allocate at least 5% of their capacity for EV chargers. This regulation has spurred significant investment and expansion of charging infrastructure across various sectors, including retail, hotels, and parking operators.
France Electric Vehicle Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 21.564 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 35.945 billion |
| Growth Rate | 10.76% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Vehicle Type, Propulsion Type, Drive Type, Component |
| Companies |
|
France Electric Vehicle Market Segmentation:
BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Passenger Vehicle
- Commercial Vehicle
- Others
BY PROPULSION TYPE
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
BY DRIVE TYPE
- Front Wheel Drive
- Rear Wheel Drive
- All Wheel Drive
BY COMPONENT
- Battery Cells & Packs
- Onboard Chargers & Motor
- Brake, Wheel & Suspension
- Others
BY END USER
- Public
- Private
- Commercial