Report Overview
Germany Electric Commercial Vehicles Highlights
Germany Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Size:
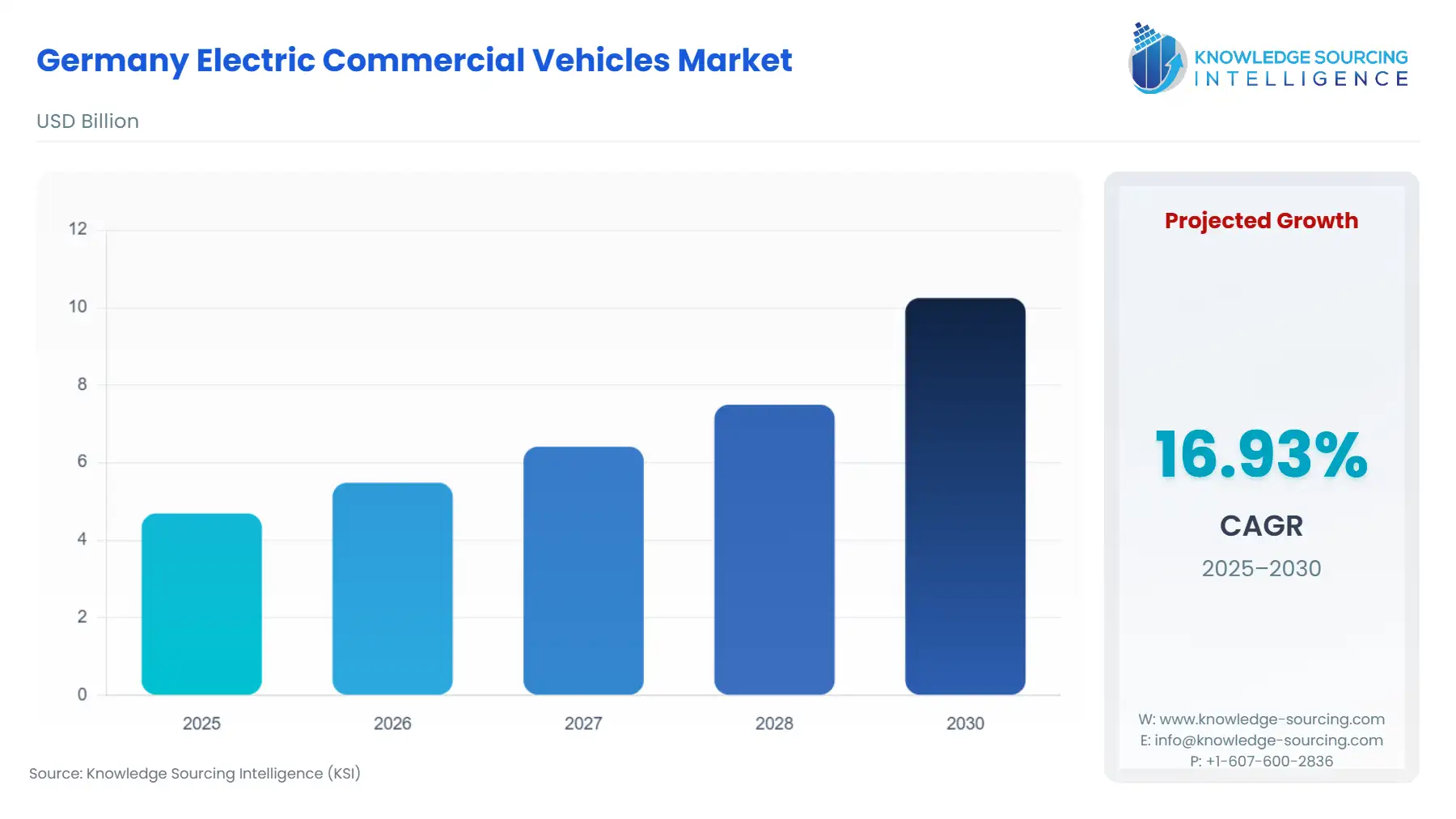
The Germany Electric Commercial Vehicles Market is predicted to surge at a CAGR of 16.93%, growing to USD 10.25 billion in 2030 from USD 4.69 billion in 2025.
The German Electric Commercial Vehicles Market stands as a pivotal segment in Europe's decarbonization strategy, navigating a complex intersection of stringent climate mandates, fluctuating government incentives, and the practical challenges of commercial fleet operation. The market trajectory is no longer driven solely by early adopters, but is increasingly governed by corporate sustainability commitments and the economic calculation of total cost of ownership (TCO) in the face of punitive CO$_2$ regulations. Germany's transport sector, historically reliant on diesel, is being forced into a structural transformation where compliance with EU-level emissions standards necessitates rapid fleet renewal with zero-emission alternatives, fundamentally shifting demand from conventional powertrains to electric models across all weight classes.
Germany Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
The most significant catalyst propelling the rise of electric commercial vehicles is the escalating stringency of European Union CO$_2$ emission standards. The regulatory framework, which targets a 50% reduction in average emissions for new vans by 2030, translates directly into a hard compliance requirement for fleet operators and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). This necessitates the acquisition of zero-emission vehicles to dilute fleet-average emissions, thereby creating a systemic, non-discretionary demand for electric vans and light-duty trucks. Furthermore, the German government's increase in the truck toll price, which includes a climate tax component, drastically raises the operating cost of internal combustion engine (ICE) trucks. This policy decision directly improves the TCO proposition for electric trucks by internalizing the environmental cost of diesel, thus accelerating the financial incentive for logistics companies to shift their procurement to electric alternatives to mitigate rising operational expenses.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge constraining market expansion is the substantial upfront capital expenditure required for electric commercial vehicles compared to their diesel counterparts. The high initial price point, driven largely by the battery cost, acts as a significant entry barrier, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). This financial friction was starkly highlighted by the market's negative reaction to the phase-out of national purchase subsidies, proving that demand remains price-elastic. The key opportunity lies in the integration of connectivity and telematics. Systems that offer real-time data on battery state-of-charge, optimal routing based on charging availability, and predictive maintenance directly address operational uncertainties. This technological integration enhances fleet efficiency and lowers lifetime operating expenses, thereby bolstering the business case and increasing customer demand by reducing perceived performance risk.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
Electric commercial vehicles, being physical products, are critically dependent on the battery supply chain, where raw materials like lithium, nickel, cobalt, and graphite are essential. The pricing dynamics of these materials are largely determined by global supply concentrated in a few regions, creating price volatility and geopolitical supply risk. For the German market, the necessity for electric commercial vehicles translates into a specific, high-volume demand for battery cells, making the stability and cost of the cathode active material (CAM)—the most expensive component—a direct determinant of final vehicle price. Disruptions in the supply of materials like lithium and nickel directly inflate the cost of electric trucks, creating upward pressure on final vehicle pricing and thus acting as a constraint on mass-market demand penetration.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global supply chain for electric commercial vehicles is characterized by a central dependency on battery cell production, primarily located in Asia, particularly China. While German OEMs are moving to localize battery assembly and, in some cases, cell production within Europe, the key upstream components—processed raw materials and refined intermediate products—still face significant reliance on non-European sourcing. This dependency introduces logistical complexities and vulnerability to external trade restrictions or political events. The focus for German manufacturers is therefore on securing long-term, direct procurement agreements for critical raw materials and establishing regionalized battery manufacturing capacity to insulate the domestic vehicle production from global supply chain shocks.
Germany Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Government Regulations:
The regulatory environment exerts direct, non-negotiable pressure on the demand structure for the German Electric Commercial Vehicles Market.
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
European Union |
CO$_2$ Standards for Heavy-Duty Vehicles (HDV) |
Mandates a 90% reduction in CO$_2$ emissions for new HDVs by 2040 (proposed). This creates an existential imperative for manufacturers to shift production, fueling non-discretionary demand for battery-electric and fuel-cell trucks for fleet renewal. |
|
Germany |
Commercial Vehicle Alternative Drives Subsidy (KsNi) |
While now terminated, its initial high value directly stimulated procurement demand. Its cancellation demonstrates a direct, immediate link between financial incentives and short-term commercial demand volatility. |
|
Germany |
Federal Truck Toll (Toll Collect) Climate Component |
The inclusion of a climate-related surcharge on the truck toll raises the operational cost of diesel vehicles, thus shifting the TCO equilibrium and making the adoption of toll-exempt or reduced-toll electric trucks financially superior, directly driving demand. |
Germany Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segment Analysis:
- By Vehicle Type: Light-Duty Trucks (LDTs)
The Light-Duty Truck segment, encompassing vans and smaller distribution vehicles, exhibits robust and immediate demand driven by urban logistics and "last-mile" delivery services. The specific growth catalyst here is the high daily utilization and predictable, localized operating routes characteristic of these applications. LDTs operate within a manageable range profile, often less than 200 km per day, which fits perfectly within the current technical limits of battery capacity, minimizing range anxiety. Furthermore, the mandatory low-emission zones (LEZs) in German cities directly penalize ICE vehicles in core operating areas, providing a powerful, localized incentive for fleet managers to procure electric LDTs. The ability to utilize depot charging overnight also simplifies infrastructure rollout, lowering the TCO barrier for this specific segment and accelerating the demand for smaller electric delivery fleets.
- By Application: Logistics and Transportation
The Logistics and Transportation application segment is fundamentally shaped by the confluence of corporate sustainability mandates and a TCO analysis influenced by externalized costs. Large logistics providers operating in Germany are increasingly compelled by their commercial clients, who have their own upstream emissions targets, to document and reduce their Scope 3 emissions. This creates a B2B demand pull for zero-emission transport solutions. The core driver is not merely vehicle performance but the overall operational savings derived from reduced energy costs (electricity vs. diesel) and lower maintenance requirements, which significantly favour electric vehicles over their lifespan. The rollout of high-range electric tractor units, such as the Mercedes-Benz eActros 600, directly addresses the long-haul requirements of this segment, unlocking demand for high-mileage, trunking applications that were previously technically infeasible.
Germany Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Competitive Analysis:
The German Electric Commercial Vehicles market is dominated by incumbent European giants who are strategically transitioning their core business, alongside niche innovators. The competitive landscape focuses on product range expansion, battery technology integration, and end-to-end service offerings, including charging infrastructure consultation.
- Daimler Truck AG (Mercedes-Benz Trucks): The company commands a dominant position, transitioning its flagship heavy-duty Actros line to electric. Their strategic positioning centers on high-capacity, long-haul application readiness. The launch of the eActros 600, which began customer deliveries in December 2024, directly addresses the high-volume long-haul segment with a claimed range of 500 kilometers without intermediate charging, fundamentally challenging the diesel truck's dominance in core logistics applications.
- MAN Truck & Bus SE: MAN focuses on leveraging its existing customer base and manufacturing flexibility to accelerate the transition. Their strategy involves a "mixed production" model, manufacturing both electric and diesel trucks on the same assembly line. MAN began series production of its new electric truck range, including the eTGX and eTGS models, in 2025, with a target to deliver 1,000 electric trucks within the year. This flexible production allows them to rapidly scale supply based on evolving market trends.
Germany Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Developments:
- February 2025: DHL Group and Scania announced a joint development to test an Extended Range Electric Vehicle (EREV) heavy-duty truck. This vehicle features a fuel-powered generator alongside its electric powertrain, acting as a range extender to overcome current charging infrastructure limitations for long-haul routes. The EREV, with a possible range of up to 800 kilometers, will be deployed by DHL's Post & Parcel Germany division for parcel transport between Berlin and Hamburg, with the goal of achieving over 80% CO2? emissions reduction compared to diesel.
- May 2025: Following the start of series production for the flagship eActros 600 long-haul truck at the end of 2024, Mercedes-Benz Trucks began to expand its second-generation battery-electric truck portfolio in early 2025. This expansion includes new variants of the eActros family, designed to cover a wider range of heavy-duty applications beyond the long-haul segment. The vehicles leverage the eActros 600's core technology, featuring a high battery capacity of over 600 kWh and an efficient electric drive axle.
Germany Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 4.69 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 10.25 billion |
| Growth Rate | 16.93% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Vehicle Type, Propulsion Type, Power Output, Application |
| Companies |
|
Germany Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segmentation
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Buses and Coaches
- Trucks
- Light-Duty Trucks
- Medium-Duty Trucks
- Heavy-Duty Trucks
- Vans
- BY PROPULSION TYPE
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEV)
- BY POWER OUTPUT
- Up to 150 kW
- 150-250 kW
- Above 250 kW
- BY APPLICATION
- Logistics and Transportation
- Public Transportation
- Construction (Excavators, Loaders, Others)
- Mining
- Agriculture (Tractors, Harvesters, Others)
- Others