Report Overview
Global Probiotics Ingredients Market Highlights
Probiotics Ingredients Market Size:
The Global Probiotics Ingredients Market will grow from USD 3.3 billion in 2026 to USD 4.7 billion in 2031, at a 5.8% CAGR.
The Global Probiotics Ingredients Market is fundamentally structured by the convergence of increasing consumer focus on preventive healthcare and significant regulatory shifts in the food and animal feed industries. Probiotic ingredients, defined as live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host, operate at the core of the functional nutrition movement.
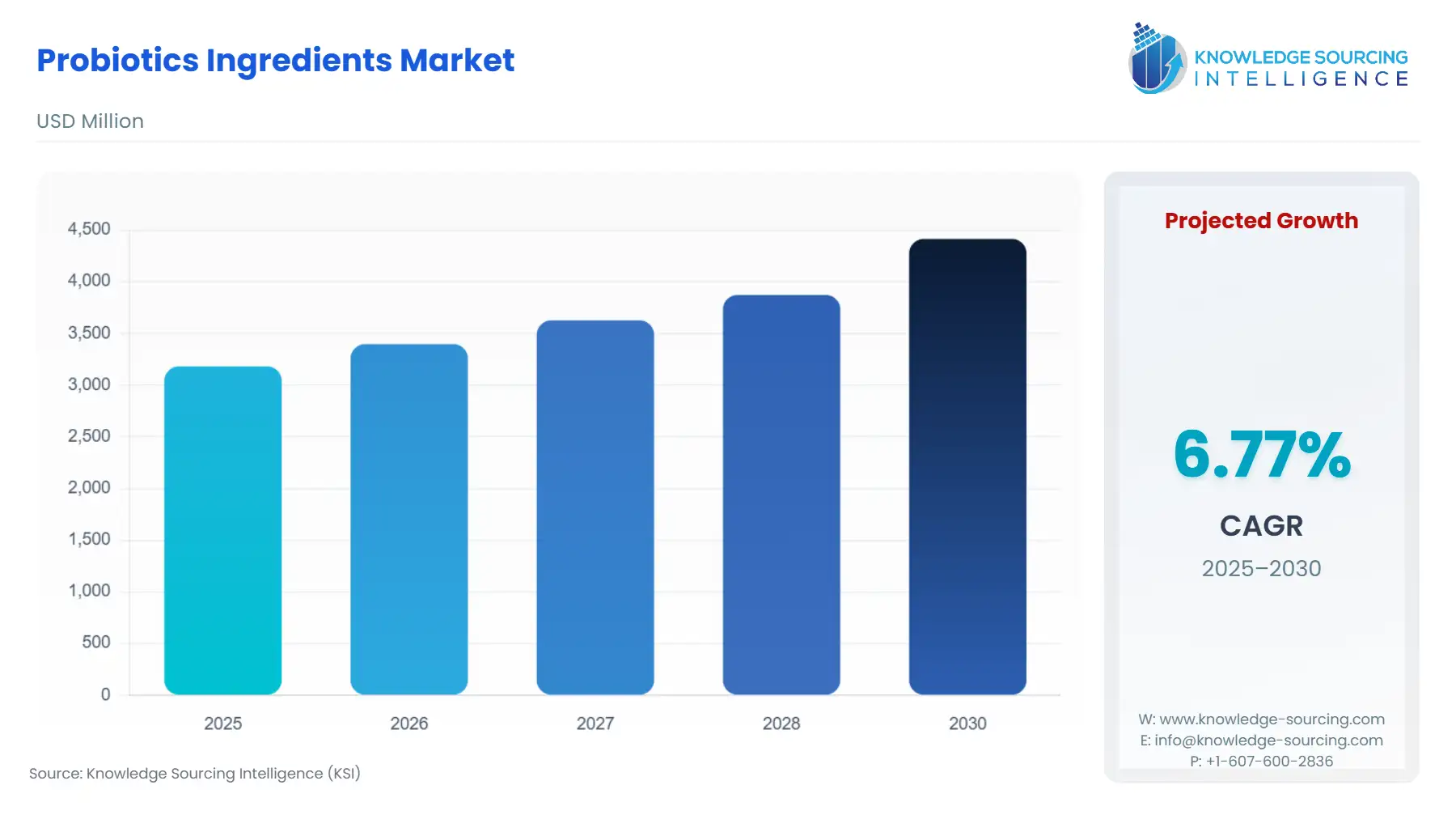
Market expansion is not driven by generic health trends but by strain-specific scientific substantiation, forcing suppliers to move beyond commodity production to offer differentiated, clinically backed ingredients. This is evident in the industry's investment in advanced delivery technologies, such as microencapsulation, which addresses the crucial challenge of ensuring microbial viability throughout the manufacturing, shelf life, and gastrointestinal transit phases, thereby sustaining and increasing end-user demand for high-efficacy final products.
The Global Probiotics Ingredients Market is fundamentally structured by the convergence of increasing consumer focus on preventive healthcare and significant regulatory shifts in the food and animal feed industries. Probiotic ingredients, defined as live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host, operate at the core of the functional nutrition movement. Market expansion is not driven by generic health trends but by strain-specific scientific substantiation, forcing suppliers to move beyond commodity production to offer differentiated, clinically backed ingredients. This is evident in the industry's investment in advanced delivery technologies, such as microencapsulation, which addresses the crucial challenge of ensuring microbial viability throughout the manufacturing, shelf life, and gastrointestinal transit phases, thereby sustaining and increasing end-user demand for high-efficacy final products.
Global Probiotics Ingredients Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Consumer awareness of the gut-brain axis and the established links between the gut microbiome and immune function directly elevates ingredient demand; consumers actively seek supplements and functional foods containing verifiable immune-supportive strains. The global trend of governments phasing out antibiotic growth promoters (AGPs) in livestock production, primarily in response to antimicrobial resistance (AMR) concerns, forces animal feed manufacturers to replace AGPs with performance-enhancing probiotics, generating substantial industrial demand for stable Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium ingredients. Concurrently, advancements in microencapsulation and cryoprotection technologies improve the ingredients’ stability and shelf life, making them viable for integration into diverse, shelf-stable formats like functional confectionery and snack bars, broadening product application.
Challenges and Opportunities
A primary challenge is the technical complexity of maintaining ingredient stability and viability throughout complex food matrices, processing heat, and extended shelf life, which necessitates high capital investment in advanced delivery systems like microencapsulation. Regulatory ambiguity across jurisdictions, particularly the European Union's restrictive position on generic health claims, presents a commercial hurdle, limiting broad marketing. However, this restraint concurrently creates a major opportunity for market differentiation: manufacturers investing in costly, strain-specific clinical trials for substantiated health outcomes (e.g., specific digestive or immune benefits) gain a premium market position and drive demand for their proprietary, verifiable ingredients, especially in the high-value dietary supplement segment.
Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
Probiotics ingredients are biological products whose core raw materials are microbial strains cultivated in specialized fermentation media. Key input costs include bulk nutrients like specific sugars, proteins (e.g., soy or milk hydrolysates), and growth factors required for large-scale microbial biomass production. Energy consumption for sterilization, fermentation control, and freeze-drying (lyophilization) is also a substantial cost component. The pricing of final probiotic ingredients is highly inelastic to the cost of simple commodity inputs but rather determined by the value of the proprietary strain, the complexity of the stabilization technology (e.g., encapsulation layers), and the depth of the supporting clinical data. Suppliers commanding a strong portfolio of patented, clinically verified strains maintain high margins, insulating them from typical agricultural commodity price volatility.
Supply Chain Analysis
The supply chain is a high-value, high-complexity vertical, beginning with the proprietary strain bank management and specialized fermentation in controlled bioreactors, primarily located in Europe and North America. Key hubs include Denmark, France, and the United States, reflecting the legacy of leading bioscience firms. The critical logistical complexity is the cold-chain requirement for live strains and the investment in stabilization technologies (e.g., lyophilization into powders or microencapsulation) to create shelf-stable ingredients suitable for global distribution. This supply chain is characterized by a strong dependency on intellectual property (IP), proprietary knowledge of fermentation optimization, and rigorous Quality Control (QC) testing to ensure minimum guaranteed Colony Forming Units (CFUs) in the final ingredient before shipping to end-product manufacturers.
Probiotics Ingredients Market Government Regulations
Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
European Union | Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 (Health Claims Regulation) / European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) | EFSA’s strict stance prohibiting generic health claims (including the use of the term "probiotic" on food/supplement labels) forces manufacturers to pivot marketing toward non-regulated jurisdictions and to invest heavily in scientific dossiers for specific, approved claims, thereby channeling demand to evidence-backed strains. |
United States | Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) Status / Food and Drug Administration (FDA) | The GRAS process enables faster market access for novel probiotic strains by requiring a scientific consensus of safety before use in food and beverages. This lowers the commercialization barrier for proven ingredients, directly accelerating the supply of new, safe strains. |
India | Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) (Draft Probiotics Guidelines) | The introduction of strain-specific guidelines for evaluation and labelling aims to standardize quality. This regulatory clarity increases consumer trust and preference for approved, verifiable ingredients, creating a competitive advantage for companies that comply with the new testing and safety mandates. |
Probiotics Ingredients Market Segment Analysis
By Application: Fermented Foods & Drinks
The Fermented Foods & Drinks segment, encompassing products like yogurts, cultured milks, and functional juices, represents the most volume-intensive application for probiotic ingredients. These products provide a natural, culturally accepted, and highly convenient delivery matrix for live bacteria. Consumers perceive this route as more "natural" than capsules or tablets, resulting in high daily-consumption frequency. The primary growth driver is the "daily wellness" imperative, where consumers integrate small, functional health components into their routine diet. Manufacturers of final products seek ingredients that possess high acid and bile tolerance to survive the food matrix environment and the digestive tract, as well as characteristics that do not negatively impact the sensory profile (flavor, texture) of the final food product. Ingredient suppliers capable of providing stable, flavor-neutral strains of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus that thrive within dairy or plant-based ferments secure large-volume contracts in this segment.
By Type: Bifidobacterium Strain
The Bifidobacterium segment commands high demand due to its strong, peer-reviewed clinical association with general gut health, immune system modulation, and its critical presence in the infant gut microbiome. The specific growth driver for this segment is the scientific evidence of specific health benefits across diverse life stages, particularly the application in Early Life Nutrition (ELN) and targeted adult digestive health. Ingredient manufacturers differentiate their Bifidobacterium offerings by demonstrating efficacy in supporting the intestinal barrier function and reducing symptoms associated with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), often targeting specific patented strains (e.g., B. lactis or B. longum). The demand is non-interchangeable; formulation manufacturers specifically require Bifidobacterium strains to align with consumer expectations and the clinical rationale for digestive health products, making scientific literature the primary purchasing rationale over mere cost. This segment’s growth is further fueled by the rising adoption in combination with Lactobacillus in synbiotic formulations.
Probiotics Ingredients Market Geographical Analysis
US Market Analysis
The US market for probiotics ingredients is characterized by high growth, driven primarily by the dietary supplements sector, where flexible regulatory frameworks (e.g., the GRAS process) allow for rapid commercialization of new strains. Local demand is heavily influenced by a high prevalence of consumer-driven health claims, focusing on benefits like immune support, stress reduction (gut-brain axis), and specific digestive relief. The market rewards premium ingredients backed by randomized controlled trials, creating a commercial environment where suppliers emphasize strain-specific IP and clinical substantiation to command higher pricing, with less price sensitivity than in food applications.
Brazil Market Analysis
The Brazilian market is the largest in South America, with demand for probiotic ingredients concentrated in fermented dairy products like yogurts and milk beverages. Local demand is strongly influenced by a culture of functional food consumption and a consumer base actively seeking natural solutions for digestive wellness. Regulatory requirements, which often distinguish between foods and supplements, channel the majority of ingredient volume into the high-volume, cost-sensitive food manufacturing sector. Ingredient suppliers compete on providing stable Lactobacillus strains that can withstand local food processing techniques while remaining cost-competitive.
German Market Analysis
The German market operates under the stringent influence of the EU's Health Claims Regulation, which directly restricts marketing claims. This regulatory headwind pushes ingredient demand toward highly technical and certified applications such as infant formula and medical nutrition, where specific strains are approved or recognized for particular physiological effects. German ingredient purchasers prioritize verifiable quality, stability, and production compliance (e.g., ISO and HACCP certification) over innovative, but unsubstantiated, novel strains, resulting in a stable, but slow-growth, premium ingredient segment.
UAE Market Analysis
The UAE market serves as a major distribution and consumption hub in the Middle East, driven by a high disposable income and a strong preference for imported, premium functional foods and supplements. Local demand factors include a fast-paced urban lifestyle and growing chronic health concerns, leading to an increasing acceptance of Western-style dietary supplements. Ingredient demand favors stable, dry-form ingredients (powders/capsules) that can withstand the logistical and ambient temperature challenges of the region while maintaining certified potency.
China Market Analysis
China represents the single largest volume opportunity in Asia-Pacific, propelled by government-led public health campaigns focusing on preventive nutrition and the integration of traditional Chinese medicine principles with modern functional ingredients. Ingredient demand is high across all applications, particularly for Bifidobacterium strains in infant formulas and Lactobacillus strains in traditional fermented beverages and dairy products. The market is competitive, demanding high-capacity manufacturing and compliance with China's specific food safety and import regulations, favoring suppliers with local production or strong local partnerships.
Probiotics Ingredients Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
The Global Probiotics Ingredients Market is dominated by a few large, integrated bioscience and ingredients companies that control vast proprietary strain collections, specialized fermentation capacity, and extensive clinical dossiers. Competition hinges not on price alone, but fundamentally on scientific IP, strain stability, and application support. Leading players differentiate themselves by offering full-service solutions, moving beyond ingredient supply to offering formulation expertise and regulatory guidance to their downstream customers.
Kerry Group, Plc
Kerry Group, Plc is a global leader in taste and nutrition, with its probiotic ingredient strategy integrated into its wider functional food and beverage solutions platform. Its strength lies in providing a broad portfolio of ingredients, including branded strains like GanedenBC°30 (Bacillus coagulans GBI-30, 6086), which is known for its high spore stability and ability to survive harsh manufacturing conditions. Kerry’s strategic positioning is focused on applications in functional foods and beverages, leveraging its flavor and texture expertise to integrate probiotics seamlessly into complex matrices, overcoming the sensory challenges that often hinder mass-market adoption of probiotic ingredients.
Novonesis Group
Novonesis Group, formed by the merger of Novozymes and Chr. Hansen is positioned as a biosolutions powerhouse with a commanding presence across the probiotics, enzymes, and fermentation-based ingredients markets. This combined entity controls one of the world's largest collections of proprietary microbial strains, including industry-leading probiotic cultures for food, human health, and animal feed. Their strategic imperative is to leverage deep R&D capabilities and massive-scale fermentation capacity to address complex biological challenges, driving demand through scientifically validated, high-potency ingredients in both the human nutrition and animal health sectors, particularly where the shift from antibiotics is accelerating.
DSM-Firmenich
DSM-Firmenich, another product of a major industry merger, is strategically focused on being a creation and innovation partner in nutrition, health, and beauty. The company's probiotics ingredient strength comes from its Health, Nutrition & Care business, where it emphasizes science-backed personalized nutrition and targeted health solutions. Its portfolio includes a range of highly stable Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains. DSM-Firmenich utilizes its extensive global application laboratories and R&D network to co-develop innovative probiotic-enhanced products, ensuring its ingredients meet the precise formulation requirements of its pharmaceutical and high-value dietary supplement customers globally.
Probiotics Ingredients Market Developments
August 2025: Novonesis announced “GROW,” its strategic plan to 2030, which includes significant capital expenditure in innovation and commercial capabilities to support core business acceleration. This investment, with elevated CapEx at the start of the period, aims to secure sustained high growth and cater to increasing global demand, including for probiotics ingredients.
Probiotics Ingredients Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 3.3 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 4.7 billion |
| Forecast Unit | Billion |
| Growth Rate | 5.8% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Type, Form, Application, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Probiotics Ingredients Market Segmentation:
PROBIOTICS INGREDIENTS MARKET BY TYPE
Bacteria
Lactobacillus
Bifidobacterium
Yeast
PROBIOTICS INGREDIENTS MARKET BY FORM
Dry/Powder
Liquid
PROBIOTICS INGREDIENTS MARKET BY APPLICATION
Fermented Foods & Drinks
Dietary Supplement
Animal Feed
Others
PROBIOTICS INGREDIENTS MARKET BY GEOGRAPHY
North America
USA
Canada
Mexico
South America
Brazil
Argentina
Others
Europe
Germany
France
United Kingdom
Spain
Others
Middle East and Africa
Saudi Arabia
UAE
Israel
Others
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
South Korea
Indonesia
Taiwan
Others