Report Overview
Indonesia Sugar Market - Highlights
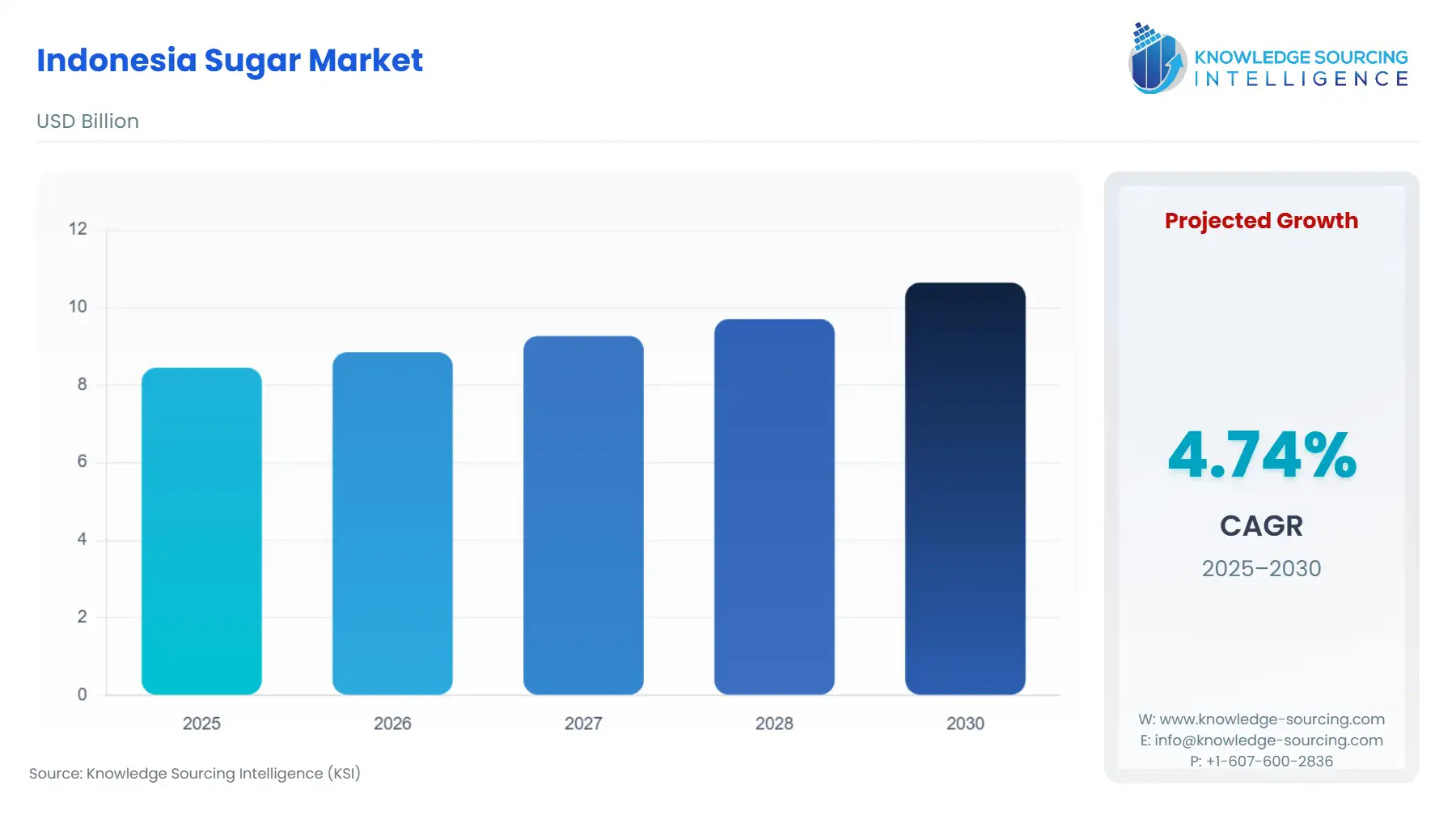
Indonesia Sugar Market Size
The Indonesia sugar market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.74% from US$8.449 billion in 2025 to US$10.648 billion in 2030.
Indonesia Sugar Market Trends:
Changes in local consumption patterns, governmental regulations, climatic circumstances, and global market dynamics influence the Indonesian sugar market. There is a huge domestic demand for sugar due to the country's expanding population. Furthermore, sugarcane production and cultivation are influenced in Indonesia by local and global weather conditions, fueling the sugar market in the nation. In addition to this, technological developments, foreign exchange rates, and pricing differences all influence the market's complexity. Concerns about sustainability, customer preferences, and the effectiveness of logistics and infrastructure systems are also significant factors driving the market growth.
The pricing and supply of sugar are significantly influenced by trade agreements, subsidies, and import taxes, among other government policies. For instance, as per the Government of Indonesia, one million hectares of land in the province of Papua were given to the government to increase sugar production and attain national self-sufficiency. The government claimed that the site would be accessible to foreign and domestic companies that are eager to build a sugar industry in the nation. It further added that several investors had already begun sowing sugar cane seeds around the region.
The robust demand for sugar in the food and beverage sector continues to drive the Indonesian sugar market demand. Sugar is a flexible component that is widely used in the creation of a wide range of food and drink items, which influences both domestic consumption patterns and market dynamics. According to the survey conducted by the National Library of Medicine, in Indonesia, instant coffee was the most often consumed sugar-sweetened beverage (SSB) (29.4%) among the 340,032 homes studied, whereas produced liquid milk was the least frequently preferred (5.7%). 25% of the families in this survey drank mineral water, the sole unsweetened beverage, and spent an average of IDR 44,129 (US$2.9) per home per month on it. Although produced milk was the least popular beverage, families spent the most money on it (IDR 84,285 or US$5.5 on average) per month. Households, on the other hand, spend the least on tea drinks and carbonated beverages (on average IDR 35,999 or US$2.4).
Furthermore, market participants in the Indonesian sugar business employ various tactics such as product diversification, supply chain optimization, sustainability practices, and technology adoption to effectively traverse complicated market dynamics and maintain competitiveness in a constantly evolving sector.
Indonesia Sugar Market Growth Drivers:
Increasing production and consumption are projected to propel the Indonesia sugar market expansion.
The Indonesian sugar market growth is significantly influenced by the country's domestic sugar consumption. The demand for sugar is strong due to the vast and expanding population, which has a direct impact on the level of production, import-export regulations, and general stability of the market.
According to OECD estimates, Indonesia's sugar consumption rose from 27.67 kg in 2022 to around 28.23 kg in 2023. Less social distancing and travel limitations are anticipated to decrease domestic sugar consumption as Indonesia extends its COVID-19 immunization program, which was introduced in January 2021. On the other hand, rising demand in the food and beverage sector is anticipated to raise refined sugar consumption.
Furthermore, the production of sugar has a major effect on the pricing, supply, and market dynamics of sugar in Indonesia. Sufficient domestic production lessens the need for imports and promotes market stability by helping to fulfill the demand for sugar. For instance, the growth of private sugar mills results in higher production in 2022–2023. It is predicted that El Nino, which typically raises the amount of sugar in sugarcane and keeps private sugar mills' land expansion, would boost plantation white sugar output even more in 2023–2024, reaching 2.6 million metric tonnes (MMT). However, it is anticipated that imports of raw sugar will rise mostly as a result of increased refinery demand. The Government of Indonesia (GOI) has granted permission to import 991,000 tonnes of plantation white sugar in 2022–2023 to lower and stabilize retail prices.
As per the USDA report, the retail price of plantation white sugar has grown due to higher production costs and growing demand. A National Food Agency guideline on reference prices for buying and selling soybeans, shallots, chiles, beef, buffalo meat, and sugar was released by the GOI in December 2022 to control pricing. Plantation white sugar reference prices are established at Rp. 11,500/kg ($768/MT) for producers and Rp. 13,500–Rp. 14,500/kg ($901–968/MT) for consumers. As of 2022, the new reference price at the consumer level is Rp. 13,500 per kg ($901/MT), an increase of 0 to 7.4%. The average retail price is Rp 14,400/kg ($961/MT), up 0.8 percent from Rp 14,283/kg ($954/MT).
In addition, shifting dietary trends, health concerns, and customer tastes all affect the sugar market, causing producers to modify their methods of production and have an effect on the food and beverage industry. To navigate the complexity of the market and guarantee a sustainable and responsive sugar sector, stakeholders have a thorough awareness of domestic consumption trends and production.
The growing food and beverage sector is anticipated to fuel the Indonesian sugar market.
The rapidly growing food and beverage sector will highly fuel the Indonesian sugar market. Indonesia's growing economy translates into an increase in sugar demand because this is the largest part of the majority of foods and other related consumables. Urbanization and high salaries have led to increased consumption of processed meals, sugar-sweetened beverages, and other sugary snacks. This trend is being driven by increased demand for syrups, soft drinks, baked goods, and confectionery products. Indonesians' growing health consciousness has raised knowledge of natural and organic sweeteners; yet, traditional sugar continues to be the norm in most households and sectors.
The Indonesian Food and Beverage Producers Association has said that high sugar prices will likely force the players to increase product prices. This is because the balance between supply and demand has become tight in the market. To respond to this growth in demand, the government has increased raw sugar import quotas to be able to satisfy the needs of local refineries. For example, import allocations of raw sugar have been enhanced to 3.6 million tons for the period 2023-2024, stressing dependence on local production as well as imports to satisfy consumption locally.
In addition, with the expected growth of e-commerce and modern retail channels in Indonesia, the availability of processed food products is likely to increase, thereby fuelling sugar demand. All these factors put together will position the Indonesian sugar market for strong growth as it adjusts to changing consumer preferences within the dynamic food and beverage landscape.
Indonesia Sugar Market is analyzed into the following segments:
By source, cane sugar is anticipated to hold a substantial market share
Cane sugar is a refined sugar derived from sugar cane and is a pure source of carbohydrates. Indonesia holds high potential for cane sugar production as the country is witnessing a positive growth towards the expansion of its private sugar mills, which use domestically produced sugarcane to produce sugar. According to the USDA’s “Sugar Annual” report issued in April 2023, for the market year 2022/2023, 3.6 million tons of sugarcane were utilized for sugar production, which represented an 11.1% increase over the market year 2021/2022. Furthermore, as per the same source, cane sugar production stood at 2,400 Metric Tons in 2022, which signified a 4.34% increase over 2,300 Metric Tons produced in 2021. Additionally, the report further states that production is expected to reach 2,600 Metric Tons in 2023.
Moreover, the booming domestic sugar consumption has provided a further boost to the market demand for cane sugar. According to the USDA, in 2022, Indonesia’s sugar consumption reached 7.8 MMT, which showcased a 2.6% increase over 2021’s consumption scale. Additionally, rapid population growth and improvement in sugar refineries and infrastructure are also accelerating the overall market demand. According to the data taken from the Indonesian Sugar Council and the Directorate General of Plantations, in 2022, milled sugarcane production reached 36.4 million tons, which experienced an increase of 4.2 million tons in comparison to 2021. The booming demand for refined white sugar from the food & beverage sector has also led to an upward market trajectory.
Indonesia Sugar Market Key Developments:
Nov 2025: Indonesia aims to achieve white-sugar self-sufficiency by 2026, accelerating its earlier roadmap; the plan includes intensifying production via ratoon field clearing, seed improvement, irrigation upgrades, and expanding sugarcane plantations by 500,000 hectares.
Nov 2025: The government projects 2025 sugar output at 2.75 million tons from 538,000 hectares, its highest in five years.
Feb 2025: To stabilize domestic prices, Indonesia approved the import of 200,000 tons of raw sugar for its national food reserve, even as production rises.
April 2024: Indonesia intends to build a sugar-based economy in Papua, with the goal of increasing domestic sugar output and reducing dependency on imports. The government is preparing one million hectares of land for investors interested in developing sugar plants, with plans to construct 20 to 30 facilities capable of processing up to 12,000 tonnes of cane per day. This effort supports Indonesia's objective of being sugar self-sufficient by 2028. Agriculture Minister Amran Sulaiman emphasised the need for high-quality seedlings and advanced technologies in increasing yields, as the country currently imports a substantial amount of sugar. The project is designed to benefit local businesses and increase food security in the region.
Indonesia Sugar Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2025 | USD 8.449 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2030 | USD 10.648 billion |
| Forecast Unit | Billion |
| Growth Rate | 4.74% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Segmentation | Form , Source , Use, Distribution Channel |
| Companies |
|
Indonesia Sugar Market Segmentation:
By Form
Granulated
Powdered
Syrup
By Source
Cane Sugar
Beet Sugar
By Use
Food And Beverage
Pharmaceuticals
By Distribution Channel
Online
Offline