Report Overview
Mexico Electric Commercial Vehicles Highlights
Mexico Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Size:
The Mexico Electric Commercial Vehicles Market is expected to advance at a CAGR of 15.99%, growing to USD 1.35 billion in 2030 from USD 0.643 billion in 2025.
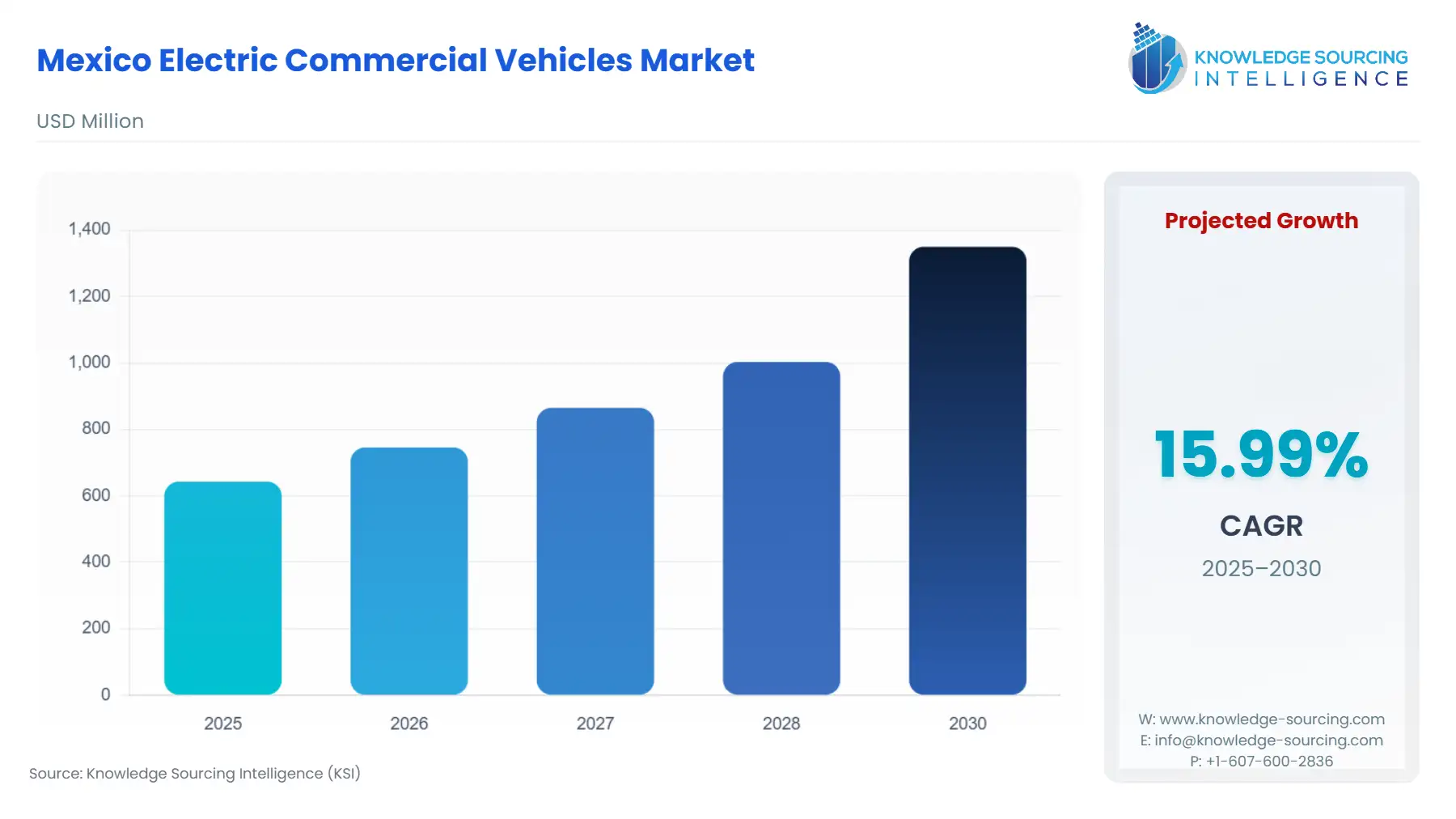
The Mexican electric commercial vehicles market is fundamentally characterized by a dual momentum of public sector mandate and a rising logistical necessity, constrained by capital expenditure barriers. Mexico’s position as a major global automotive manufacturing hub is strategically leveraging nearshoring trends, aiming to integrate the production of electric vehicles and battery components into the North American supply chain. This transition is actively supported by governmental fiscal incentives designed to lower the barrier to entry for fleet operators. The immediate opportunity resides in high-utilization commercial fleet segments, such as last-mile logistics and metropolitan public transport, where the TCO advantage of electric propulsion can rapidly overcome the substantial initial investment challenge. For the market to reach its potential, however, the regulatory push for decentralized and interoperable charging infrastructure must materialize into an accessible national network, particularly for heavy-duty applications.
Mexico Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
Stringent governmental emissions and climate policies act as the single most influential growth catalyst. The Mexican government's decree for an 86% immediate tax deduction on new electric and hybrid vehicle investments, effective through 2026, directly lowers the effective purchase price for commercial buyers. This fiscal incentive significantly improves the return on investment (ROI) calculation for fleet modernization, thus immediately accelerating demand for new Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) across light-duty and heavy-duty segments. Additionally, the increasing demand for sustainable logistics, driven by corporate Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) commitments and the expansion of e-commerce, compels major logistics and retail corporations to electrify last-mile delivery fleets, driving concentrated demand for electric vans and light-duty trucks in urban centers.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge constraining widespread market adoption is the high initial cost of eCVs compared to their internal combustion engine (ICE) counterparts. This high capital expenditure creates a substantial financial hurdle for small and medium-sized fleet operators, significantly limiting mass-market production beyond large, well-capitalized corporations. A compounding constraint is the underdeveloped public charging infrastructure. As of 2025, only 7.5% of the total charging points in Mexico are publicly accessible, creating logistical risks and 'range anxiety' for commercial vehicles, which require predictable and high-power charging for continuous operation. This constraint directly suppresses demand for long-haul electric trucks. The core opportunity lies in the regulatory environment, specifically the recent General Administrative Provisions on Electromobility by the CRE. This new framework, which standardizes connection and requires data on charging infrastructure, creates a clear, regulated path for private sector investment in fast-charging networks, an imperative that directly unlocks demand by improving operational feasibility and reducing fleet downtime.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
Electric Commercial Vehicles are physical products, making their pricing intrinsically linked to critical raw materials. The eCV value chain's most significant cost component is the lithium-ion battery pack, whose pricing dynamics are directly influenced by global lithium, nickel, cobalt, and graphite markets. Mexico serves as an increasingly integrated manufacturing hub, particularly for the North American supply chain, with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) like Ford and General Motors assembling batteries and eCVs domestically. However, the country remains a net importer of key battery components and refined raw materials, sourcing from Asian suppliers (e.g., LG Chem, Samsung SDI, BYD, CATL). The price volatility of these globally traded battery minerals therefore exerts direct upward pressure on the final price of a locally manufactured eCV, hindering the crucial goal of achieving price parity with diesel trucks, which would otherwise unleash mass-market requirements.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The eCV supply chain in Mexico is bifurcated. Vehicle assembly largely occurs in established automotive clusters, such as the Bajío region (Guanajuato, Aguascalientes, San Luis Potosí) and Coahuila (Ramos Arizpe). These hubs benefit from proximity to the U.S. market and USMCA tariff advantages, making them strategic locations for nearshoring. The critical logistical complexity, however, centers on the Tier 1 components—specifically the traction battery and power electronics—which are predominantly imported, often from Asian suppliers. This dependency introduces vulnerability to geopolitical friction, customs delays, and international price fluctuations, complicating local content requirements and heightening the cost of goods sold. The long-term stability of the Mexican eCV market expansion is thus dependent on a successful transition from pure assembly to full vertical integration of battery cell and module production, a capital-intensive shift currently underway.
Mexico Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
Federal Government |
Immediate Deduction Decree (e.g., 86% deduction for new electric and hybrid vehicles) |
Directly reduces the capital expenditure for commercial fleets, serving as the most significant financial catalyst for immediate demand. |
|
Energy Regulatory Commission (CRE) |
General Administrative Provisions on Electromobility (A/108/2024) |
Standardizes the technical and administrative requirements for connecting charging infrastructure, removing regulatory uncertainty and enabling faster private investment, which directly addresses range anxiety and unlocks fleet operator demand. |
|
Mexico City |
'Hoy No Circula' Scheme |
Restricts the circulation of older, high-emission ICE vehicles on certain days, creating a functional imperative for fleet renewal toward exempted electric models, thereby driving localized metropolitan demand. |
Mexico Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segment Analysis:
- By Application: Public Transportation
The public transportation segment, encompassing both urban buses and coaches, demonstrates a distinct and concentrated demand structure, largely independent of retail consumer preferences. This segment’s growth is driven by municipal and state-level policy mandates for urban decarbonization and air quality improvement, exemplified by initiatives in Mexico City and Monterrey to integrate electric buses into their fleets. The procurement model is typically large-scale, often involving public-private partnerships where third parties finance, operate, and maintain the vehicles. This bulk-purchase, TCO-focused model mitigates the high initial capital cost that deters private fleets. Suppliers who can offer a comprehensive ecosystem—vehicle, charging infrastructure, and long-term maintenance contracts—capture this demand. The deployment of 55 pure electric buses to Mexico City's Metrobús Line 4, with a 5,845 tons per year carbon reduction target, validates this segment as a high-volume, policy-driven demand center.
- By Propulsion Type: Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
The Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) segment is the definitive growth vector, driven by the zero tailpipe emission standard. Unlike Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) or Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), which are transitional technologies, BEVs offer the necessary compliance for increasingly strict urban emission zones and corporate Net Zero mandates. The need for BEVs is most pronounced in high-mileage, closed-loop, or urban 'hub-and-spoke' logistics operations where daily route predictability allows for controlled depot charging. The fiscal incentive offering an 86% immediate deduction explicitly covers BEVs, further solidifying their demand proposition. The efficiency of a single-powertrain, lower maintenance costs, and the exemption from city-specific restrictions like the 'Hoy No Circula' scheme directly translate into a superior long-term TCO, fueling the demand for light-duty electric vans and delivery trucks optimized for metropolitan distribution.
Mexico Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Competitive Analysis:
The Mexican Electric Commercial Vehicles market is defined by a dynamic competition between established global OEMs and aggressive, often state-backed, international entrants, particularly from Asia. Established heavy-duty truck manufacturers with long-standing operational and servicing networks hold a competitive advantage in the high-tonnage sector. Conversely, new players are capturing last-mile delivery and public transport segments with a strong focus on price and electric-only product portfolios.
- Daimler Truck: This legacy manufacturer leverages its dominant position in the North American heavy-duty truck market (Trucks North America unit sales of 195,014 in 2023) and its extensive dealership and service infrastructure in Mexico. The company's strategy is to transition its existing, deeply integrated customer base to its electric offerings, such as the Mercedes-Benz eActros and eCanter (under the FUSO brand, with the 7C18e deployed for internal waste logistics at Berlin Brandenburg Airport). Daimler Truck's competitive advantage is its ecosystem support and a phased approach that minimizes adoption risk for large-scale, long-haul fleet customers.
- BYD: The company is a key competitor in the transit and heavy-duty electric segment, positioning itself as a zero-emission specialist. BYD's strategic focus in Mexico has centered on high-profile public transport contracts. In a significant move, BYD delivered the first batch of 20, out of a total of 55, 15-meter pure electric buses to the Mexico City Metrobús Line 4. Their competitive edge is their vertical integration, manufacturing their own battery packs (Blade Battery technology), which often allows for aggressive pricing and rapid product deployment in the public procurement sector. The company has, however, paused plans for a major EV factory in Mexico, citing US tariff uncertainty.
Mexico Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Developments:
- August 2025: The domestically produced Taruk electric bus, manufactured in Mexico, attracted substantial international commercial interest, with a potential order of between 10,000 to 20,000 units from the United States over the next two years. This development signals a significant step for Mexico as an electric commercial vehicle manufacturing hub, moving beyond local adoption to become a key exporter in the e-mobility sector. The ambitious target demonstrates confidence in the vehicle's design and production capabilities to meet the high-volume demand of the North American heavy-duty market.
- September 2024: The Energy Regulatory Commission (CRE) published Accord A/108/2024, the "General Administrative Provisions on Electromobility," establishing the technical and administrative requirements for integrating EV and PHEV charging infrastructure into the National Electric System. This new regulation signals governmental commitment to standardizing the rollout and operation of charging networks, an essential precursor to large-scale fleet electrification.
Mexico Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 0.643 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 1.35 billion |
| Growth Rate | 15.99% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Vehicle Type, Propulsion Type, Power Output, Application |
| Companies |
|
Mexico Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segmentation:
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Buses and Coaches
- Trucks
- Light-Duty Trucks
- Medium-Duty Trucks
- Heavy-Duty Trucks
- Vans
- BY PROPULSION TYPE
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEV)
- BY POWER OUTPUT
- Up to 150 kW
- 150-250 kW
- Above 250 kW
- BY APPLICATION
- Logistics and Transportation
- Public Transportation
- Construction (Excavators, Loaders, Others)
- Mining
- Agriculture (Tractors, Harvesters, Others)
- Others