Report Overview
Mexico Electric Vehicle Components Highlights
Mexico Electric Vehicle Components Market Size:
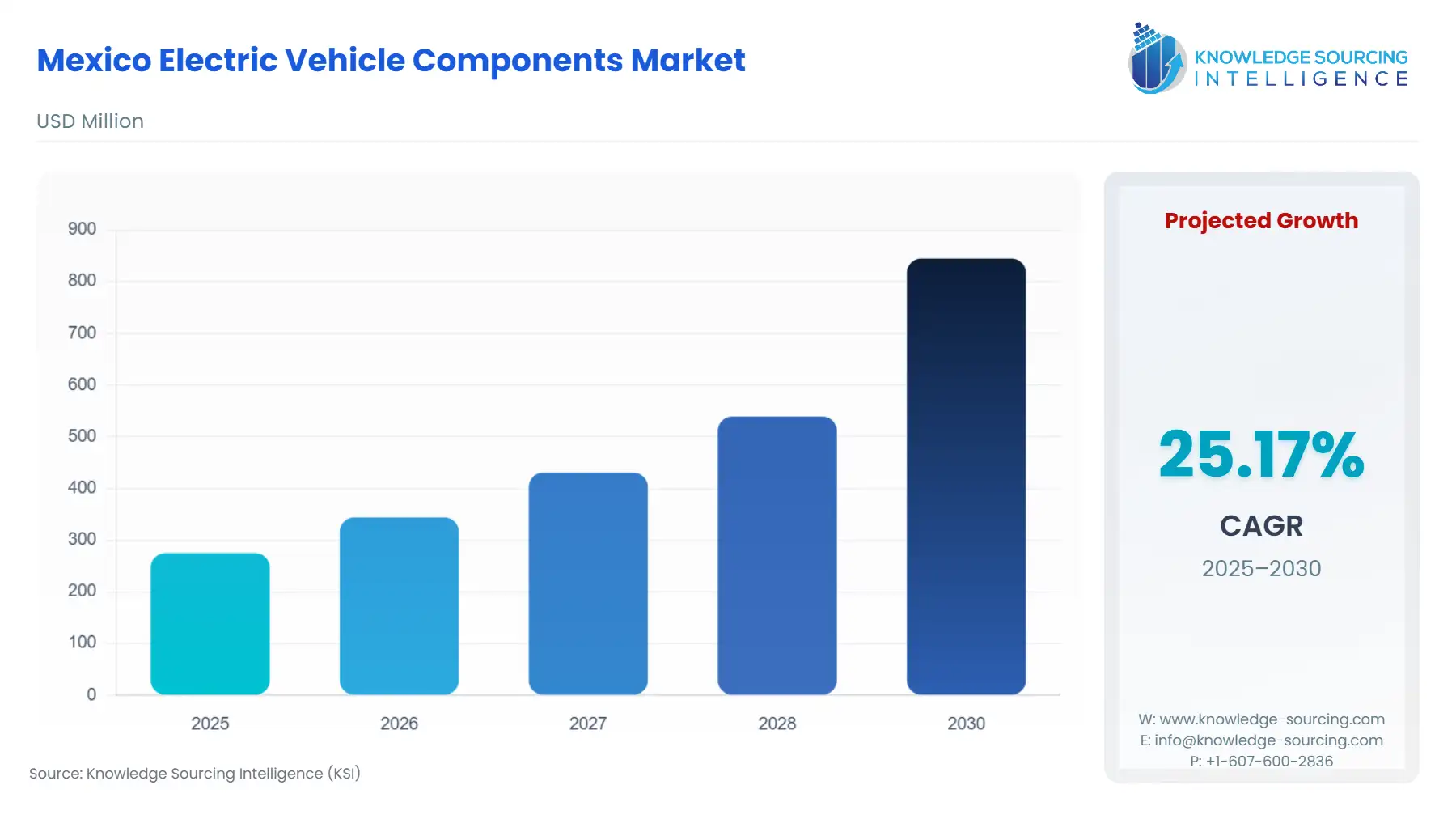
The Mexico Electric Vehicle Components Market is forecast to increase at a CAGR of 25.17%, reaching USD 0.845 billion in 2030 from USD 0.275 billion in 2025.
The Mexican Electric Vehicle Components Market is undergoing a fundamental transformation, transitioning from a historical focus on internal combustion engine (ICE) parts to a North American electromobility anchor. This pivot is inextricably linked to geopolitical trade incentives and a strategic move by global automotive manufacturers to optimize their supply chains for battery electric vehicles (BEVs). Mexico's mature automotive production ecosystem, coupled with lower labour costs relative to its northern neighbours, provides a compelling foundation for producing high-value, high-volume EV sub-assemblies. The resulting market dynamics favour component suppliers capable of meeting aggressive localization targets and integrating advanced manufacturing processes to serve a burgeoning, export-driven OEM segment.
Mexico Electric Vehicle Components Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
The primary catalyst for component demand stems from the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) rules of origin. The requirement for a progressively higher Regional Value Content (RVC) in vehicles to qualify for duty-free trade directly compels OEMs to localize the production of high-value core components such as battery packs, electric motors, and inverters within the North American region. This trade framework, therefore, is a major growth factor for Mexican component manufacturers. Furthermore, OEM investment in new domestic EV production capacity provides tangible demand. For example, Ford is producing the Mustang Mach-E in Cuautitlán, and General Motors invested in its Ramos Arizpe plant for battery assembly, while BMW is set to manufacture the electric SUV iX3 in San Luis Potosí. These operational facilities create a firm, verified demand pull for local components to support their high-volume vehicle assembly lines.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The key challenge facing the market is a deficit in local charging infrastructure and grid stability, which constrains domestic EV adoption. A limited public charging network (approximately 3,300 public points as of 2023) creates consumer range anxiety, thereby slowing the penetration of BEVs into the Mexican consumer market and limiting the size of the Aftermarket segment's component requirement. Conversely, this challenge presents a clear opportunity: the necessary expansion of EV infrastructure, including private and public charging stations, will directly generate new component demand for specialized hardware such as Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE), power control units, and advanced DC-DC converters required for fast-charging.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
As the Mexico Electric Vehicle Components Market is centered on physical products—specifically battery packs, power electronics, and electric motors—raw material dynamics are paramount. The federal government's 2022 declaration of lithium as a strategic mineral positions the state to manage the resource's value chain. This move, focused on deposits in the Sonora region, indicates a long-term strategy to internalize the most volatile part of the EV battery supply chain. Successfully developing this vertical integration would insulate local component manufacturers from global price shocks and supply dependencies for lithium-ion battery cells, reducing the overall cost basis and boosting local demand for cell-to-module and module-to-pack assembly components.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The Mexican EV component supply chain is a distinct extension of the established North American automotive logistical network, characterized by a Tier 1 and Tier 2 manufacturing concentration in the Northern and Central states (Nuevo León, Coahuila, Guanajuato, and San Luis Potosí). The logistical complexity is defined by a primary dependency on cross-border transport to the U.S. assembly plants, making "just-in-time" delivery a logistical imperative. Key production hubs are increasingly seeing a clustering of specialized suppliers; for instance, the concentration of brake control and power steering systems from companies like ZF Group in Querétaro demonstrates the co-location of component specialists to service multiple OEMs. The dependence on Asian-sourced battery cells for pack assembly remains a key vulnerability, although efforts to localize lithium processing seek to mitigate this long-term dependency.
Mexico Electric Vehicle Components Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
Mexico Federal Government |
USMCA (United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement) |
The 75% RVC requirement for auto parts incentivizes component nearshoring, creating a direct, non-negotiable pull for local manufacturing of core EV components to maintain duty-free export access. |
|
Mexico Federal Government |
50% Zero-Emission Vehicle (ZEV) Production Goal by 2030 |
This ambitious, non-binding production target announced in 2022 drives OEM investments to upgrade Mexican plants for BEV assembly, which translates directly into increased demand for locally produced motor, inverter, and power electronics systems. |
|
Mexico Federal Government |
Strategic Mineral Declaration (Lithium, 2022) |
The nationalization of lithium's value chain management is a prerequisite step to localizing battery cell production, fundamentally reshaping the long-term supply and cost structure for the most critical EV component. |
Mexico Electric Vehicle Components Market Segment Analysis:
- By Component Type: Battery Pack
The battery pack segment is the central axis of the Mexican EV component market due to its high cost and strategic importance, which is directly amplified by USMCA RVC rules. The segment is overwhelmingly driven by the OEMs' need for local assembly and integration to meet North American content thresholds. Since the vast majority of BEVs assembled in Mexico are for export, the demand is not tied to nascent domestic sales but to high-volume manufacturing contracts from companies like Ford and GM. The immediate growth driver is the "cell-to-pack" process localization, where imported cells are assembled into modules and packs on Mexican soil. This focuses demand on component sub-segments like thermal management systems, Battery Management Systems (BMS), and high-voltage cabling and connectors, all of which are critical for the final integration and safe operation of the vehicle.
- By End-User: OEMs
The Original Equipment Manufacturers segment is the dominant, immediate, and high-volume demand driver for the entire Mexican EV component market. This requirement is not market-driven by local sales but supply-chain-driven by global production mandates and the trade imperative of the USMCA. The establishment of dedicated EV assembly lines requires suppliers to invest in proximity to the OEM plants to ensure rapid, synchronous delivery, which is fundamental for modern automotive production cadence. This proximity imperative creates firm demand for Tier 1 and Tier 2 suppliers that can provide just-in-time logistics for complex assemblies like e-Axle systems, integrated power modules, and specialized Body & Chassis parts designed specifically for BEV platforms. The OEM segment's purchasing power and long-term contracts offer the stability necessary to justify significant component manufacturing capacity investment in Mexico.
Mexico Electric Vehicle Components Market Competitive Analysis:
The competitive landscape is defined by established Tier 1 global suppliers with a pre-existing footprint in Mexico's ICE market who are now pivoting their production capabilities to electric components. Their strategic positioning leverages decades of operational experience and established logistical ties with the major OEMs.
- ZF Group: The company leverages its deep history in conventional powertrains and chassis systems, focusing its strategic positioning on core EV components that integrate mechanical and electronic systems. Its expansion in Querétaro, which includes Brake Control Systems and Electric Power Assisted Steering Systems, showcases a clear pivot to mechatronic components that are critical for modern EV safety and autonomy. This strategy capitalizes on the commonality between high-tech ICE and EV chassis demands while servicing the growing number of EV platforms.
- DANA Incorporated: DANA's focus on drivetrain and e-propulsion systems positions it as a specialist in the e-Axle component category. The company’s announcement of a high percentage of new business operations attributed to EV platform services reflects a full-scale transition. DANA’s key products include integrated e-Propulsion systems, which combine the electric motor, inverter, and gearbox into a single unit, creating a high-value, assembly-ready component required by OEMs seeking to simplify their BEV architecture.
Mexico Electric Vehicle Components Market Developments:
- ZF Group Expansion of Queretaro Facility (February 2023): ZF Group announced a significant expansion of its manufacturing operations in Querétaro by over 80,000 m², establishing a new distribution center. This capacity addition is specifically aimed at meeting the rising demand for its chassis technologies, including Brake Control Systems and Electric Power Assisted Steering Systems, directly supporting North American EV manufacturing objectives.
- Tesla Gigafactory Nuevo León Announcement (March 2023): Tesla's formal announcement of a new Gigafactory in Nuevo León, an investment expected to be approximately US$5 billion, signalled a massive future demand generator for local components. The project, intended to be a major EV production hub, will require a localized supply chain for battery components, body and chassis parts, and specialized power electronics.
Mexico Electric Vehicle Components Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 0.643 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 1.35 billion |
| Growth Rate | 15.99% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component Type, Vehicle Type, Technology, End User |
| Companies |
|
Mexico Electric Vehicle Components Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT TYPE
- Battery Pack
- Electric Motor
- Power Electronics
- Inverter
- Converter (DC-DC)
- On-Board Charger
- Thermal Management System
- Body & Chassis
- Other Components
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Passenger Cars
- Commercial Vehicles
- Two-Wheelers & Three-Wheelers
- BY TECHNOLOGY
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
- BY END-USER
- OEMS
- Aftermarket