Report Overview
Spain Electric Vehicle Market Highlights
Spain Electric Vehicle Market Size:
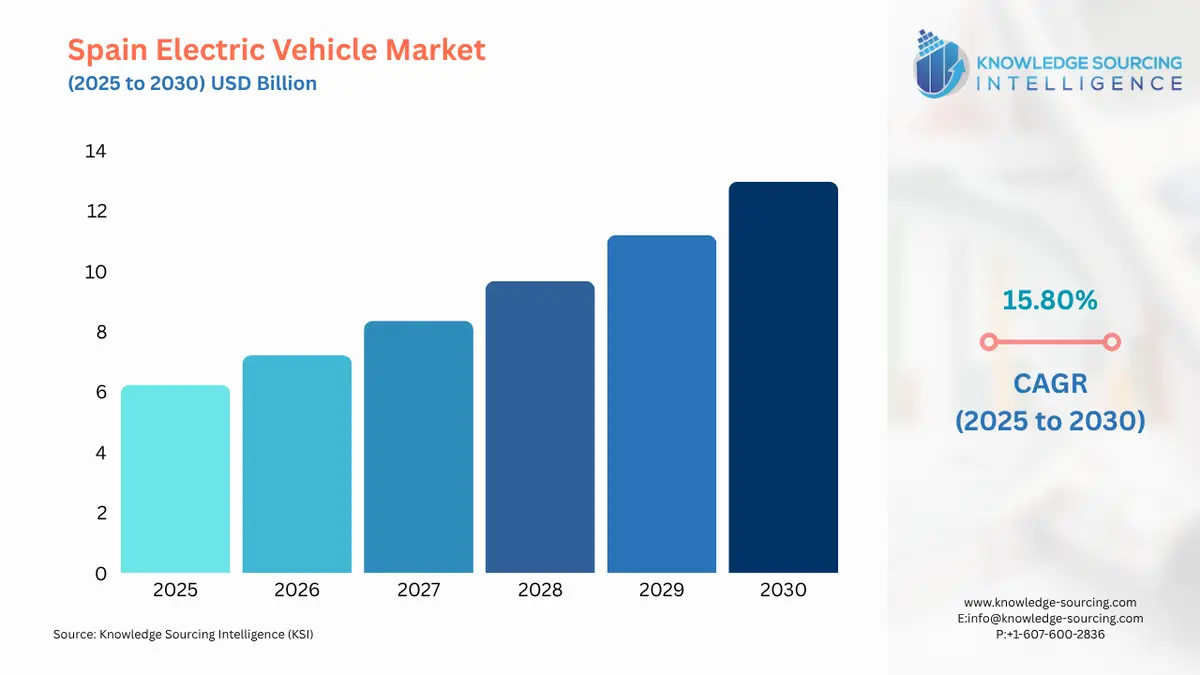
The Spain Electric Vehicle Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.80%, reaching USD 12.973 billion in 2030 from USD 6.230 billion in 2025.
The Spanish electric vehicle market is in a transformative phase, driven by a confluence of supportive policies, evolving consumer preferences, and a diversifying product landscape. This momentum, while strong, faces distinct challenges, including the pace of charging infrastructure rollout and the intermittent availability of government subsidies. The market's trajectory is characterized by a rapid shift away from traditional internal combustion engines, propelled by a growing awareness of environmental imperatives and the long-term economic benefits of electric mobility.
Spain Electric Vehicle Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
Government incentives and regulatory frameworks are the most significant growth catalysts. The MOVES III Plan, which offers subsidies for EV purchases and charging infrastructure installation, directly reduces the financial barrier for consumers, making electric vehicles a more viable option. This financial support, combined with a 15% personal income tax deduction for purchases, directly increases the consumer's purchasing power, thereby stimulating demand. Furthermore, the expansion of public charging infrastructure, driven by both private investment and government targets, directly mitigates range anxiety, a critical factor that has historically constrained demand. The increasing availability of fast-charging stations along major corridors makes long-distance travel feasible, encouraging more drivers to consider an EV for their primary vehicle.
- Challenges and Opportunities
A primary challenge is the inconsistent application and depletion of government funding, as seen in the exhaustion of funds in high-volume regions like Madrid and Catalonia. This inconsistency creates market uncertainty and can stall sales momentum, as consumer demand is heavily reliant on these subsidies. Another challenge is the slower electrification of heavy-duty commercial vehicles, a segment critical for Spain's logistics sector, which has not received consistent aid.
Opportunities for growth are concentrated in expanding charging infrastructure and diversifying product offerings. The push for highway electrification and destination charging, particularly in a country with a robust tourism sector, presents a significant opportunity. As urban fleets transition to electric vehicles to comply with low-emission zone regulations, this creates a concentrated, high-volume demand for depot and urban charging solutions. The increasing availability of affordable, small-segment EV models is also a key opportunity to democratize the market and attract a broader base of private buyers.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The electric vehicle market, as a physical product, is intrinsically linked to the supply chain and pricing of key raw materials, most notably lithium, cobalt, and nickel for batteries. The global dynamics of these materials directly influence the final cost of the vehicle. Fluctuations in commodity prices can create pricing volatility, which may either increase or decrease the final cost for the consumer, thereby influencing the market. Battery technology advancements and the development of new chemistries also play a role in mitigating this pricing risk and improving vehicle range and performance.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global EV supply chain is a complex network with critical dependencies. Battery production is dominated by Asian hubs, particularly China, which holds a commanding position in the processing of raw materials and cell manufacturing. This dependency creates logistical complexities and potential vulnerabilities for European and Spanish manufacturers. European-based assembly plants, while growing in number, still rely on a global network for components. The Spanish automotive industry, with its significant manufacturing base, is working to integrate into this new supply chain, leveraging local production to mitigate some of these global dependencies.
Spain Electric Vehicle Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
Spain (National) |
MOVES III Program |
This incentive program offers direct subsidies for the purchase of electric vehicles and the installation of charging points, directly stimulating consumer demand by reducing the initial cost barrier. |
|
Spain (National) |
National Integrated Energy and Climate Plan (PNIEC) 2021-2030 |
This plan sets national targets for EV adoption and public charger deployment, providing a clear regulatory roadmap that catalyzes both public and private sector investment in the EV ecosystem, thereby enabling market growth. |
|
European Union |
Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulation (AFIR) |
This EU-wide regulation mandates the installation of minimum charging capacities along the core Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T) at specific intervals, ensuring the development of a coherent charging network and alleviating long-distance range anxiety for Spanish drivers. |
Spain Electric Vehicle Market Segment Analysis:
- Passenger Vehicle
The demand for electric passenger vehicles in Spain is driven primarily by a combination of government subsidies, technological advancements, and shifting consumer behaviour. The MOVES III Plan has made electric cars financially accessible to a wider demographic, particularly when combined with personal income tax deductions. This has directly propelled the sales of both Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs). Furthermore, the quadrupling of available electrified models since 2019, with a notable increase in the more affordable small and mid-size segments, addresses a key growth constraint related to price and choice. The growing maturity of the charging infrastructure also directly contributes to demand by mitigating the long-standing issue of range anxiety. As the network of fast and ultra-fast chargers expands, consumers gain confidence in the practicality of using an EV for both daily commutes and longer journeys. The market is witnessing a direct correlation between the availability of financial incentives, a broader selection of models, and the accelerated adoption of electric passenger vehicles.
- Private End User
The private end users segment is a crucial driver for the Spanish EV market, propelled by a distinct set of motivations. For these consumers, the decision to purchase an EV is a combination of financial practicality and environmental consciousness. The immediate reduction in operational costs, including lower fuel and maintenance expenses, serves as a powerful incentive over the vehicle's lifetime. Government grants under the MOVES III program directly lower the initial purchase price, while tax incentives further sweeten the value proposition. Beyond the financial aspect, a growing segment of private buyers is motivated by a desire to reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to cleaner urban environments. The rising presence of urban low-emission zones (ZBE), such as those in Madrid and Barcelona, also directly impacts demand by making EVs the only viable option for unrestricted access. The increasing availability of home charging solutions, coupled with the expansion of public charging networks, provides the necessary convenience and security to attract private individuals who require reliable and accessible charging for their daily routines.
Spain Electric Vehicle Market Competitive Analysis:
The Spanish EV market features a competitive landscape with a mix of established automotive groups and new entrants. Key players are leveraging their industrial presence and strategic investments to capture market share.
- Volkswagen Group España: A dominant force in the Spanish automotive industry, Volkswagen Group leverages its established manufacturing base and diversified portfolio of brands, including Volkswagen, CUPRA, and SEAT. The company's strategy focuses on a platform approach, utilizing the MEB+ electric modular platform to achieve economies of scale and accelerate the rollout of new electric models. This strategy is exemplified by the planned 2026 launch of the "Electric Urban Car Family," which targets the high-volume small car segment, directly addressing the demand for more affordable EVs.
- Iberdrola España: As a major utility company, Iberdrola has positioned itself as a key enabler of electric mobility by investing heavily in the charging infrastructure. Its focus on building one of the largest public charging networks and providing comprehensive home and business charging solutions directly supports vehicle adoption. The company’s partnerships, such as the one with AEDIVE, a business association for the promotion of electric mobility, reinforce its commitment to electrifying heavy-duty transport, a critical and underserved market segment.
Spain Electric Vehicle Market Developments:
- September 2025: Iberdrola España announced it has surpassed 10,000 public charging points in operation. This milestone is part of a broader strategic effort to expand its network across the country, directly addressing a key growth constraint by improving charging accessibility for EV drivers.
- August 2025: Alimerka, a Spanish supermarket chain, and Iberdrola España collaborated to install 238 charging points for electric vehicles at Alimerka supermarkets. This partnership expands the network of destination charging points, providing greater convenience for consumers and encouraging EV use in everyday activities.
- April 2025: The Spanish government, through the Council of Ministers, extended the MOVES III Program, allocating an additional 400 million euros to the incentive scheme. This extension ensures the continuation of crucial subsidies for EV purchases and charging infrastructure, directly supporting and stabilizing market expansion.
Spain Electric Vehicle Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 6.230 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 12.973 billion |
| Growth Rate | 15.80% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Vehicle Type, Propulsion Type, Drive Type, End User |
| Companies |
|
Spain Electric Vehicle Market Segmentation:
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Passenger Vehicle
- Commercial Vehicle
- Others
- BY PROPULSION TYPE
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
- BY DRIVE TYPE
- Front Wheel Drive
- Rear Wheel Drive
- All Wheel Drive
- BY COMPONENT
- Battery Cells & Packs
- Onboard Chargers & Motor
- Brake, Wheel & Suspension
- Others
- BY END USER
- Public
- Private
- Commercial