Report Overview
UK Electric Vehicle Components Highlights
UK Electric Vehicle Components Market Size:
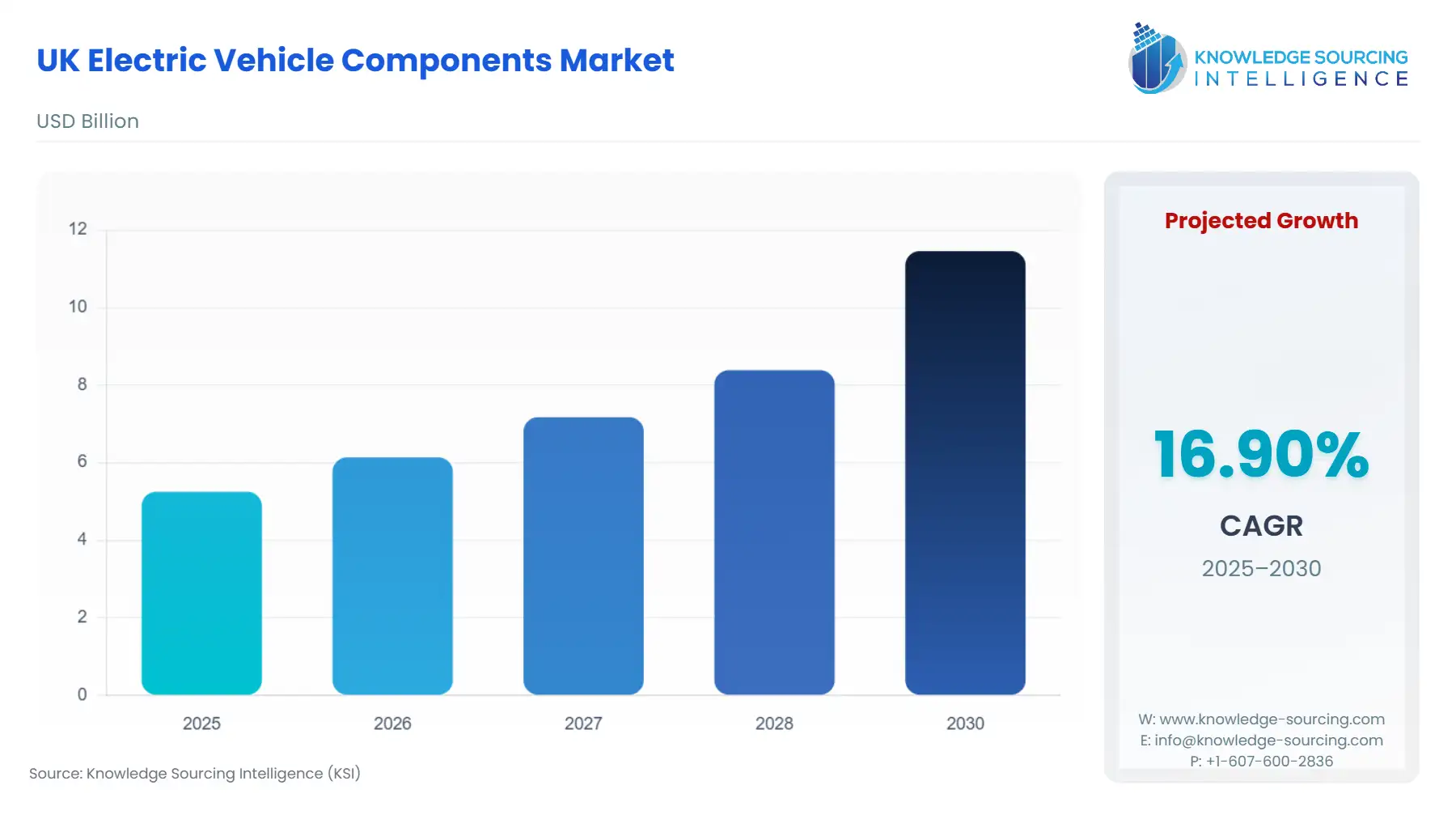
The UK Electric Vehicle Components Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 16.90%, climbing to USD 11.46 billion in 2030 from USD 5.25 billion in 2025.
The UK Electric Vehicle Components Market operates under the dual pressure of ambitious decarbonisation policy and acute supply chain constraints. The government's regulatory framework, particularly the ZEV Mandate, establishes a non-negotiable floor for EV adoption, translating directly into a mandatory volume demand for all core EV components. This regulatory catalyst is forcing a dramatic re-tooling and re-positioning of the legacy automotive manufacturing base. However, the market’s inherent vulnerability stems from a heavy reliance on imported battery cells and associated materials, coupled with high domestic energy costs that challenge the global competitiveness of local component producers. Strategic investment, often co-funded by public grants, is therefore focused on building localised capacity to mitigate supply risk and secure the future domestic assembly pipeline.
UK Electric Vehicle Components Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
The primary catalyst for market expansion is the Zero Emission Vehicle (ZEV) Mandate, which came into effect in January 2024. This policy directly increases demand for battery packs, electric motors, and power electronics by legally enforcing a minimum proportion of zero-emission vehicle sales. Failure to comply results in financial penalties, effectively making the procurement and integration of EV components an economic imperative for all major vehicle manufacturers operating in the UK. Furthermore, the expansion of the public charging network, often supported by government-backed infrastructure funds, reduces range anxiety and pulls consumer demand for new EVs. This consumer-side adoption reinforces OEM necessity to secure component supply for higher production volumes of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), particularly in the burgeoning fleet and light commercial vehicle segments.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The market faces significant headwinds from high domestic energy costs, which elevate the operational expense for energy-intensive component manufacturing processes, such as battery cell production. This constraint makes UK component manufacturing less competitive against European and Asian hubs, inhibiting investment in critical areas. A key opportunity is the Automotive Transformation Fund (ATF), a government-backed initiative designed to de-risk and unlock private capital for large-scale industrialisation. By offering grants for capital investment in battery and e-drivetrain manufacturing, the ATF directly lowers the financial barrier for new domestic capacity. This support is strategically positioned to create a localised ecosystem, substantially reducing dependence on long, single-source global supply chains for parts like Electric Motors and Inverters.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
As a market focused on physical products (battery packs, electric motors, power electronics), the supply of key raw materials remains critical. The pricing of battery cells is fundamentally linked to global market prices for lithium, nickel, and cobalt. While long-term contracts can mitigate immediate volatility, the UK's nascent battery cell production capability is largely dependent on securing stable, long-term international supply agreements for refined materials. Price volatility in these commodities flows through the value chain, directly impacting the final cost of the Battery Pack, which constitutes the most expensive single component of an EV, thus influencing overall OEM profitability and consumer pricing.
Supply Chain Analysis
The UK's EV component supply chain is characterised by a heavy, critical dependency on Asia-Pacific (specifically China, South Korea, and Japan) for lithium-ion battery cells and, to a lesser extent, certain advanced power electronic semiconductor components. Production of these items is highly concentrated, introducing significant geopolitical and logistical risks. The domestic supply chain for components beyond final assembly, such as e-axles, specialist wiring harnesses, and thermal management systems, remains underdeveloped. This logistical complexity necessitates high inventory levels or reliance on complex, expensive air freight, adding structural costs to UK-assembled vehicles. Localised production announcements, such as new electric motor manufacturing capacity, aim to reduce reliance on continental European supply chains, especially for high-volume platform parts.
UK Electric Vehicle Components Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
UK (Great Britain) |
Zero Emission Vehicle (ZEV) Mandate |
Mandates increasing sales targets for zero-emission cars and vans, creating guaranteed baseline volume demand for all core EV components (battery, motor, power electronics) for OEMs to avoid punitive fines. |
|
UK |
Automotive Transformation Fund (ATF) / Advanced Propulsion Centre (APC) |
Provides direct government funding and de-risking capital grants for R&D and scale-up of battery, electric motor, and power electronics manufacturing, directly stimulating new domestic supply. |
|
UK |
Product Safety and Metrology Regulations |
Enforces stringent safety and quality standards for all components, particularly battery systems, which necessitates significant investment in local testing, validation, and advanced manufacturing processes by component suppliers. |
UK Electric Vehicle Components Market Segment Analysis:
- By Component Type: Battery Pack
The battery pack segment is the unequivocal nexus of demand, driven by the increasing energy density requirements of BEVs to meet consumer expectations for longer driving range. The ZEV mandate’s escalating targets for BEV sales directly translate into a mandatory, proportional increase in demand for the entire battery pack assembly, including cells, Battery Management Systems (BMS), and thermal management sub-components. The current imperative is for higher kilowatt-hour (kWh) capacity to serve the family car and commercial van segments. The primary growth factor is localisation, as local vehicle assembly mandates and logistical costs for large, heavy packs encourage OEMs to favour supply from domestic or near-shore gigafactories, such as the AESC facility in Sunderland, to mitigate supply chain disruption and import tariffs.
- By End-User: OEMs
The OEM segment represents the overwhelming majority of demand for new EV components. This requirement is intrinsically linked to the vehicle production schedules of major manufacturers with UK plants, such as Nissan, Jaguar Land Rover, and Ford. The growth driver here is platform integration and supply security. OEMs require guaranteed high-volume supply of standardised components—particularly electric motors and power electronics—that can be scaled across multiple vehicle architectures. The OEM procurement strategy prioritises suppliers who can co-locate or provide robust contractual commitments, driven by the need to comply with local content rules (Rules of Origin) for preferential trade treatment. This ensures components are designed and supplied to the exact specifications of the final vehicle, integrating seamlessly into the manufacturing process.
UK Electric Vehicle Components Market Competitive Analysis:
The UK EV component competitive environment is bifurcated, featuring established global Tier 1 automotive suppliers alongside a growing ecosystem of specialist, innovation-driven UK-based SMEs, heavily reliant on government support to scale.
- A-E-S-C (Envision AESC): Positioned as a foundational pillar of the UK's EV ecosystem, AESC's primary strategic asset is its commitment to the Sunderland gigafactory. The company's positioning focuses on high-volume battery cell and module production, securing long-term contracts with major UK vehicle manufacturers like Nissan. The key product is their latest generation of high-energy-density lithium-ion battery cells, which are critical for meeting the range demands of modern BEVs.
- Ford: With a significant investment in the Halewood plant, Ford has strategically transitioned from a legacy transmission manufacturer to a key domestic supplier of Electric Drive Units (EDUs). This vertical integration secures the supply of a high-value, complex component for its own high-volume European EV platforms, including the all-electric Puma Gen-E and E-Transit Custom, significantly reducing reliance on external powertrain suppliers.
UK Electric Vehicle Components Market Developments:
- July 2025: The Advanced Propulsion Centre (APC) announced multi-million-pound grants, backed by the UK government's DRIVE35 initiative. The funding included support for Astemo to manufacture electric inverters at its Bolton facility and for Dana UK Axle to put full electrification products in its plant in Witton, Birmingham, representing a significant expansion of domestic power electronics and drivetrain capacity.
- December 2024: Ford commenced production of Electric Drive Units (EDUs) at its Halewood facility in Merseyside, UK. This event followed a total investment of £380 million and established an annual production capacity of 420,000 EDUs, positioning the plant as a key hub for Ford's European electric vehicle component supply.
UK Electric Vehicle Components Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 5.25 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 11.46 billion |
| Growth Rate | 16.90% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component Type, Vehicle Type, Technology, End User |
| Companies |
|
UK Electric Vehicle Components Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT TYPE
- Battery Pack
- Electric Motor
- Power Electronics
- Inverter
- Converter (DC-DC)
- On-Board Charger
- Thermal Management System
- Body & Chassis
- Other Components
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Passenger Cars
- Commercial Vehicles
- Two-Wheelers & Three-Wheelers
- BY TECHNOLOGY
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
- BY END-USER
- OEMS
- Aftermarket