Report Overview
US 5G Fuel Cell Highlights
US 5G Fuel Cell Market Size:
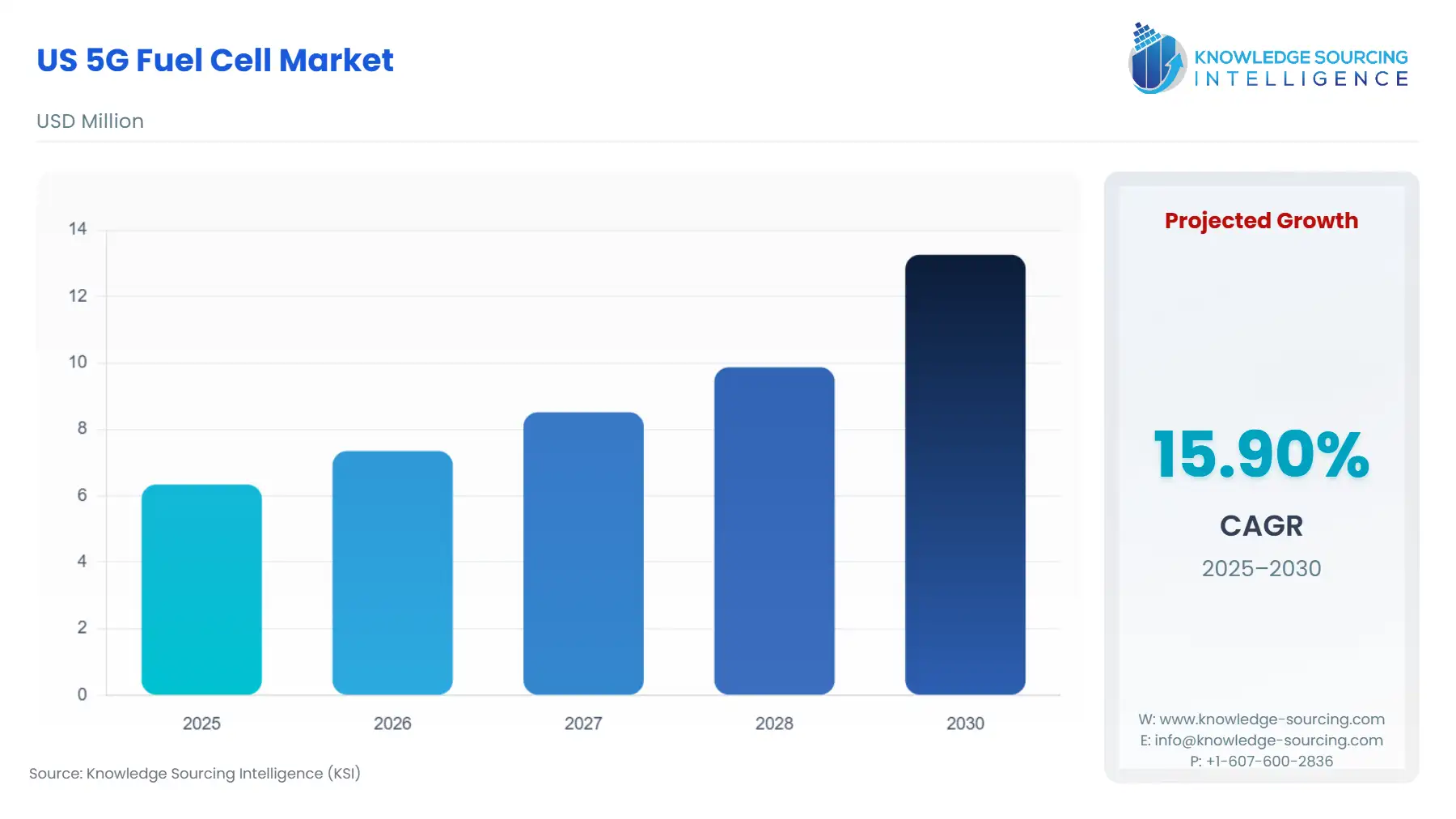
The US 5G Fuel Cell Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.90%, reaching USD 13.261 million in 2030 from USD 6.342 million in 2025.
The proliferation of fifth-generation (5G) telecommunications infrastructure across the United States establishes a foundational shift in the power requirements for critical communications networks. Unlike previous generations, 5G architecture demands unprecedented network densification, characterized by thousands of new small cell sites, distributed core functions, and micro-data centers positioned closer to the end-user. This structural evolution mandates a corresponding evolution in energy resilience, specifically requiring high-performance, low-emission backup power capable of immediate response and extended run-time to maintain ultra-reliable, low-latency connectivity. Fuel cell systems, which convert the chemical energy of hydrogen or natural gas directly into electricity with zero or near-zero emissions, have emerged as the primary alternative to incumbent diesel generator sets, offering superior environmental compliance, significantly lower noise profiles, and a scalable solution for the diverse power requirements of the modern 5G landscape.
US 5G Fuel Cell Market Analysis:
Growth Drivers
The primary market driver is the 5G Ultra-Reliability Imperative. 5G network operation inherently requires five-nines (99.999%) reliability to support mission-critical applications such as remote surgery, autonomous vehicles, and real-time smart grid management. This high-reliability mandate directly increases demand for fuel cells as a resilient backup solution with no moving parts, instant start-up capability, and superior operational stability compared to battery-only or diesel systems, especially in remote or disaster-prone areas. Furthermore, the Decarbonization of Critical Infrastructure, spurred by state-level mandates and corporate ESG goals, compels Telecom Operators and Tower & Infrastructure Providers to adopt clean energy. This trend creates non-negotiable demand for fuel cells over high-emission diesel generators to ensure network operational continuity while meeting sustainability targets.
Challenges and Opportunities
The foremost challenge is the Hydrogen Logistics and Cost Barrier, particularly the capital expenditure (CapEx) associated with establishing a distributed hydrogen fuel delivery and storage network. This complexity depresses demand by elevating the initial investment for site deployment. Conversely, a significant opportunity lies in the Convergence of AI and Edge Computing. The massive power requirements of Edge Data Centers and AI infrastructure, which must reside near the 5G core network for latency reasons, create immense, reliable demand for high-capacity, multi-megawatt fuel cell solutions. This opportunity shifts the market from small-scale backup to large-scale, continuous-duty prime power systems, validating larger investment and reducing system costs through economies of scale.
Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) fuel cells, a common type for lower power 5G sites, critically rely on Platinum Group Metals (PGMs), primarily platinum, for the catalyst layer. The volatility of PGM pricing, exacerbated by geopolitical supply chain dependencies, introduces significant cost risk into the final system price. Historically, PGM price spikes have demonstrably inflated PEM fuel cell system costs, directly constraining mass market adoption by telecom entities sensitive to CapEx. The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) addresses this systemic constraint through targeted funding, such as the $750 million announced in March 2024 under the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, focused on reducing the content of critical minerals and supporting the research and development (R&D) of PGM-free catalysts, a strategic effort essential for lowering the baseline price per kilowatt ($/kW) and stimulating long-term demand.
Supply Chain Analysis
The fuel cell supply chain in the US is bifurcated: components (stacks, membranes, catalysts) are globally sourced but increasingly undergoing domestic final assembly, while the fuel (hydrogen) supply is intensely regionalizing. Key production hubs for manufacturing components are consolidating, often near R&D centers in the Northeast and California. The dominant logistical complexity is the delivery of hydrogen, which is currently reliant on high-pressure tube trailers. The DOE's creation of Regional Clean Hydrogen Hubs (H2Hubs) across the country (e.g., in the Midwest and Gulf Coast) is a strategic intervention to decentralize hydrogen production and distribution. This hub-and-spoke model aims to create localized economies of scale, dramatically reducing the end-user cost and logistical complexity of fuel procurement for 5G site operators.
Government Regulations
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Federal (US) | Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) (2022) | The 45V Clean Hydrogen Production Tax Credit and the 48 Investment Tax Credit significantly de-risk fuel cell deployment by subsidizing clean hydrogen production and direct equipment costs. This lowers the TCO for telecom operators, thereby creating a substantial economic incentive to pivot from diesel to fuel cells. |
| Federal (US) | Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL) (2021) | BIL allocates $7 billion for Regional Clean Hydrogen Hubs (H2Hubs) and $1.5 billion for electrolyzer and fuel cell manufacturing R&D. This direct capital injection structurally addresses supply-side constraints—fuel cost and component availability—which directly accelerates commercial market readiness and adoption by 5G providers. |
| Federal (US) | Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Network Resiliency | Post-disaster (e.g., Hurricane Sandy) regulatory focus on extended power backup mandates for critical communications infrastructure directly increases demand for fuel cells, which offer longer run-times than traditional batteries, ensuring compliance and service survivability. |
US 5G Fuel Cell Market Segment Analysis:
By Deployment: High-capacity Solutions
The need for High-capacity Fuel Cell Solutions ($>50kW and multi-megawatt systems) is accelerating, driven by the shift of computational load to the network edge. 5G enables sophisticated applications like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and complex cloud rendering, which must be housed in Edge Data Centers (EDCs) located geographically closer to the end-user to meet the low-latency (sub-10ms) requirement. These EDCs represent a significant, non-interruptible critical load, distinct from simple tower backup. Companies like Bloom Energy have validated this high-capacity segment through verifiable agreements with major data center operators, such as the Equinix Data Center Power Agreement and the Brookfield $5 Billion Strategic AI Infrastructure Partnership. These developments demonstrate a direct demand for megawatt-scale fuel cell platforms to serve as continuous-duty prime power, not merely backup, effectively transforming the fuel cell from a niche telecom accessory into a core, scalable power utility for the 5G-enabled digital economy.
By End User: Telecom Operators
Telecom Operators (T-Mobile, Verizon, AT&T) represent the ultimate demand source, and their primary driver is the optimization of Operational Expenditure (OpEx) while ensuring service reliability. Fuel cells directly address this through reduced maintenance cycles and the elimination of costly, time-consuming diesel re-fueling logistics during extended grid outages, a particularly critical factor for remote tower and small cell sites. The environmental and noise pollution penalties associated with running diesel generators in residential and urban 5G node locations create a direct cost pressure that shifts the preference to quiet, zero-emission fuel cells. Furthermore, as network service agreements penalize downtime, the superior reliability and instantaneous activation of fuel cells become a competitive differentiator, solidifying them as the favored technology for guaranteeing contractual uptime and minimizing financial liability associated with service interruption.
US 5G Fuel Cell Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The US 5G Fuel Cell Market exhibits a landscape dominated by established stationary power players actively leveraging their technology for telecom applications. Competition is less about product differentiation and more about vertical integration—specifically, the control over the hydrogen supply chain and the ability to scale manufacturing to meet high-volume telecom deployment schedules. Key players focus on securing large-scale partnerships with major network operators and infrastructure firms to lock in demand.
Plug Power Inc.
Plug Power's strategic positioning centers on a comprehensive, vertically integrated green hydrogen ecosystem. The company controls not just the fuel cell hardware (Proton Exchange Membrane, PEM), but also the sourcing and delivery of the hydrogen fuel via its own electrolyzer and liquefaction network. This approach directly addresses the critical fuel supply risk that constrains telecom adoption. A key, verifiable development underscoring this strategy is the commissioning of its Louisiana hydrogen liquefaction plant (April 2025). This capacity addition significantly de-risks the hydrogen supply chain for its customers, directly enhancing the appeal and commercial viability of its 5G backup power units by guaranteeing long-term fuel availability and price stability, a critical factor for large-scale tower providers.
Bloom Energy Corp.
Bloom Energy is strategically focused on the high-capacity, mission-critical power segment using its proprietary Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) technology. While their systems operate on natural gas or hydrogen, their positioning is distinct—they target the core of the 5G network: the massive power draw of Edge and Core Data Centers. The company's focus on large-scale partnerships, such as the Brookfield $5 Billion Strategic AI Infrastructure Partnership (October 2025), solidifies its role as a provider of resilient, multi-megawatt prime power for the digital backbone that enables 5G services. This strategy leverages the SOFC's high efficiency and heat co-generation capabilities, providing a complete energy solution far exceeding the requirements of simple tower backup and capturing the highest value segment of the market.
US 5G Fuel Cell Market Recent Developments:
- October 2025: Bloom Energy announced a strategic partnership with Brookfield, with the latter committing to fund the development of $5 billion in Bloom Energy Server-powered projects for critical data center infrastructure, demonstrating an accelerated market acceptance for megawatt-scale fuel cell power as the reliable solution for the power-intensive demands of AI and 5G core network systems.
- April 2025: Plug Power confirmed the commissioning of its new hydrogen liquefaction plant in Louisiana. This facility represents a significant capacity addition to the company's vertically integrated green hydrogen network, directly improving the logistics and security of fuel supply for its PEM fuel cell products targeted at the telecom and material handling sectors.
- September 2025: Advent Technologies delivered its "Honey Badger 50™" portable High-Temperature PEM fuel cell units to the U.S. Army under a design contract. The units, fueled by methanol, provide lightweight, silent, and efficient power for critical defense applications like radio communications and battery charging in the field, supporting the DoD's need for advanced, portable power solutions.
US 5G Fuel Cell Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 6.342 million |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 13.261 million |
| Growth Rate | 15.90% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Product Type, Deployment, Power Output Range, End-User |
| Companies |
|
US 5G Fuel Cell Market Segmentation:
- BY PRODUCT TYPE
- Fuel Cell Systems
- Fuel Cell Stacks & Components
- Fuel Supply Solutions
- BY DEPLOYMENT
- Backup Power Solutions
- Off-grid / Remote Power Solutions
- Hybrid Energy Systems
- High-capacity Solutions
- BY POWER OUTPUT RANGE
- <5 kW
- 5–50 kW
- 50 kW
- BY END USER
- Telecom Operators
- Tower & Infrastructure Providers
- Government & Defense Communication Networks
- Enterprise 5G Networks