Report Overview
US AI in Finance Highlights
US AI in Finance Market Size:
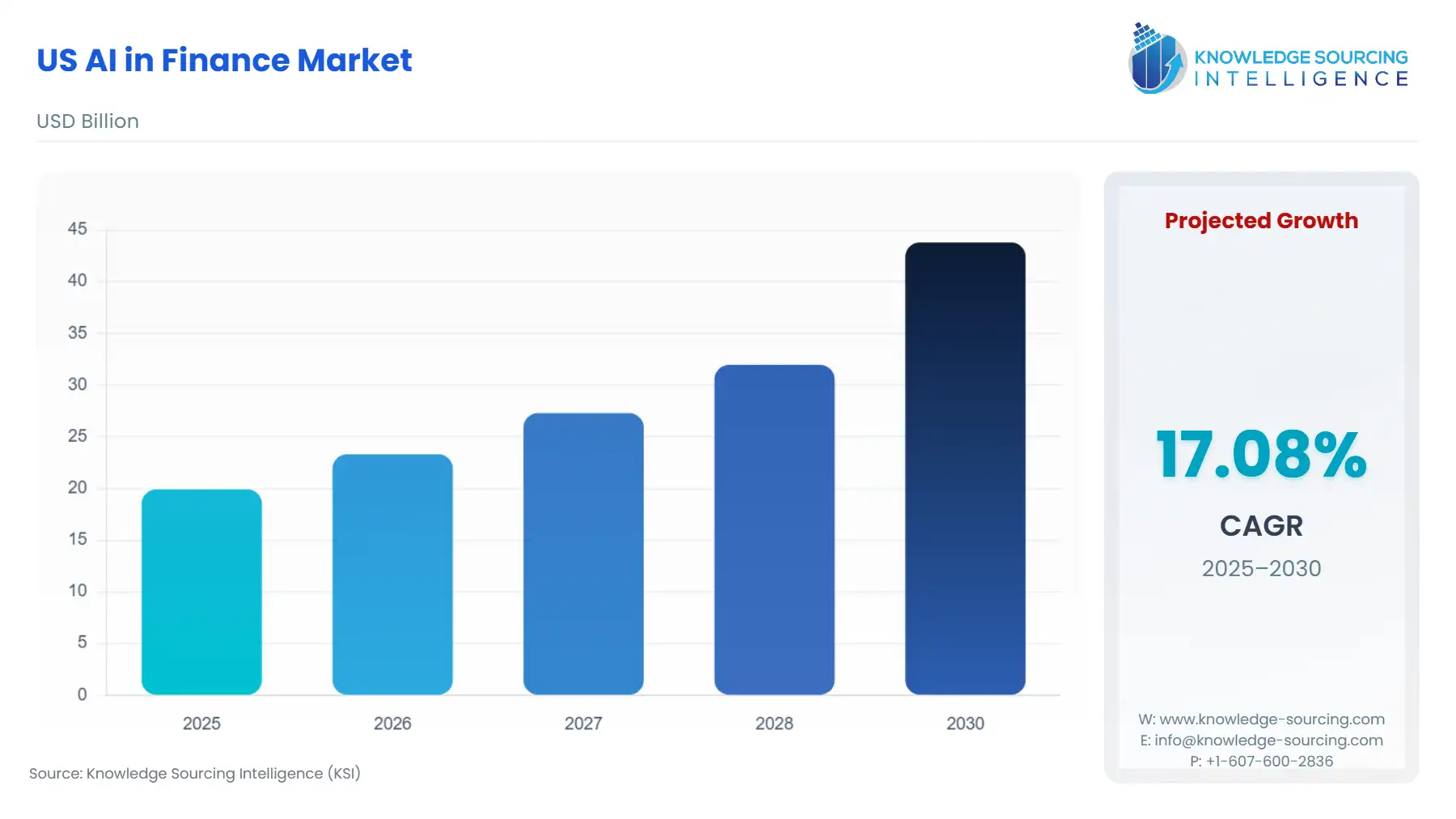
The US AI in Finance Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 17.08%, reaching USD 43.812 billion in 2030 from USD 19.915 billion in 2025.
The US AI in Finance market is experiencing a profound transformation, moving beyond initial pilot phases to institutional-grade deployment across core banking, lending, and investment functions. This growth is intrinsically linked to the financial services sector's continuous drive for operational alpha and regulatory compliance.
The integration of advanced machine learning models, particularly Generative AI, is establishing new paradigms for efficiency, risk mitigation, and personalized customer engagement. The industry's imperative to manage escalating data volumes, coupled with the need to navigate an increasingly complex and retrospective regulatory environment, is solidifying the role of AI as a foundational technology rather than a peripheral tool.
US AI in Finance Market Analysis:
Growth Drivers
Escalating operational complexity and the volume of unstructured data serve as primary growth catalysts. Financial institutions encounter a significant burden from complex global regulations and a constantly evolving fraud landscape. This directly fuels the demand for AI-driven solutions capable of processing text, identifying anomalies, and automating compliance reporting. Moreover, the commercial success of firms that utilize AI to access alternative credit data, such as Upstart, validates AI's capacity to increase loan volume and improve risk-adjusted returns, thus propelling adoption across the consumer finance segment. The deployment of proprietary LLM platforms by major banks highlights the internal drive for efficiency gains in coding and knowledge management, creating a direct demand for technology that replaces or augments basic financial professional tasks.
Challenges and Opportunities
A critical market constraint is the pervasive "black box" nature of complex AI models, which complicates the required explainability for regulatory bodies like the CFPB, creating compliance-related friction that constrains immediate deployment. This challenge, however, generates a substantial opportunity for vendors specializing in "Explainable AI" (XAI) and model governance frameworks, directly driving demand for solutions that provide model transparency and audit trails. Furthermore, the persistent threat of bias and disparate impact in AI-driven lending decisions, which can result in legal action, compels institutions to invest in sophisticated model testing and auditing tools. The opportunity lies in leveraging AI's capacity to improve financial inclusion by accurately assessing risk for underserved populations using alternative data, which necessitates new AI models that can withstand regulatory scrutiny.
Supply Chain Analysis
The US AI in Finance market, being software- and service-centric, possesses a global, non-physical supply chain defined by intellectual property, high-value data, and computational infrastructure. Key production hubs reside in major US technology and finance centers, which act as centers for algorithm development and data science talent. The supply chain's primary dependencies are high-performance computing (HPC) infrastructure, predominantly cloud-based platforms provided by hyperscalers, and the uninterrupted supply of massive, high-quality, labeled financial data sets required for model training. Logistical complexities center on data governance, cross-border data transfer regulations, and the recruitment and retention of specialized AI engineering talent, rather than physical logistics. A critical dependency is the availability of open-source or proprietary Large Language Models, which form the bedrock of many financial Generative AI applications.
Government Regulations
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) | Guidance confirms existing consumer financial protection laws (e.g., ECOA, Fair Housing Act) apply to AI credit models. This mandates Explainable AI (XAI) features, increasing demand for transparent and auditable AI solutions, particularly in the lending and credit scoring segments. |
| United States | Executive Order 14110 on "Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Development and Use of Artificial Intelligence" (2023) | Directs various agencies to issue AI-related guidance and standards. This compels financial institutions to establish detailed corporate governance structures and risk management frameworks for AI, stimulating demand for third-party AI governance and risk management platforms. |
| United States | Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) | Accounting rules for intangible assets and software development. Impacts how financial institutions and fintech companies capitalize or expense the significant development costs associated with building proprietary AI models, influencing internal investment strategies and vendor reliance. |
US AI in Finance Market Segment Analysis:
By Application: Back Office
The Back Office segment is driven by the imperative to streamline resource-intensive, data-heavy operational tasks, directly increasing demand for AI. This includes automated document processing, regulatory compliance monitoring, and financial reporting automation. Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a core growth driver here, as financial institutions must process vast amounts of unstructured text—contracts, internal communications, and regulatory updates—for compliance checks. For instance, the necessity to rapidly implement and track compliance with new federal or state-level regulations, or to monitor for signs of internal fraud via email analysis, propels the adoption of NLP-based Contract Intelligence platforms, like the technology leveraged by JPMorgan Chase's COiN. The application of machine learning for financial crime compliance, particularly Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) processes, creates a high-stakes demand environment, as regulatory penalties for non-compliance are severe. AI solutions that reduce false positive alerts in AML systems directly translate into cost savings and greater operational efficiency, making them an essential investment rather than a discretionary IT upgrade.
By User: Personal Finance
The Personal Finance segment experiences its primary growth catalyst from consumers' expectation for instant, personalized, and digitally native financial experiences. This consumer-side demand directly drives financial institutions to adopt AI-powered tools for credit scoring, personalized recommendations, and customer interaction. The core growth driver is the structural advantage AI confers in credit decisioning, enabling institutions to shift from traditional, rigid FICO score models to a more inclusive, dynamic assessment using alternative data sources, as leveraged by companies like Upstart. AI-driven credit models allow for significantly higher approval rates at lower loss rates for specific borrower segments, which directly increases a financial firm's addressable market and profitability. Furthermore, the rising use of AI-powered chatbots and virtual financial assistants directly addresses the demand for 24/7 customer support and hyper-personalized money management advice, driving adoption of large language models and sentiment analysis for enhanced user engagement and reduced call center costs.
US AI in Finance Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The competitive landscape in US AI in Finance is bifurcated between incumbent financial giants that build proprietary AI, often through substantial internal R&D, and specialist fintechs that focus on niche AI applications, often delivered via a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model. Major banks leverage their vast internal data infrastructure and capital reserves to gain a competitive edge by creating proprietary models tailored to their specific risk appetite and existing customer base. Specialist firms, conversely, compete through rapid deployment, technological superiority in a specific AI sub-field, and ease of integration.
JPMorgan Chase
As one of the world's largest financial institutions, JPMorgan Chase positions itself strategically as both a developer and adopter of proprietary AI. The firm maintains a significant competitive advantage through its massive proprietary data reservoirs and substantial investment in its AI research teams. Its strategy focuses on integrating AI across its operations, from automating trading strategies to enhancing internal productivity. The 2024 launch of its proprietary LLM Suite for employees, for instance, underscores its dedication to transforming internal knowledge management and software development, using AI to increase developer efficiency and provide instantaneous access to internal knowledge bases, securing a significant competitive moat in operational alpha.
Upstart Holdings
Upstart Holdings operates as a leading AI lending marketplace, distinct from traditional financial institutions. Its strategic positioning hinges entirely on the superiority and explainability of its proprietary AI model, which uses over 1,600 variables, including educational and employment data, to assess credit risk more accurately than traditional models. This model allows its partner banks and credit unions to approve more borrowers at lower annualized percentage rates, particularly for those with thin credit files, which directly addresses the market's demand for greater financial inclusion. Upstart's business model, which primarily generates fee revenue from referral and servicing, aligns its success directly with the performance and continued refinement of its core AI engine.
US AI in Finance Market Recent Developments:
- May 2025: Upstart announced a forward-flow commitment of $1.2 billion from funds managed by affiliates of Fortress Investment Group LLC. This agreement is a capacity addition development, providing funding stability for a significant volume of loans originated through Upstart’s AI lending platform. It demonstrates sustained institutional investor confidence in the performance and risk-assessment accuracy of Upstart’s proprietary AI models in the consumer lending market, solidifying the demand for its AI-driven financial products.
- August 2024: JPMorgan Chase officially launched its internal LLM Suite, a proprietary generative AI platform for its employees across the firm. This product launch serves as an internal knowledge base, assists with content generation, and facilitates querying on specific corporate documents and presentations. The development signifies a major internal capacity addition aimed at enhancing employee productivity and accelerating software development processes through AI-assisted coding, directly impacting the middle and back office segments of the firm’s operations.
US AI in Finance Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 19.915 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 43.812 billion |
| Growth Rate | 17.08% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Type, Deployment Model, User, Application |
| Companies |
|
US AI in Finance Market Segmentation:
- BY TYPE
- Natural Language Processing
- Large Language Models
- Sentiment analysis
- Image recognition
- Others
- BY DEPLOYMENT MODEL
- On-Premise
- Cloud
- BY USER
- Personal Finance
- Consumer Finance
- Corporate Finance
- BY APPLICATION
- Back Office
- Middle office
- Front Office