The Essential Guide to Sunscreen: Protecting Your Skin From Harmful UV Rays

The sunscreen market is witnessing significant growth worldwide as consumers become increasingly aware of the importance of protecting their skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. Sunscreens play a crucial role in preventing sunburns, premature aging, and skin cancer, making them an essential part of daily skincare routines. In this article, we will explore the latest trends, innovations, and consumer preferences shaping the sunscreen market.
Sunscreen is not just a summertime essential; it's a year-round necessity for maintaining healthy skin. As we soak in the warmth of the sun's rays, it's crucial to shield our skin from the damaging effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the importance of sunscreen, how it works, tips for choosing the right sunscreen, proper application techniques, and dispelling common myths surrounding its use. By understanding the significance of sunscreen and adopting proper sun protection practices, we can safeguard our skin against sunburns, premature aging, and the risk of skin cancer.
Skin cancer stands as the prevailing form of cancer in the United States, with current statistics suggesting that one out of every five Americans will experience a skin cancer diagnosis in their lifetime. Each day, an estimated 9,500 individuals in the U.S. receive a skin cancer diagnosis, underscoring the widespread impact of this disease. Research indicates that nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), encompassing basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), affects over 3 million Americans annually. Over 1 million individuals in the United States are currently coping with melanoma. It was anticipated that 197,700 new instances of melanoma emerged in the U.S. during 2022, comprising 97,920 cases classified as noninvasive (in situ) and 99,780 deemed invasive. Invasive melanoma is forecasted to rank as the fifth most frequently diagnosed cancer for both males, with 57,180 cases, and females, with 42,600 cases, in the year 2022.
Figure 1: Number of Cases of Invasive Melanoma in the USA, in 2022
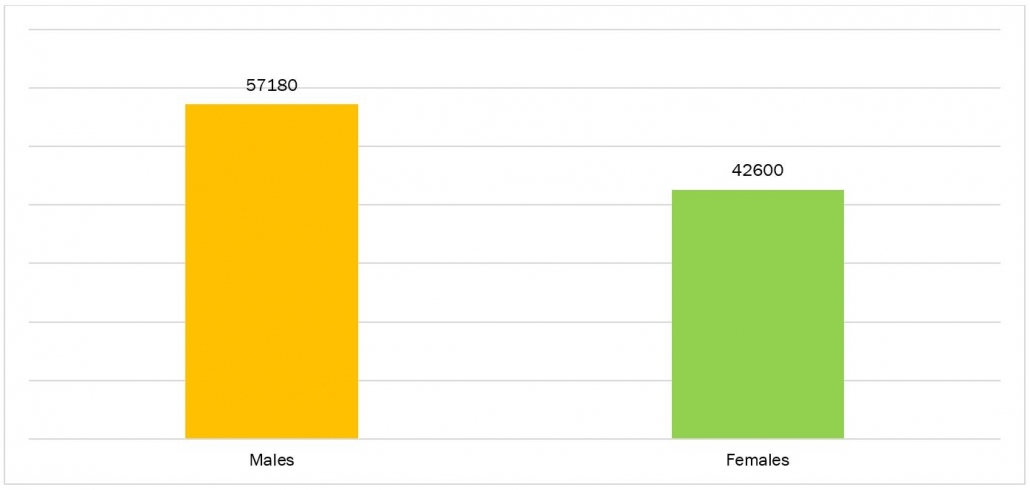 Source: American Academy of Dermatology Association
In Canada, over 80,000 instances of skin cancer are identified annually. This significant number underscores the urgency of adopting preventive measures against this pervasive health concern. Given that exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation is linked to approximately 80% to 90% of skin cancer cases, the importance of sunscreen in blocking UV radiation is heavily emphasized.
Figure 2: Percentage of Skin Cancer Cases in Canada
Source: American Academy of Dermatology Association
In Canada, over 80,000 instances of skin cancer are identified annually. This significant number underscores the urgency of adopting preventive measures against this pervasive health concern. Given that exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation is linked to approximately 80% to 90% of skin cancer cases, the importance of sunscreen in blocking UV radiation is heavily emphasized.
Figure 2: Percentage of Skin Cancer Cases in Canada
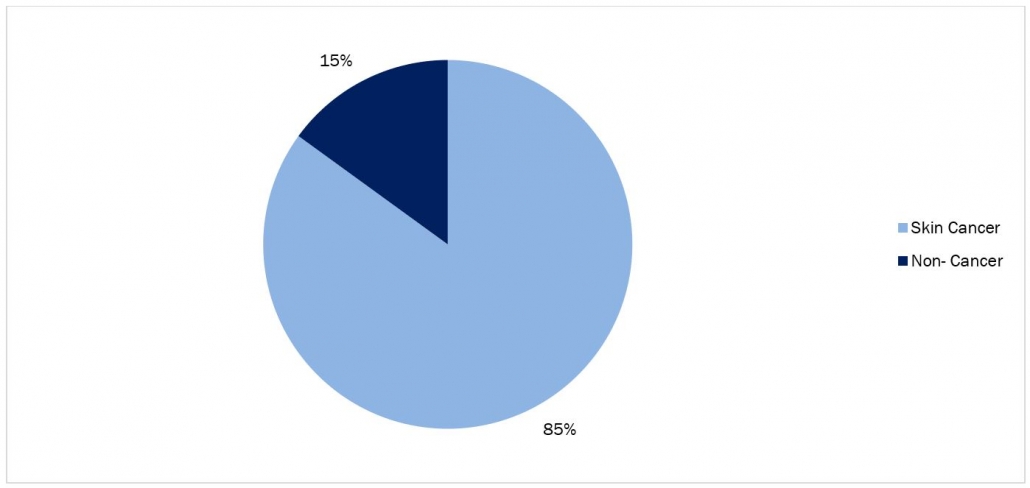 Source: PubMed Central
Sunscreen serves as a pivotal tool in not only preventing skin cancers but also in reducing the incidence of sunburns and skin photoaging. By shielding the skin from harmful UV rays, sunscreen plays a crucial role in safeguarding individuals from the adverse effects of sun exposure, promoting overall skin health and well-being. It serves as a cornerstone in comprehensive sun protection strategies, alongside other preventive measures such as seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and limiting outdoor activities during peak sun hours.
The sun emits two types of harmful UV radiation: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin, leading to premature aging, while UVB rays primarily cause sunburns and contribute to the development of skin cancer. Sunscreen is a barrier between our skin and these harmful rays, reducing our risk of sun damage and long-term skin issues. By applying sunscreen daily, we can significantly lower our chances of developing skin cancer, including melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
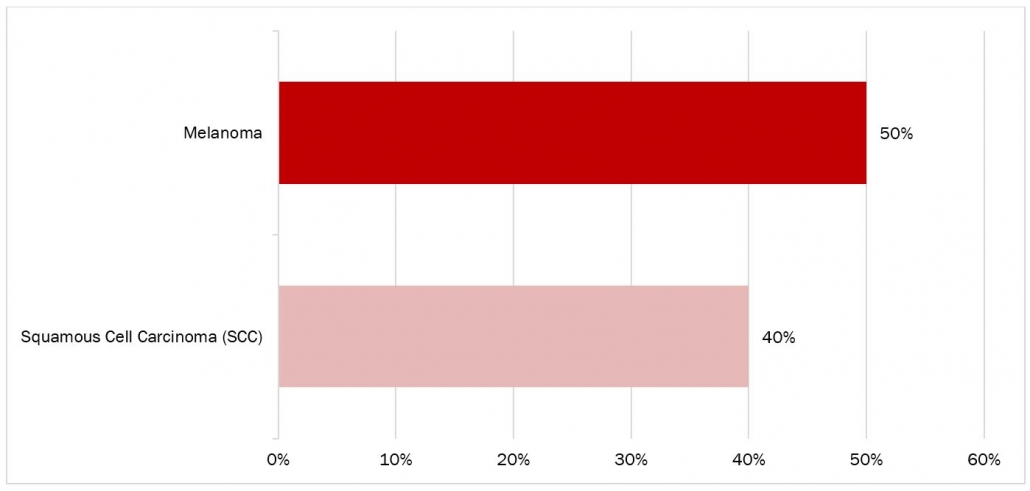
Research indicates that consistently applying SPF 15 sunscreen every day, following the recommended guidelines, can significantly decrease the likelihood of developing squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) by approximately 40 percent. Moreover, it can also reduce the risk of melanoma, a more aggressive form of skin cancer, by as much as 50 percent. These findings underscore the importance of incorporating sunscreen into daily skincare routines as a proactive measure against skin cancer. By diligently applying sunscreen with at least SPF 15, individuals can substantially mitigate their risk of both SCC and melanoma, promoting long-term skin health and well-being.
Figure 3: Percentage of Reduction in the Risk of Development of SCC and Melanoma by the Use of Sunscreen
Source: PubMed Central
Sunscreen serves as a pivotal tool in not only preventing skin cancers but also in reducing the incidence of sunburns and skin photoaging. By shielding the skin from harmful UV rays, sunscreen plays a crucial role in safeguarding individuals from the adverse effects of sun exposure, promoting overall skin health and well-being. It serves as a cornerstone in comprehensive sun protection strategies, alongside other preventive measures such as seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and limiting outdoor activities during peak sun hours.
The sun emits two types of harmful UV radiation: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin, leading to premature aging, while UVB rays primarily cause sunburns and contribute to the development of skin cancer. Sunscreen is a barrier between our skin and these harmful rays, reducing our risk of sun damage and long-term skin issues. By applying sunscreen daily, we can significantly lower our chances of developing skin cancer, including melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
Research indicates that consistently applying SPF 15 sunscreen every day, following the recommended guidelines, can significantly decrease the likelihood of developing squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) by approximately 40 percent. Moreover, it can also reduce the risk of melanoma, a more aggressive form of skin cancer, by as much as 50 percent. These findings underscore the importance of incorporating sunscreen into daily skincare routines as a proactive measure against skin cancer. By diligently applying sunscreen with at least SPF 15, individuals can substantially mitigate their risk of both SCC and melanoma, promoting long-term skin health and well-being.
Figure 3: Percentage of Reduction in the Risk of Development of SCC and Melanoma by the Use of Sunscreen
 Source: PubMed Central
Sunscreen works by absorbing, reflecting, or scattering UV radiation before penetrating the skin. Chemical (organic) sunscreens contain active ingredients that absorb UV rays, while physical (mineral-based) sunscreens create a protective barrier on the skin's surface, reflecting and scattering UV radiation. Both types of sunscreens offer effective protection, but individuals with sensitive skin may prefer mineral-based sunscreens, as they are less likely to irritate.
Selecting the right sunscreen is essential for ensuring adequate protection against UV radiation. When choosing a sunscreen, consider factors such as skin type, SPF rating, and broad-spectrum protection against both UVA and UVB rays. Individuals with fair or sensitive skin may benefit from higher SPF ratings, while those with darker skin tones should still opt for sunscreen to prevent long-term damage. Additionally, look for water-resistant formulas, fragrance-free options, and non-comedogenic formulations if you have acne-prone or sensitive skin.
The American Academy of Dermatology advises the consistent application of sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher for individuals of all skin types, despite the higher incidence of skin cancers among White individuals compared to those with darker skin tones. However, there is a lack of research assessing the efficacy of regular sunscreen use in reducing skin cancer risk among non-White populations. For children older than 6 months and adults, the Canadian Dermatology Association recommends the use of broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or higher. Studies comparing sunscreens with SPF 100 to those with SPF 50 have demonstrated the superiority of the former in preventing sunburns in real-world settings, including beach and high-altitude skiing environments.
Proper application of sunscreen is key to its effectiveness. Apply sunscreen generously to all exposed skin areas, including the face, neck, ears, and hands, at least 15 minutes before sun exposure. Don't forget often overlooked areas like the lips, scalp, and tops of feet. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if swimming, sweating, or engaging in activities that cause sunscreen to wear off. Remember, no sunscreen offers 100% protection, so it's crucial to combine sunscreen use with other sun protection measures, such as seeking shade and wearing protective clothing.
Despite the widespread use of sunscreen, many myths persist surrounding its effectiveness and safety. One common misconception is that sunscreen is unnecessary on cloudy days. However, UV radiation can penetrate clouds, so sunscreen is still essential even when it's overcast. Additionally, some people believe that a "base tan" offers protection against sunburns, but this is untrue. Any change in skin color indicates damage from UV radiation. Another myth is that higher SPF ratings provide significantly more protection than lower ones. While higher SPF ratings do offer slightly more protection, no sunscreen can block all UV rays completely.
Safety concerns regarding sunscreen often revolve around its chemical ingredients. However, extensive research supports the safety and efficacy of sunscreen in protecting against sun damage and skin cancer. The benefits of using sunscreen far outweigh any potential risks associated with its chemical ingredients. Nevertheless, individuals concerned about chemical ingredients may opt for mineral-based sunscreens, which contain zinc oxide or titanium dioxide and provide effective protection without chemical additives. Ultimately, sunscreen should be viewed as an essential component of a comprehensive sun protection strategy, alongside protective clothing, hats, and seeking shade during peak sun hours.
The prevalent adverse reactions associated with sunscreens typically involve subjective discomfort such as stinging and burning sensations without visible rash, as well as irritant contact dermatitis and the potential for clogging pores. In rare cases, chemical sunscreen components may provoke allergic reactions, including allergic contact dermatitis and photoallergic contact dermatitis. Among the ingredients most frequently linked to these allergic reactions are octocrylene, oxybenzone, and octyl methoxycinnamate.
Key Developments
In September 2023, BASF introduces TinomaxTM CC, a novel sunscreen ingredient catering to the rising need for versatile solutions featuring enhanced SPF and UVA protection. TinomaxTM CC addresses customers' increasing demand for multifunctional products while offering improved sensory perception due to its homogeneous particle shape. Moreover, the product profile aligns with customers' sustainability objectives, further enhancing its appeal in the market.
In January 2023, Beiersdorf's research and development department, the team behind the NIVEA brand, utilized their extensive knowledge of skin and research capabilities to create a customized cosmetic sunscreen product for Charlotte, a young girl with a rare light condition known as EPP. Through research findings on visible, high-energy light, it was determined that the cosmetic sunscreen needed to incorporate special light-scattering pigments to prevent light penetration into Charlotte's skin. This adaptation allowed Charlotte to safely enjoy brief periods of sunlight exposure, ultimately improving her quality of life.
In 2023, La Roche-Posay continued its partnership as the exclusive Official Sunscreen Partner of the US Open for the second consecutive year. Individuals who played outdoor sports experienced significantly higher exposure to ultraviolet radiation, thereby increasing their risk of skin cancer.
In May 2022, L'Oréal, a cosmetics company, unveiled a new UV filtering technology, heralding it as the most significant breakthrough in sun care over the last three decades. Named UVMune 400, this innovation aims to provide efficient protection against ultra-long UVA radiation, which constitutes 30% of previously unfiltered sun rays. The first brand under the L'Oréal umbrella to incorporate this technology into its product range is La Roche-Posay's Anthelios franchise.
In May 2022, Eucerin, a skincare brand under Beiersdorf, revealed its plans to enter the sun protection market in the United States with the introduction of its Eucerin Sun line. The Eucerin sun care range features a holistic antioxidant complex comprising five active components, aiming not only to provide sun protection but also to enhance the appearance of skin health.
In February 2022, Beiersdorf established an innovation center in the United States to expedite local innovation and establish itself as the primary hub for excellence in therapeutic over-the-counter (OTC) and sun care products.
In conclusion, sunscreen is a vital tool for protecting our skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. By incorporating sunscreen into our daily skincare routines and following proper application techniques, we can significantly reduce our risk of sunburns, premature aging, and skin cancer. Remember to choose a sunscreen that suits your skin type, apply it generously and regularly, and combine its use with other sun protection measures for optimal skin health. With the right precautions, we can enjoy the sun safely and maintain healthy, radiant skin for years to come.
Source: PubMed Central
Sunscreen works by absorbing, reflecting, or scattering UV radiation before penetrating the skin. Chemical (organic) sunscreens contain active ingredients that absorb UV rays, while physical (mineral-based) sunscreens create a protective barrier on the skin's surface, reflecting and scattering UV radiation. Both types of sunscreens offer effective protection, but individuals with sensitive skin may prefer mineral-based sunscreens, as they are less likely to irritate.
Selecting the right sunscreen is essential for ensuring adequate protection against UV radiation. When choosing a sunscreen, consider factors such as skin type, SPF rating, and broad-spectrum protection against both UVA and UVB rays. Individuals with fair or sensitive skin may benefit from higher SPF ratings, while those with darker skin tones should still opt for sunscreen to prevent long-term damage. Additionally, look for water-resistant formulas, fragrance-free options, and non-comedogenic formulations if you have acne-prone or sensitive skin.
The American Academy of Dermatology advises the consistent application of sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher for individuals of all skin types, despite the higher incidence of skin cancers among White individuals compared to those with darker skin tones. However, there is a lack of research assessing the efficacy of regular sunscreen use in reducing skin cancer risk among non-White populations. For children older than 6 months and adults, the Canadian Dermatology Association recommends the use of broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or higher. Studies comparing sunscreens with SPF 100 to those with SPF 50 have demonstrated the superiority of the former in preventing sunburns in real-world settings, including beach and high-altitude skiing environments.
Proper application of sunscreen is key to its effectiveness. Apply sunscreen generously to all exposed skin areas, including the face, neck, ears, and hands, at least 15 minutes before sun exposure. Don't forget often overlooked areas like the lips, scalp, and tops of feet. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if swimming, sweating, or engaging in activities that cause sunscreen to wear off. Remember, no sunscreen offers 100% protection, so it's crucial to combine sunscreen use with other sun protection measures, such as seeking shade and wearing protective clothing.
Despite the widespread use of sunscreen, many myths persist surrounding its effectiveness and safety. One common misconception is that sunscreen is unnecessary on cloudy days. However, UV radiation can penetrate clouds, so sunscreen is still essential even when it's overcast. Additionally, some people believe that a "base tan" offers protection against sunburns, but this is untrue. Any change in skin color indicates damage from UV radiation. Another myth is that higher SPF ratings provide significantly more protection than lower ones. While higher SPF ratings do offer slightly more protection, no sunscreen can block all UV rays completely.
Safety concerns regarding sunscreen often revolve around its chemical ingredients. However, extensive research supports the safety and efficacy of sunscreen in protecting against sun damage and skin cancer. The benefits of using sunscreen far outweigh any potential risks associated with its chemical ingredients. Nevertheless, individuals concerned about chemical ingredients may opt for mineral-based sunscreens, which contain zinc oxide or titanium dioxide and provide effective protection without chemical additives. Ultimately, sunscreen should be viewed as an essential component of a comprehensive sun protection strategy, alongside protective clothing, hats, and seeking shade during peak sun hours.
The prevalent adverse reactions associated with sunscreens typically involve subjective discomfort such as stinging and burning sensations without visible rash, as well as irritant contact dermatitis and the potential for clogging pores. In rare cases, chemical sunscreen components may provoke allergic reactions, including allergic contact dermatitis and photoallergic contact dermatitis. Among the ingredients most frequently linked to these allergic reactions are octocrylene, oxybenzone, and octyl methoxycinnamate.
Key Developments
In September 2023, BASF introduces TinomaxTM CC, a novel sunscreen ingredient catering to the rising need for versatile solutions featuring enhanced SPF and UVA protection. TinomaxTM CC addresses customers' increasing demand for multifunctional products while offering improved sensory perception due to its homogeneous particle shape. Moreover, the product profile aligns with customers' sustainability objectives, further enhancing its appeal in the market.
In January 2023, Beiersdorf's research and development department, the team behind the NIVEA brand, utilized their extensive knowledge of skin and research capabilities to create a customized cosmetic sunscreen product for Charlotte, a young girl with a rare light condition known as EPP. Through research findings on visible, high-energy light, it was determined that the cosmetic sunscreen needed to incorporate special light-scattering pigments to prevent light penetration into Charlotte's skin. This adaptation allowed Charlotte to safely enjoy brief periods of sunlight exposure, ultimately improving her quality of life.
In 2023, La Roche-Posay continued its partnership as the exclusive Official Sunscreen Partner of the US Open for the second consecutive year. Individuals who played outdoor sports experienced significantly higher exposure to ultraviolet radiation, thereby increasing their risk of skin cancer.
In May 2022, L'Oréal, a cosmetics company, unveiled a new UV filtering technology, heralding it as the most significant breakthrough in sun care over the last three decades. Named UVMune 400, this innovation aims to provide efficient protection against ultra-long UVA radiation, which constitutes 30% of previously unfiltered sun rays. The first brand under the L'Oréal umbrella to incorporate this technology into its product range is La Roche-Posay's Anthelios franchise.
In May 2022, Eucerin, a skincare brand under Beiersdorf, revealed its plans to enter the sun protection market in the United States with the introduction of its Eucerin Sun line. The Eucerin sun care range features a holistic antioxidant complex comprising five active components, aiming not only to provide sun protection but also to enhance the appearance of skin health.
In February 2022, Beiersdorf established an innovation center in the United States to expedite local innovation and establish itself as the primary hub for excellence in therapeutic over-the-counter (OTC) and sun care products.
In conclusion, sunscreen is a vital tool for protecting our skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. By incorporating sunscreen into our daily skincare routines and following proper application techniques, we can significantly reduce our risk of sunburns, premature aging, and skin cancer. Remember to choose a sunscreen that suits your skin type, apply it generously and regularly, and combine its use with other sun protection measures for optimal skin health. With the right precautions, we can enjoy the sun safely and maintain healthy, radiant skin for years to come.
 Source: American Academy of Dermatology Association
In Canada, over 80,000 instances of skin cancer are identified annually. This significant number underscores the urgency of adopting preventive measures against this pervasive health concern. Given that exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation is linked to approximately 80% to 90% of skin cancer cases, the importance of sunscreen in blocking UV radiation is heavily emphasized.
Figure 2: Percentage of Skin Cancer Cases in Canada
Source: American Academy of Dermatology Association
In Canada, over 80,000 instances of skin cancer are identified annually. This significant number underscores the urgency of adopting preventive measures against this pervasive health concern. Given that exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation is linked to approximately 80% to 90% of skin cancer cases, the importance of sunscreen in blocking UV radiation is heavily emphasized.
Figure 2: Percentage of Skin Cancer Cases in Canada
 Source: PubMed Central
Sunscreen serves as a pivotal tool in not only preventing skin cancers but also in reducing the incidence of sunburns and skin photoaging. By shielding the skin from harmful UV rays, sunscreen plays a crucial role in safeguarding individuals from the adverse effects of sun exposure, promoting overall skin health and well-being. It serves as a cornerstone in comprehensive sun protection strategies, alongside other preventive measures such as seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and limiting outdoor activities during peak sun hours.
The sun emits two types of harmful UV radiation: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin, leading to premature aging, while UVB rays primarily cause sunburns and contribute to the development of skin cancer. Sunscreen is a barrier between our skin and these harmful rays, reducing our risk of sun damage and long-term skin issues. By applying sunscreen daily, we can significantly lower our chances of developing skin cancer, including melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
Research indicates that consistently applying SPF 15 sunscreen every day, following the recommended guidelines, can significantly decrease the likelihood of developing squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) by approximately 40 percent. Moreover, it can also reduce the risk of melanoma, a more aggressive form of skin cancer, by as much as 50 percent. These findings underscore the importance of incorporating sunscreen into daily skincare routines as a proactive measure against skin cancer. By diligently applying sunscreen with at least SPF 15, individuals can substantially mitigate their risk of both SCC and melanoma, promoting long-term skin health and well-being.
Figure 3: Percentage of Reduction in the Risk of Development of SCC and Melanoma by the Use of Sunscreen
Source: PubMed Central
Sunscreen serves as a pivotal tool in not only preventing skin cancers but also in reducing the incidence of sunburns and skin photoaging. By shielding the skin from harmful UV rays, sunscreen plays a crucial role in safeguarding individuals from the adverse effects of sun exposure, promoting overall skin health and well-being. It serves as a cornerstone in comprehensive sun protection strategies, alongside other preventive measures such as seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and limiting outdoor activities during peak sun hours.
The sun emits two types of harmful UV radiation: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin, leading to premature aging, while UVB rays primarily cause sunburns and contribute to the development of skin cancer. Sunscreen is a barrier between our skin and these harmful rays, reducing our risk of sun damage and long-term skin issues. By applying sunscreen daily, we can significantly lower our chances of developing skin cancer, including melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
Research indicates that consistently applying SPF 15 sunscreen every day, following the recommended guidelines, can significantly decrease the likelihood of developing squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) by approximately 40 percent. Moreover, it can also reduce the risk of melanoma, a more aggressive form of skin cancer, by as much as 50 percent. These findings underscore the importance of incorporating sunscreen into daily skincare routines as a proactive measure against skin cancer. By diligently applying sunscreen with at least SPF 15, individuals can substantially mitigate their risk of both SCC and melanoma, promoting long-term skin health and well-being.
Figure 3: Percentage of Reduction in the Risk of Development of SCC and Melanoma by the Use of Sunscreen
 Source: PubMed Central
Sunscreen works by absorbing, reflecting, or scattering UV radiation before penetrating the skin. Chemical (organic) sunscreens contain active ingredients that absorb UV rays, while physical (mineral-based) sunscreens create a protective barrier on the skin's surface, reflecting and scattering UV radiation. Both types of sunscreens offer effective protection, but individuals with sensitive skin may prefer mineral-based sunscreens, as they are less likely to irritate.
Selecting the right sunscreen is essential for ensuring adequate protection against UV radiation. When choosing a sunscreen, consider factors such as skin type, SPF rating, and broad-spectrum protection against both UVA and UVB rays. Individuals with fair or sensitive skin may benefit from higher SPF ratings, while those with darker skin tones should still opt for sunscreen to prevent long-term damage. Additionally, look for water-resistant formulas, fragrance-free options, and non-comedogenic formulations if you have acne-prone or sensitive skin.
The American Academy of Dermatology advises the consistent application of sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher for individuals of all skin types, despite the higher incidence of skin cancers among White individuals compared to those with darker skin tones. However, there is a lack of research assessing the efficacy of regular sunscreen use in reducing skin cancer risk among non-White populations. For children older than 6 months and adults, the Canadian Dermatology Association recommends the use of broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or higher. Studies comparing sunscreens with SPF 100 to those with SPF 50 have demonstrated the superiority of the former in preventing sunburns in real-world settings, including beach and high-altitude skiing environments.
Proper application of sunscreen is key to its effectiveness. Apply sunscreen generously to all exposed skin areas, including the face, neck, ears, and hands, at least 15 minutes before sun exposure. Don't forget often overlooked areas like the lips, scalp, and tops of feet. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if swimming, sweating, or engaging in activities that cause sunscreen to wear off. Remember, no sunscreen offers 100% protection, so it's crucial to combine sunscreen use with other sun protection measures, such as seeking shade and wearing protective clothing.
Despite the widespread use of sunscreen, many myths persist surrounding its effectiveness and safety. One common misconception is that sunscreen is unnecessary on cloudy days. However, UV radiation can penetrate clouds, so sunscreen is still essential even when it's overcast. Additionally, some people believe that a "base tan" offers protection against sunburns, but this is untrue. Any change in skin color indicates damage from UV radiation. Another myth is that higher SPF ratings provide significantly more protection than lower ones. While higher SPF ratings do offer slightly more protection, no sunscreen can block all UV rays completely.
Safety concerns regarding sunscreen often revolve around its chemical ingredients. However, extensive research supports the safety and efficacy of sunscreen in protecting against sun damage and skin cancer. The benefits of using sunscreen far outweigh any potential risks associated with its chemical ingredients. Nevertheless, individuals concerned about chemical ingredients may opt for mineral-based sunscreens, which contain zinc oxide or titanium dioxide and provide effective protection without chemical additives. Ultimately, sunscreen should be viewed as an essential component of a comprehensive sun protection strategy, alongside protective clothing, hats, and seeking shade during peak sun hours.
The prevalent adverse reactions associated with sunscreens typically involve subjective discomfort such as stinging and burning sensations without visible rash, as well as irritant contact dermatitis and the potential for clogging pores. In rare cases, chemical sunscreen components may provoke allergic reactions, including allergic contact dermatitis and photoallergic contact dermatitis. Among the ingredients most frequently linked to these allergic reactions are octocrylene, oxybenzone, and octyl methoxycinnamate.
Key Developments
In September 2023, BASF introduces TinomaxTM CC, a novel sunscreen ingredient catering to the rising need for versatile solutions featuring enhanced SPF and UVA protection. TinomaxTM CC addresses customers' increasing demand for multifunctional products while offering improved sensory perception due to its homogeneous particle shape. Moreover, the product profile aligns with customers' sustainability objectives, further enhancing its appeal in the market.
In January 2023, Beiersdorf's research and development department, the team behind the NIVEA brand, utilized their extensive knowledge of skin and research capabilities to create a customized cosmetic sunscreen product for Charlotte, a young girl with a rare light condition known as EPP. Through research findings on visible, high-energy light, it was determined that the cosmetic sunscreen needed to incorporate special light-scattering pigments to prevent light penetration into Charlotte's skin. This adaptation allowed Charlotte to safely enjoy brief periods of sunlight exposure, ultimately improving her quality of life.
In 2023, La Roche-Posay continued its partnership as the exclusive Official Sunscreen Partner of the US Open for the second consecutive year. Individuals who played outdoor sports experienced significantly higher exposure to ultraviolet radiation, thereby increasing their risk of skin cancer.
In May 2022, L'Oréal, a cosmetics company, unveiled a new UV filtering technology, heralding it as the most significant breakthrough in sun care over the last three decades. Named UVMune 400, this innovation aims to provide efficient protection against ultra-long UVA radiation, which constitutes 30% of previously unfiltered sun rays. The first brand under the L'Oréal umbrella to incorporate this technology into its product range is La Roche-Posay's Anthelios franchise.
In May 2022, Eucerin, a skincare brand under Beiersdorf, revealed its plans to enter the sun protection market in the United States with the introduction of its Eucerin Sun line. The Eucerin sun care range features a holistic antioxidant complex comprising five active components, aiming not only to provide sun protection but also to enhance the appearance of skin health.
In February 2022, Beiersdorf established an innovation center in the United States to expedite local innovation and establish itself as the primary hub for excellence in therapeutic over-the-counter (OTC) and sun care products.
In conclusion, sunscreen is a vital tool for protecting our skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. By incorporating sunscreen into our daily skincare routines and following proper application techniques, we can significantly reduce our risk of sunburns, premature aging, and skin cancer. Remember to choose a sunscreen that suits your skin type, apply it generously and regularly, and combine its use with other sun protection measures for optimal skin health. With the right precautions, we can enjoy the sun safely and maintain healthy, radiant skin for years to come.
Source: PubMed Central
Sunscreen works by absorbing, reflecting, or scattering UV radiation before penetrating the skin. Chemical (organic) sunscreens contain active ingredients that absorb UV rays, while physical (mineral-based) sunscreens create a protective barrier on the skin's surface, reflecting and scattering UV radiation. Both types of sunscreens offer effective protection, but individuals with sensitive skin may prefer mineral-based sunscreens, as they are less likely to irritate.
Selecting the right sunscreen is essential for ensuring adequate protection against UV radiation. When choosing a sunscreen, consider factors such as skin type, SPF rating, and broad-spectrum protection against both UVA and UVB rays. Individuals with fair or sensitive skin may benefit from higher SPF ratings, while those with darker skin tones should still opt for sunscreen to prevent long-term damage. Additionally, look for water-resistant formulas, fragrance-free options, and non-comedogenic formulations if you have acne-prone or sensitive skin.
The American Academy of Dermatology advises the consistent application of sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher for individuals of all skin types, despite the higher incidence of skin cancers among White individuals compared to those with darker skin tones. However, there is a lack of research assessing the efficacy of regular sunscreen use in reducing skin cancer risk among non-White populations. For children older than 6 months and adults, the Canadian Dermatology Association recommends the use of broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or higher. Studies comparing sunscreens with SPF 100 to those with SPF 50 have demonstrated the superiority of the former in preventing sunburns in real-world settings, including beach and high-altitude skiing environments.
Proper application of sunscreen is key to its effectiveness. Apply sunscreen generously to all exposed skin areas, including the face, neck, ears, and hands, at least 15 minutes before sun exposure. Don't forget often overlooked areas like the lips, scalp, and tops of feet. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if swimming, sweating, or engaging in activities that cause sunscreen to wear off. Remember, no sunscreen offers 100% protection, so it's crucial to combine sunscreen use with other sun protection measures, such as seeking shade and wearing protective clothing.
Despite the widespread use of sunscreen, many myths persist surrounding its effectiveness and safety. One common misconception is that sunscreen is unnecessary on cloudy days. However, UV radiation can penetrate clouds, so sunscreen is still essential even when it's overcast. Additionally, some people believe that a "base tan" offers protection against sunburns, but this is untrue. Any change in skin color indicates damage from UV radiation. Another myth is that higher SPF ratings provide significantly more protection than lower ones. While higher SPF ratings do offer slightly more protection, no sunscreen can block all UV rays completely.
Safety concerns regarding sunscreen often revolve around its chemical ingredients. However, extensive research supports the safety and efficacy of sunscreen in protecting against sun damage and skin cancer. The benefits of using sunscreen far outweigh any potential risks associated with its chemical ingredients. Nevertheless, individuals concerned about chemical ingredients may opt for mineral-based sunscreens, which contain zinc oxide or titanium dioxide and provide effective protection without chemical additives. Ultimately, sunscreen should be viewed as an essential component of a comprehensive sun protection strategy, alongside protective clothing, hats, and seeking shade during peak sun hours.
The prevalent adverse reactions associated with sunscreens typically involve subjective discomfort such as stinging and burning sensations without visible rash, as well as irritant contact dermatitis and the potential for clogging pores. In rare cases, chemical sunscreen components may provoke allergic reactions, including allergic contact dermatitis and photoallergic contact dermatitis. Among the ingredients most frequently linked to these allergic reactions are octocrylene, oxybenzone, and octyl methoxycinnamate.
Key Developments
In September 2023, BASF introduces TinomaxTM CC, a novel sunscreen ingredient catering to the rising need for versatile solutions featuring enhanced SPF and UVA protection. TinomaxTM CC addresses customers' increasing demand for multifunctional products while offering improved sensory perception due to its homogeneous particle shape. Moreover, the product profile aligns with customers' sustainability objectives, further enhancing its appeal in the market.
In January 2023, Beiersdorf's research and development department, the team behind the NIVEA brand, utilized their extensive knowledge of skin and research capabilities to create a customized cosmetic sunscreen product for Charlotte, a young girl with a rare light condition known as EPP. Through research findings on visible, high-energy light, it was determined that the cosmetic sunscreen needed to incorporate special light-scattering pigments to prevent light penetration into Charlotte's skin. This adaptation allowed Charlotte to safely enjoy brief periods of sunlight exposure, ultimately improving her quality of life.
In 2023, La Roche-Posay continued its partnership as the exclusive Official Sunscreen Partner of the US Open for the second consecutive year. Individuals who played outdoor sports experienced significantly higher exposure to ultraviolet radiation, thereby increasing their risk of skin cancer.
In May 2022, L'Oréal, a cosmetics company, unveiled a new UV filtering technology, heralding it as the most significant breakthrough in sun care over the last three decades. Named UVMune 400, this innovation aims to provide efficient protection against ultra-long UVA radiation, which constitutes 30% of previously unfiltered sun rays. The first brand under the L'Oréal umbrella to incorporate this technology into its product range is La Roche-Posay's Anthelios franchise.
In May 2022, Eucerin, a skincare brand under Beiersdorf, revealed its plans to enter the sun protection market in the United States with the introduction of its Eucerin Sun line. The Eucerin sun care range features a holistic antioxidant complex comprising five active components, aiming not only to provide sun protection but also to enhance the appearance of skin health.
In February 2022, Beiersdorf established an innovation center in the United States to expedite local innovation and establish itself as the primary hub for excellence in therapeutic over-the-counter (OTC) and sun care products.
In conclusion, sunscreen is a vital tool for protecting our skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. By incorporating sunscreen into our daily skincare routines and following proper application techniques, we can significantly reduce our risk of sunburns, premature aging, and skin cancer. Remember to choose a sunscreen that suits your skin type, apply it generously and regularly, and combine its use with other sun protection measures for optimal skin health. With the right precautions, we can enjoy the sun safely and maintain healthy, radiant skin for years to come.Get in Touch
Interested in this topic? Contact our analysts for more details.
Latest Thought Articles

Top OSAT Companies Driving Semiconductor Assembly and Test Services Worldwide
Recently
EV Charging Stations Market Outlook: Smart Charging, Fast Charging, and Regional Expansion
Recently
Future of Corporate Wellness: Global Trends and Regional Outlook
Recently
Regional Breakdown of the Mechanical Keyboard Market: Who Leads and Why?
Recently