Report Overview
Indonesia Electric Commercial Vehicles Highlights
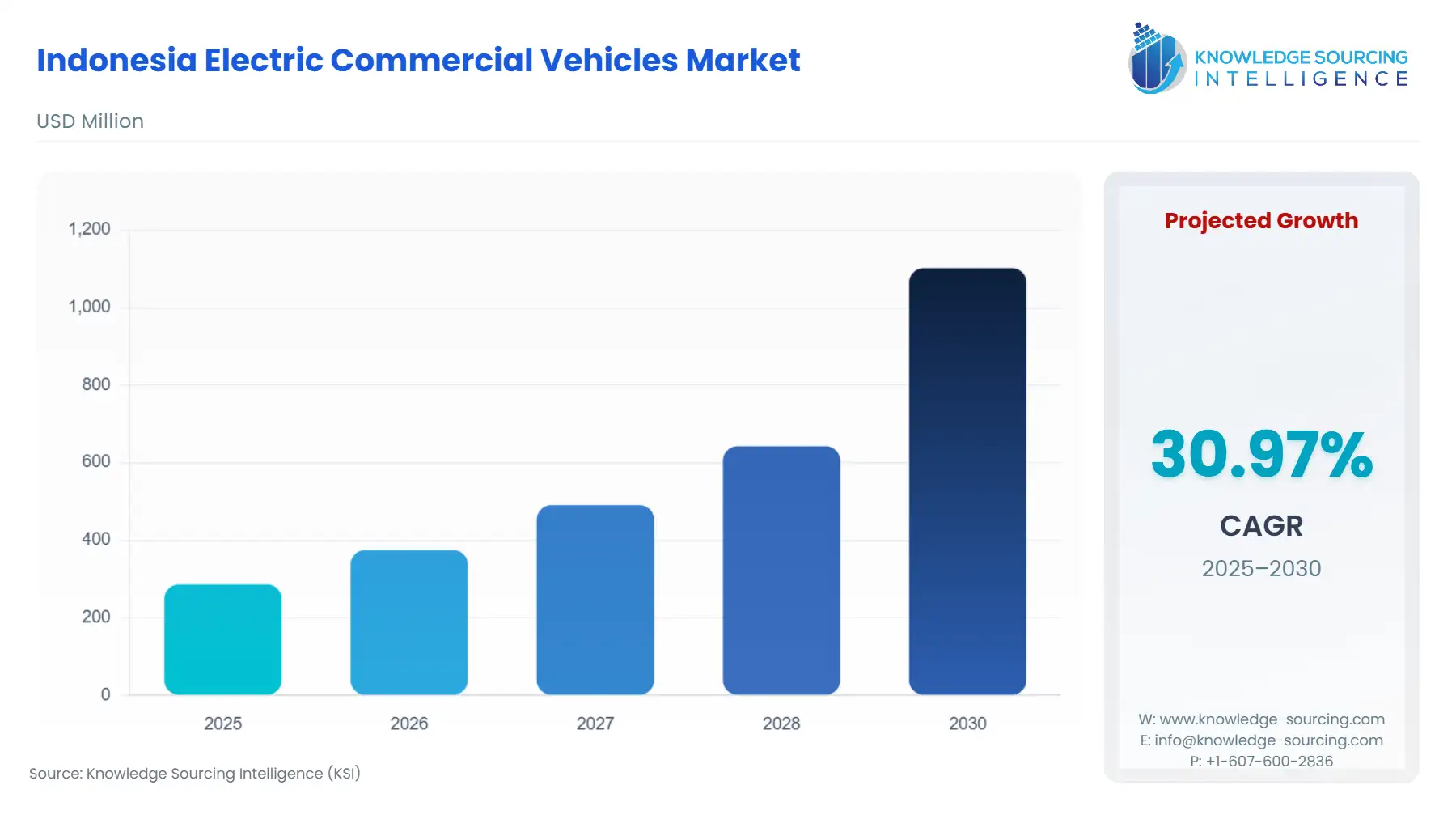
Indonesia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Size:
The Indonesia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 30.97%, reaching USD 1.102 billion in 2030 from USD 0.286 billion in 2025.
The Indonesian Electric Commercial Vehicles (eCV) market is entering a critical inflection point, transitioning from pilot programs and trials to initial commercial deployment, principally catalyzed by targeted government policy. The strategic importance of the sector is underscored by the nation's dual economic and environmental imperative: establishing a world-class domestic battery supply chain leveraging its vast nickel reserves and reducing urban emissions. This confluence of policy stimulus and raw material abundance creates a unique market dynamic, distinct from other Asian markets. While adoption remains in its nascent stage, particularly outside major metropolitan areas, the early market is characterized by assertive commitment from incumbent Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and logistics enterprises focused on achieving corporate sustainability targets and optimizing total cost of ownership (TCO) in highly congested urban environments.
Indonesia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The Indonesian government’s fiscal and non-fiscal incentives are the primary catalyst driving immediate commercial demand. Specifically, the introduction of 0% import duty and the government-borne luxury goods sales tax (PPnBM) for certain four-wheeled BEVs directly lowers the capital expenditure (CapEx) barrier for fleet operators. This reduction in the initial purchasing cost makes the TCO for ECVs—already competitive due to lower operational and maintenance expenses—significantly more attractive than internal combustion engine (ICE) alternatives, directly spurring demand for fleet renewal and expansion. Furthermore, the rapid expansion of the e-commerce sector necessitates high-efficiency, reliable, and sustainable last-mile delivery fleets, accelerating demand for electric vans and light-duty trucks tailored for urban logistics.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge facing the eCV market is the nascent charging infrastructure, particularly for medium- and heavy-duty vehicles outside of the Greater Jakarta area. The limited public and fleet depot charging availability increases range anxiety and complicates route planning, thereby constraining the commercial adoption rate, especially for long-haul logistics. Conversely, this constraint presents a clear opportunity for companies specializing in integrated charging solutions, including mobile charging units and depot-based rapid charging infrastructure. Another critical opportunity arises from the rising global demand for ethical and sustainable supply chains, which incentivizes local manufacturers to develop low-carbon nickel processing, potentially creating a premium-tier domestic supply of battery components that supports high-demand, high-performance BEVs.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
Electric commercial vehicles constitute a physical product market, making raw material dynamics central to long-term pricing and demand stability. Indonesia's position as the world's largest nickel producer is a strategic advantage. The vast supply of domestically mined nickel creates a sustained downward pressure on global nickel prices. Since nickel is a critical, often the most expensive, cathode material in high-performance batteries (NMC/NCA), an abundant domestic supply can significantly reduce the manufacturing cost of locally-produced batteries. This domestic cost advantage allows OEMs to offer more competitively priced eCVs, which in turn directly drives increased market expansion by making the total vehicle acquisition cost lower than in regions relying on imported nickel.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global supply chain for eCVs remains reliant on Asia, with China being the dominant hub for battery cell production. Indonesia’s supply chain is evolving rapidly, driven by the 2020 ban on raw nickel ore exports, which mandated downstream processing. This policy is shifting the supply chain’s value capture from raw material export to refined material and component manufacturing. Key logistical complexities include the high energy intensity and carbon footprint of nickel processing from laterite ore, which creates a tension between the government's industrialization goals and the sustainability objectives of global OEMs. The current dependency is on imported key components, particularly motors, power electronics, and high-purity cathode materials, which poses a supply risk and necessitates substantial future foreign direct investment to achieve a fully integrated, localized supply chain.
Indonesia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
Indonesia |
Presidential Regulation No. 55/2019 (as amended) & MOF Regulations 2024 (e.g., No. 8-10 of 2024) |
Directly lowers the market entry cost for BEVs through 0% import duty, 1% VAT, and exemption from Luxury Goods Sales Tax (PPnBM) for specific criteria, significantly accelerating demand by improving CapEx. |
|
Indonesia |
Domestic Component Level (TKDN) Requirements |
Mandates progressive local content requirements (e.g., up to 80% by 2030), compelling OEMs to invest in local production facilities and component sourcing. This forces a structural shift in demand toward locally-manufactured and assembled vehicles. |
|
Indonesia |
Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources (ESDM) |
Regulates the development of EV charging infrastructure (SPKLU), reducing range anxiety and enhancing operational feasibility for commercial fleets, a critical factor for sustained market growth. |
Indonesia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segment Analysis:
- By Application: Logistics and Transportation
The Logistics and Transportation segment is the primary growth factor for the eCV market in Indonesia. Rapid urbanization and the exponential growth of the e-commerce sector, which generated substantial revenue in 2022, directly translate into an urgent need for efficient, low-emission, and silent delivery vehicles. Electric light-duty trucks and vans are essential for navigating the congested "last-mile" delivery routes in metropolitan areas like Jakarta. The segment is specifically driven by corporate sustainability commitments from major logistics providers and retail companies seeking to lower their Scope 3 emissions. The TCO advantage of BEVs, which feature fewer moving parts, lower fuel costs, and reduced road tax incentives, offers a clear economic incentive for high-utilization commercial fleets, driving consistent demand for Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) platforms. This segment’s expansion is concentrated on vehicles with a power output up to 150 kW, optimized for range and payload within urban constraints.
- By Propulsion Type: Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
The Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) segment dominates the current and projected demand in the Indonesian ECV market. The need for BEVs is overwhelmingly driven by strong government incentives, which are heavily skewed towards fully electric powertrains over Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) or Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs). Fleet operators prioritize BEVs because the zero-tailpipe emission capability is critical for meeting municipal air quality targets and for companies that leverage their green credentials in marketing. Furthermore, Indonesia’s strategic nickel policy, aimed at dominating the global EV battery supply chain, implicitly favours the full BEV platform as the vehicle that maximises domestic value capture. The availability of proven, light-duty BEV models, such as the Mitsubishi Fuso eCanter, has provided fleet managers with verifiable operational data, reducing the perceived risk of adopting a new technology and accelerating fleet conversion cycles.
Indonesia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
The competitive landscape for electric commercial vehicles is currently defined by legacy commercial vehicle incumbents and new entrants, particularly from Asia, leveraging local production strategies. Competition is shifting from technology trials to local assembly and delivery capacity.
- Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation (MFTBC): MFTBC, via its distributor PT Krama Yudha Tiga Berlian Motors (KTB), holds a strategically advantageous position as the FUSO brand’s largest overseas market. MFTBC’s key product, the all-electric light-duty eCanter, is positioned to lead the carbon neutrality shift in the country. Their strategy involves comprehensive customer trials with major logistics providers and the subsequent commencement of sales, initially targeting the Greater Jakarta area. The eCanter's market positioning is bolstered by its extensive global track record, with over 12 million kilometers of on-road use, which serves to lower the adoption risk for Indonesian fleet operators.
- Hino Motors, Ltd.: A major incumbent in the Indonesian commercial vehicle market, Hino Motors is strategically focused on global carbon neutrality. The company’s focus on electric platforms is evidenced by its announcement to display the Hino Dutro Z EV at international mobility shows, signalling a clear intent to transition its popular light-duty truck range to electric power. Hino's core strength lies in its established, nationwide dealer network and deep integration with existing Indonesian commercial vehicle operators, allowing for an efficient rollout and support system for new electric models.
Indonesia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Developments:
- July 2024: Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation Begins Sales and Delivers First eCanter Unit
MFTBC, through its local partner, commenced sales of the light-duty electric eCanter in Indonesia and handed over the first unit to customer PT Yusen Logistics Indonesia. The launch followed extensive local trials and positioned the eCanter, which features an M-sized battery and a six-ton Gross Vehicle Weight (GVW), as the first series-produced electric truck delivered in the country. This development directly injected zero-emission vehicles into the commercial logistics fleet, validating the transition from pilot to operational reality.
- May 2023: Daimler Truck, Mitsubishi Fuso, Hino, and Toyota Conclude MoU on Business Integration
Daimler Truck AG, Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation, Hino Motors Ltd., and Toyota Motor Corporation signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on accelerating the development of advanced technologies and merging Mitsubishi Fuso and Hino Motors. This strategic integration is designed to pool resources for developing future technologies, including BEVs and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs), which will ultimately enable the merged entity to offer a broader and more technologically advanced range of ECVs to the Indonesian market.
Indonesia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 0.286 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 1.102 billion |
| Growth Rate | 30.97% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Vehicle Type, Propulsion, Power Output, Application |
| Companies |
|
Indonesia Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segmentation:
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Buses and Coaches
- Trucks
- Light-Duty Trucks
- Medium-Duty Trucks
- Heavy-Duty Trucks
- Vans
- BY PROPULSION TYPE
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEV)
- BY POWER OUTPUT
- Up to 150 kW
- 150-250 kW
- Above 250 kW
- BY APPLICATION
- Logistics and Transportation
- Public Transportation
- Construction (Excavators, Loaders, Others)
- Mining
- Agriculture (Tractors, Harvesters, Others)
- Others