Report Overview
Mexico Electric Vehicle Powertrain Highlights
Mexico Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Size:
The Mexico Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 27.65%, reaching USD 2.101 billion in 2030 from USD 0.62 billion in 2025.
The Mexican Electric Vehicle (EV) Powertrain Market is undergoing a rapid transition, evolving from a traditional automotive assembly base to a critical electromobility manufacturing and export hub within North America. This shift is not organic; it is a calculated response to strategic trade policy and global supply chain re-alignment. Proximity to the US market, combined with the stringent local content mandates of the US-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), compels global automakers to localize the production of high-value EV powertrain components, including battery packs, power electronics, and thermal management systems, directly fueling demand for domestic manufacturing. Mexico's established industrial ecosystem, already hosting major OEM facilities from the 'Big Three' (GM, Ford, Stellantis) and others, provides the foundational infrastructure for this high-technology pivot.
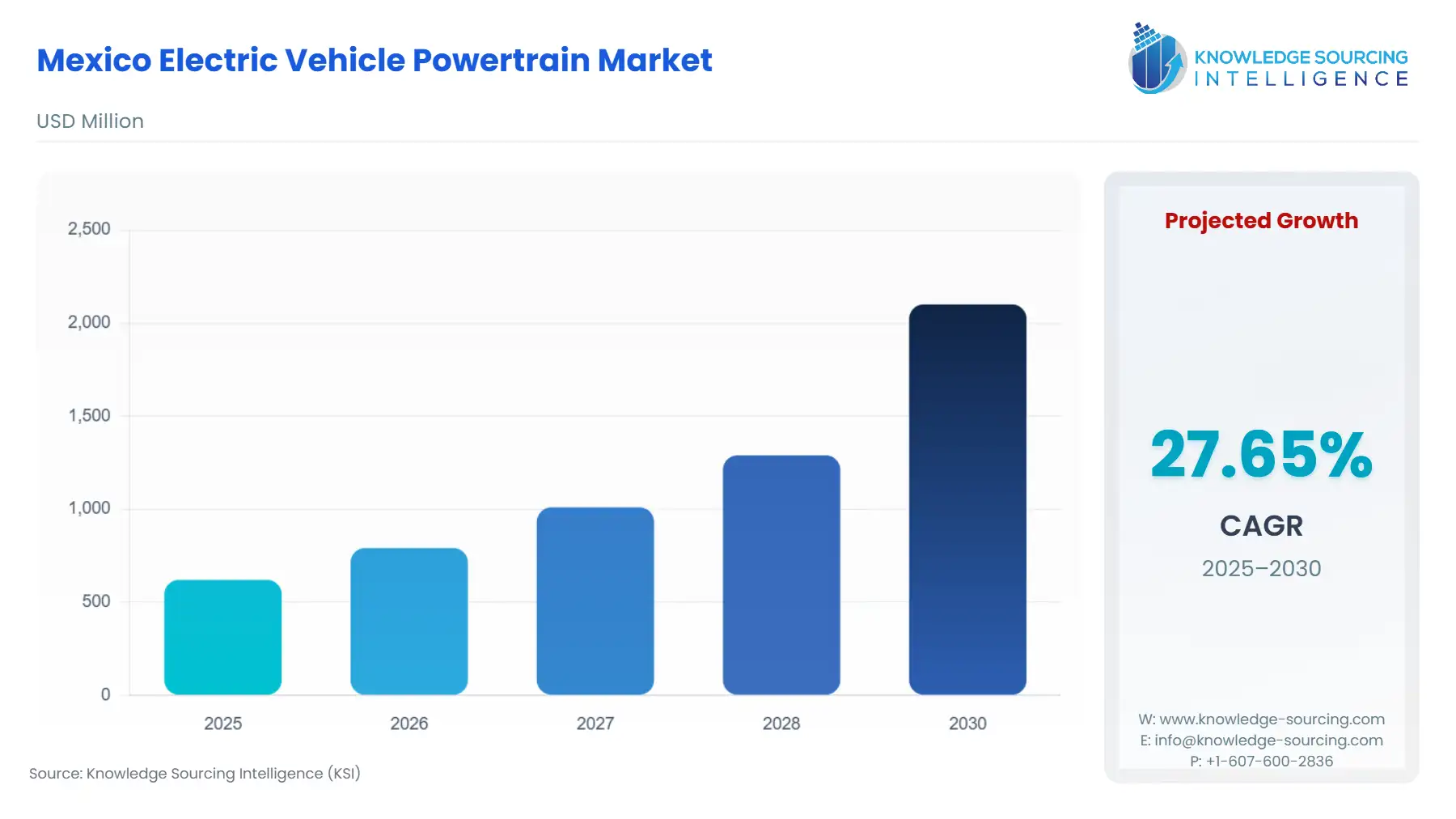
Mexico Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The primary factor propelling the market is the mandated Regional Value Content (RVC) under USMCA. The progressive increase of RVC for automotive goods to 75% incentivizes automakers to shift the sourcing and final assembly of core powertrain elements—particularly battery modules and power electronics—into the North American region. This trade framework directly increases demand for the local manufacturing of sophisticated EV powertrain components to avoid prohibitive tariffs on exports to the US. Furthermore, the surge in domestic EV sales acts as a secondary driver; a reported 70.2% increase in sales of hybrid and electric vehicles from January to November 2024 creates an immediate, albeit smaller, internal market pull for assembled powertrains and service parts.
- Challenges and Opportunities
A significant challenge is the supply and reliability of electricity and charging infrastructure. Insufficient national power generation capacity and grid stability, coupled with the limited current network of public fast-charging stations (only 3,665 public access points as of June 2025), constrain consumer confidence and adoption rates for Battery Electric Vehicles. This infrastructure constraint suppresses mass market expansion for pure BEV powertrains. Conversely, the opportunity lies in the nearshoring and high-value component localization trend. With electromobility investments of $473.8 million reported in 2Q25, the market has a critical opportunity to capture Tier 1 and Tier 2 manufacturing for power electronics and battery management systems, moving Mexico up the value chain from simple assembly to complex component fabrication.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The EV Powertrain Market is inherently a physical product market. Global pricing dynamics of key battery raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, exert indirect pressure on the final cost of the Battery Pack component. Mexico’s reliance on importing these processed materials, despite its geographical position, subjects domestic powertrain component assemblers to global commodity price volatility and supply chain concentration risks, impacting the bill of materials and constraining pricing flexibility for final vehicle manufacturers.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The supply chain is characterized by a strong, export-oriented dependence on the North American corridor. Key production hubs are concentrated in the industrial clusters of the north and central regions, including Nuevo León, San Luis Potosí, and Guanajuato, capitalizing on proximity to the US border. Logistical complexity arises from the reliance on non-regional sources for critical, high-purity battery cell components and semiconductors, forcing a dependency on trans-Pacific and transatlantic freight. The USMCA RVC mandates push for the immediate localization of Tier 1 sub-assembly, creating a complex, integrated cross-border supply chain for components like inverters, onboard chargers, and battery disconnect units.
Mexico Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
Mexico/North America |
US-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) RVC |
The 75% Regional Value Content requirement for automotive goods directly forces automakers to localize manufacturing of high-value powertrain components (e.g., batteries, power electronics) within Mexico, creating domestic supply-side demand. |
|
State of Nuevo León |
Payroll Tax Incentive (ISN) Decree |
Grants a reduction of up to 95% in payroll tax for OEMs and 70% for Tier 1 suppliers with a minimum investment of $150 million in electromobility, significantly lowering operational costs and stimulating new plant construction and capacity additions for EV components. |
|
Federal (Mexico) |
IMMEX Program (Maquiladora Program) |
Allows for the temporary, duty-free importation of goods (machinery, raw materials) for manufacturing and subsequent export, providing a crucial mechanism for efficient operation of EV powertrain component assembly and export. |
Mexico Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Segment Analysis:
- By Component: Battery Pack
The Battery Pack segment is dictated by the strategic manufacturing decisions of major North American OEMs. The Battery Pack is the single most expensive and technologically complex component of the EV powertrain, making its localization paramount to achieving the USMCA's high RVC thresholds. The announcement of major EV final assembly in Mexico by companies like Ford (Mustang Mach-E production in Cuautitlán) and the anticipated facility from Tesla in Nuevo León directly creates a massive, concentrated demand signal for proximate battery pack assembly plants. This necessity focuses on high-energy-density prismatic and pouch cells, along with sophisticated Battery Management Systems (BMS) for thermal and charge control. The market's need is shifting away from importing fully assembled packs and towards setting up 'pack assembly' operations using imported cells to maximize regional content value capture.
- By Vehicle Type: Commercial Vehicle
The Commercial Vehicle segment, including last-mile logistics fleets and urban public transportation, exhibits a distinct and growing demand profile for EV powertrains. This segment is driven by operational savings and municipal regulatory mandates, rather than consumer preference or export policy. Operators of large fleets are realizing substantial savings—up to MX$10,000 per month per vehicle, according to one major ride-hailing/logistics platform—by switching from gasoline to electric. This demonstrable cost reduction creates an immediate, pragmatic demand for highly durable, efficient, and standardized e-axle and motor solutions tailored for high-duty cycle urban use. The growth in this segment is less dependent on highway charging infrastructure and more on depot charging, making it a reliable source of domestic demand for electric powertrains in cities like Mexico City.
Mexico Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Competitive Analysis:
The competitive landscape is defined by the strategic entry and capacity expansion of global Tier 1 automotive suppliers, positioning themselves to service the North American OEM assembly plants in Mexico. These suppliers are competing primarily on proximity to OEMs, technological capability in power electronics, and the ability to source a large percentage of local content.
- Ford Motor Company
Ford's strategy centers on leveraging its existing footprint in Mexico to produce high-volume electric models for North American and global export. The company significantly scaled up its EV production capacity at its Cuautitlán assembly plant, with announced plans in 2022 to triple EV production by late 2023, primarily focusing on the Mustang Mach-E. This capacity expansion creates a locked-in, large-scale demand for specific, integrated e-powertrain units manufactured by its Tier 1 partners in the region.
- Tesla, Inc.
Tesla’s strategic positioning in Mexico, centered on its announced presence in Nuevo León, is a major, yet currently on-hold, long-term growth catalyst. The proposed investment was intended to establish a high-volume Gigafactory for next-generation electric vehicles. This future capacity, though paused, has already spurred significant activity among its global Tier 1 and Tier 2 suppliers (e.g., Quanta, Faurecia) to establish or solidify operations in the region, ready to produce high-tech components like computing units and interior systems, which are integral to the complete EV platform.
Mexico Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Developments:
- September 2024: Ford Motor Company announced a substantial investment of $273 million in its Irapuato plant in Guanajuato, rebranding it as the Irapuato Electric Powertrain Center (IEPC). This investment is dedicated to increasing the production of the Primary Drive Unit (PDU) for the Mustang Mach-E, which is assembled at Ford's Cuautitlán Izcalli plant. The conversion from gasoline transmission production to manufacturing the PDU (which includes the electric motor's stator, rotor, and transaxle) signifies a major product and facility transition in Mexico's high-value EV component manufacturing sector.
- August 2024: Ford Broadens Electrification Strategy. Ford Motor Company announced a realignment of its electrification strategy, including adjustments to its North America vehicle roadmap and a renewed focus on hybrid technologies for some larger vehicle segments. This shift reflects a cautious approach to the full-EV transition, potentially tempering the near-term demand growth rate for pure BEV powertrains in favor of hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) transmission and motor systems.
Mexico Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 0.62 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 2.101 billion |
| Growth Rate | 27.65% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Propulsion Type, Vehicle Type |
| Companies |
|
Mexico Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT
- Battery Pack
- Transmission
- Power Electronics
- Battery Management System
- Thermal Management System
- Others
- BY PROPULSION TYPE
- Battery Electric Vehicle
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Passenger Car
- Commercial Vehicle
- Others