Report Overview
South Korea Electric Commercial Highlights
South Korea Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Size:
The South Korea Electric Commercial Vehicles Market is anticipated to climb at a CAGR of 29.72%, reaching USD 3.034 billion in 2030 from USD 0.826 billion in 2025.
The South Korean Electric Commercial Vehicles (eCV) market is undergoing a structural transformation, driven by a national imperative for carbon neutrality and aggressive government policy. This environment has rapidly transitioned the sector from an emerging niche to a strategic priority for both manufacturers and fleet operators. While the passenger EV segment initially led the electrification wave, the commercial vehicle segment—comprising critical logistics and public transportation fleets—is now experiencing accelerated adoption. Government measures, including substantial purchase subsidies and strict new vehicle safety and performance regulations, directly stimulate procurement by addressing the historically high upfront capital expenditure that constrained fleet conversion. The confluence of these regulatory push factors and technological maturity in domestic manufacturing establishes a strong foundation for sustained market expansion, shifting the focus from initial adoption to optimizing operational logistics for zero-emission fleets.
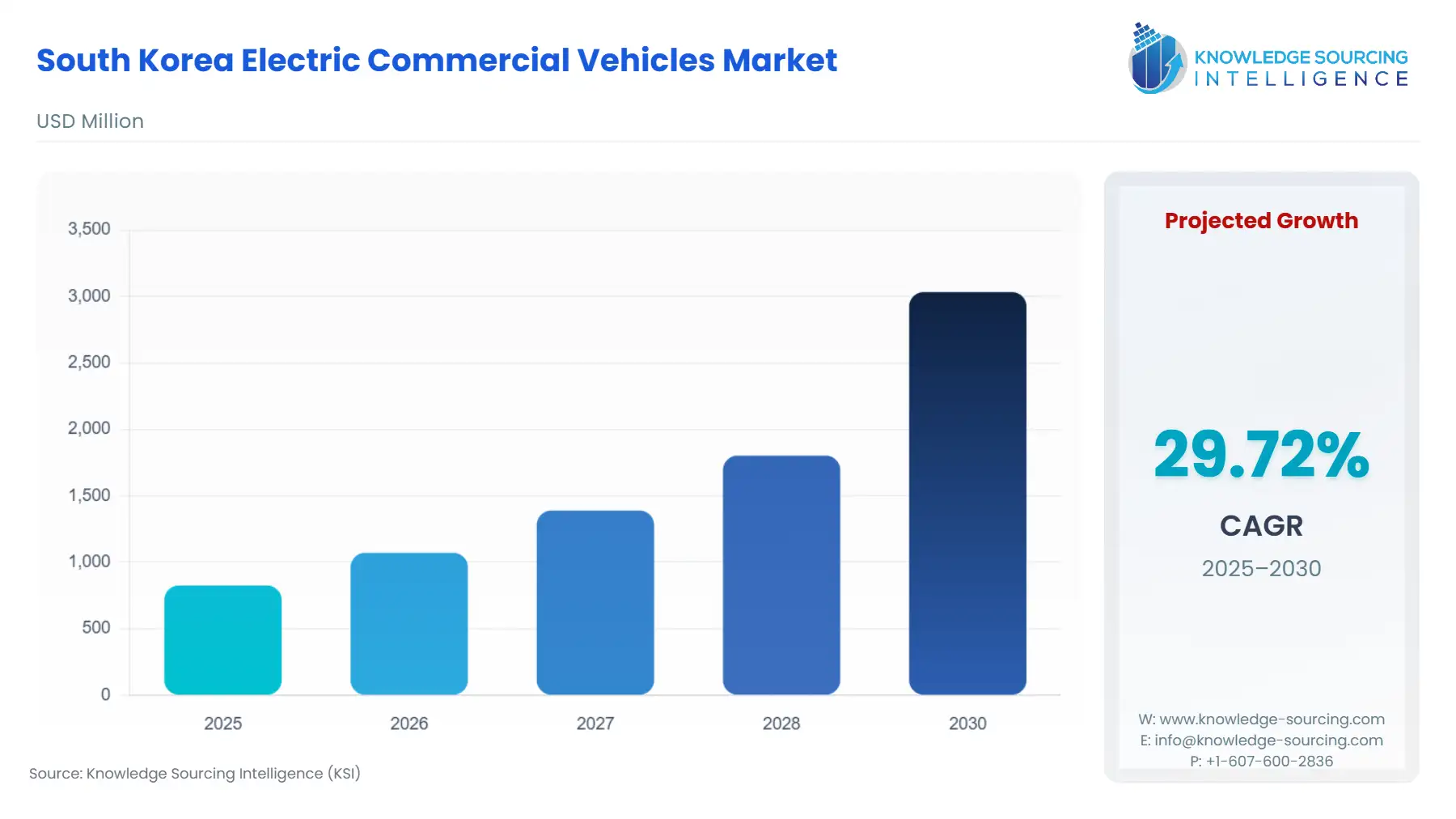
South Korea Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Government fiscal policy is the foremost catalyst, directly stimulating demand. The introduction of specific purchase subsidies for light-, medium-, and heavy-duty ECVs mitigates the significant initial capital expenditure compared to traditional Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) alternatives. For a fleet operator, these subsidies reduce the acquisition cost, thereby making the long-term operational savings from lower fuel (electricity vs. diesel) and maintenance expenses immediately financially viable. Concurrently, strict emission control rules are being enforced to meet national carbon-neutrality goals, creating a regulatory mandate that pushes large logistics and public transportation enterprises to phase out their ICE fleets, thus creating compulsory replacement demand for ECVs.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge lies in the underdeveloped charging infrastructure, which directly suppresses demand by creating operational risk. The lack of a high-power DC charging network tailored for commercial routes and depot charging necessitates prolonged downtimes, reducing vehicle utilization and increasing delivery complexity for logistics operators. This constraint makes fleet managers hesitant to commit to full EV conversion. Conversely, this challenge presents an immediate opportunity in the battery technology segment. The government’s revised subsidy rules favouring vehicles that transmit real-time battery state-of-charge data and encouraging longer-range vehicles creates an explicit demand signal for manufacturers to innovate on energy density, charging speed, and smart fleet management software to qualify for the maximum incentives.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The eCV market, a physical product, is fundamentally exposed to the battery raw material supply chain. South Korea's advanced cell manufacturers, while globally competitive, are highly dependent on external sources, particularly China, for upstream components. As of late 2023, the country imported over 96.6% of its cathode precursor chemicals and 93.7% of its synthetic graphite from Chinese sources. This dependency introduces significant geopolitical risk and price volatility to the key inputs, which account for a substantial portion of the ECV's final price. Any disruption in this supply can immediately inflate battery costs, directly reducing the affordability of ECVs and constraining demand, particularly in the price-sensitive light-duty logistics truck segment. Local manufacturers and the government are actively diversifying, with companies like POSCO investing in overseas mining and domestic lithium hydroxide extraction to create supply chain resilience.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The South Korean eCV supply chain is characterized by a high concentration of sophisticated, downstream manufacturing capabilities—specifically in battery cell production (LG Energy Solutions, Samsung SDI, SK On) and final vehicle assembly (Hyundai, Kia). The production hubs are localized, benefiting from the country's deep pool of skilled engineers. Logistical complexity primarily stems from the aforementioned heavy reliance on global supply chains for critical raw minerals and processed components like cathode/anode materials. This global dependency, while enabling high-tech production of high-energy-density Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC) batteries, creates vulnerability to international trade friction and commodity price fluctuations.
South Korea Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
South Korea |
Electric Vehicle Subsidy Regulatory Guidance (Ministry of Environment) |
Differentially expands subsidies based on battery efficiency, range, and price, directly increasing demand for high-performance, longer-range ECVs and incentivizing manufacturers to reduce production costs to meet subsidy thresholds. |
|
South Korea |
Mandatory Safety Labelling and Stricter Performance Testing for EV batteries (Automobile Management Act) |
Replaces self-certification with a government-led system, directly addressing public safety concerns (e.g., battery fires), which, if successful, builds consumer and fleet operator confidence, thereby mitigating a key psychological barrier to demand. |
|
South Korea |
Revised Subsidy Rules (Ministry of Environment) |
Only EVs transmitting real-time battery state-of-charge data are eligible for subsidies, driving demand for advanced, connected battery management systems and software-defined fleet solutions from suppliers. |
South Korea Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segment Analysis
- By Vehicle Type: Light-Duty Trucks
The Light-Duty Truck segment drives high demand primarily due to its central role in last-mile logistics and short-haul city operations. These vehicles, often used by small business owners and for urban deliveries, benefit the most from the dense urban charging infrastructure that is comparatively easier to develop than highway fast-charging networks for heavy-duty models. Government subsidies have been particularly effective in this segment, directly compensating for the higher upfront vehicle cost. This policy intervention, combined with the low daily mileage and stop-start nature of urban delivery cycles, makes the total cost of operation savings substantial and immediate, creating a powerful financial incentive that propels mass-market adoption. Moreover, local government regulations on inner-city air quality and noise pollution further constrain the use of diesel light-duty trucks, creating a regulatory push factor that solidifies the demand floor for the electric variants.
- By Application: Logistics and Transportation
The operational optimization imperative of large-scale fleet operators fuels the logistics and transportation segment’s growth. The shift to electric vehicles in this sector is not merely regulatory compliance but a strategic move to manage unpredictable fuel price volatility and minimize maintenance overhead. BEVs, with significantly fewer moving parts than their ICE counterparts, offer substantial reductions in downtime and service costs, translating directly into enhanced fleet utilization and lower operating expenditure. Furthermore, the FCEV sub-segment is gaining traction in long-haul logistics as manufacturers develop trucks with extended range capabilities, directly addressing the core anxiety of long-distance transport managers regarding range and payload. This dual-technology approach—BEVs for short-haul and FCEVs for long-haul—creates a comprehensive zero-emission solution set, assuring fleet managers they can maintain operational continuity while meeting environmental mandates.
South Korea Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Competitive Analysis:
- The South Korean eCV market is concentrated, dominated by the domestic automotive powerhouses, leveraging their established sales, service, and supply chain networks.
- Hyundai Motor Company (HMC) is positioned as the segment leader, employing a dual-platform strategy across BEV and FCEV to cover the full spectrum of commercial applications. The company’s strategic commitment to hydrogen mobility, branded HTWO, is evidenced by the deployment of the XCIENT Fuel Cell heavy-duty truck in various global logistics trials. HMC strategically targets the heavy-duty sector where the energy density and rapid refuelling of FCEV technology offer a competitive advantage over BEVs for long-haul and high-payload transport.
- Kia Corporation focuses on the Purpose-Built Vehicle (PBV) segment, which targets diverse commercial utility and modular adaptability. The company's strategic roadmap includes the launch of the PV5 and future larger models like the PV7 and PV9 by 2029, with a goal of selling 250,000 PBVs globally by 2030. This strategy positions Kia not just as a vehicle manufacturer, but as a supplier of integrated, customizable mobility solutions for fleet operators, directly meeting the varied needs of sectors like last-mile delivery and public transport.
South Korea Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Developments
- December 2024: Hyundai Motor Group deployed its XCIENT heavy-duty hydrogen fuel-cell electric trucks for clean logistics operations at its Metaplant America (HMGMA) facility, in cooperation with Glovis America, demonstrating a commitment to real-world deployment of FCEV technology.
- September 2024: Hyundai Motor Company and IVECO Group unveiled the IVECO-badged 'eMoovy' at the IAA Transportation 2024. This electric Light Commercial Vehicle (eLCV) is the first product from their partnership based on Hyundai’s advanced eLCV platform, featuring an 800V system for ultra-fast charging and an expanded 76.1 kWh battery capacity.
- May 2023: Hyundai Motor Group and LG Energy Solution (LGES) announced the establishment of an EV battery cell manufacturing joint venture in the U.S., a strategic move to secure a resilient, localized supply chain for high-volume EV battery production, mitigating global supply risks.
South Korea Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 0.826 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 3.034 billion |
| Growth Rate | 29.72% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Vehicle Type, Propulsion, Power Output, Application |
| Companies |
|
South Korea Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segmentation:
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Buses and Coaches
- Trucks
- Light-Duty Trucks
- Medium-Duty Trucks
- Heavy-Duty Trucks
- Vans
- BY PROPULSION TYPE
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEV)
- BY POWER OUTPUT
- Up to 150 kW
- 150-250 kW
- Above 250 kW
- BY APPLICATION
- Logistics and Transportation
- Public Transportation
- Construction (Excavators, Loaders, Others)
- Mining
- Agriculture (Tractors, Harvesters, Others)
- Others