Report Overview
US Electric Vehicle Powertrain Highlights
US Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Size:
The US Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18.00%, reaching USD 41.23 billion in 2030 from USD 18.022 billion in 2025.
The U.S. electric vehicle (EV) powertrain market is advancing from an early adoption phase into a high-growth environment, fundamentally restructured by assertive federal industrial policy. This shift is characterized by record EV sales volumes and a concerted, policy-driven effort to localize the complex, multi-tiered supply chain for core components like battery packs, power electronics, and integrated drive units. The transition is not merely an incremental increase in output but a complete reshaping of the value chain, compelling OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers to execute massive capital deployment in new North American manufacturing footprints. The resulting competitive landscape prioritizes component efficiency, power density, and adherence to stringent localization requirements, setting a new imperative for domestic technology leadership.
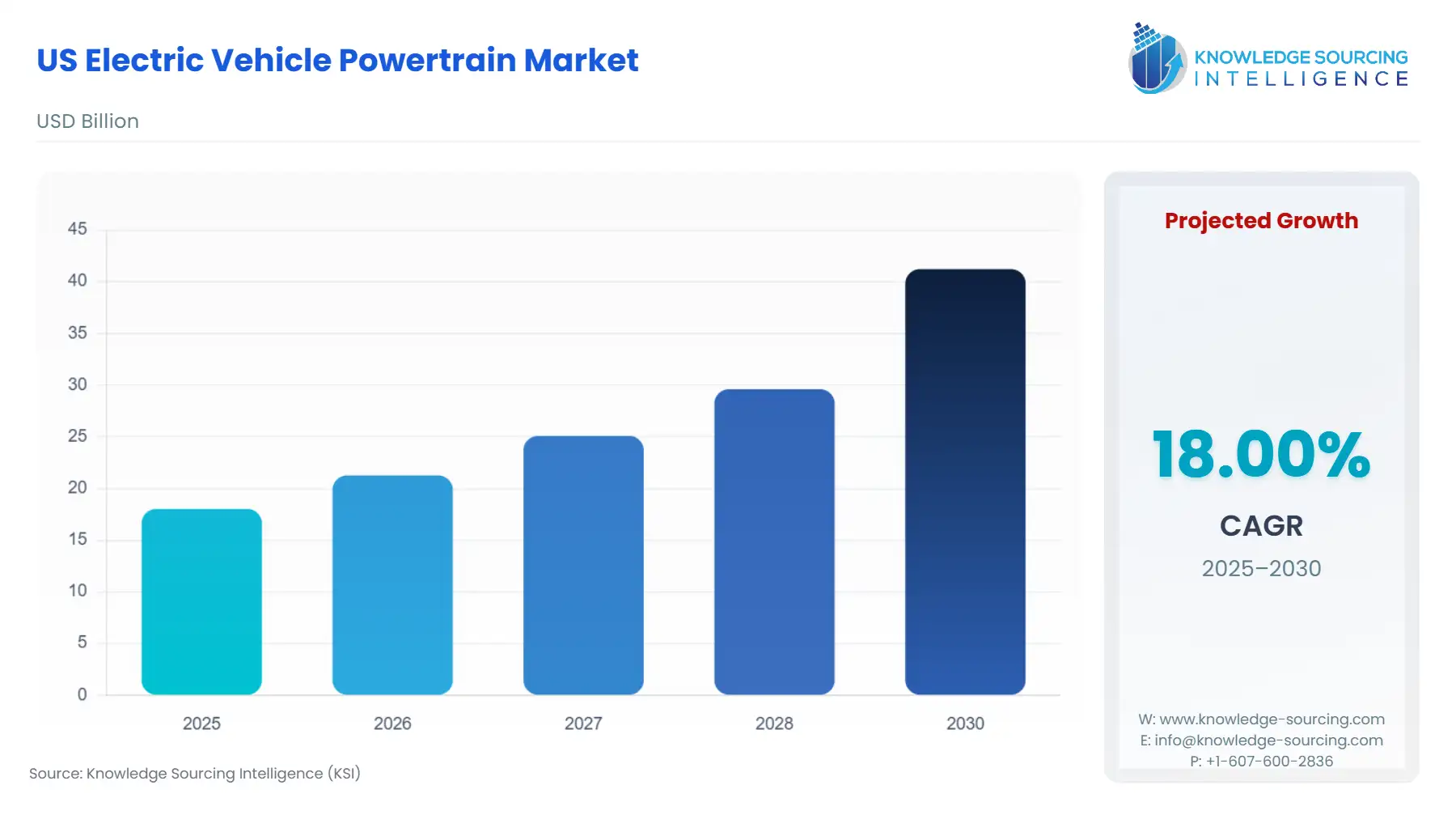
US Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The primary factor propelling the market is the regulatory incentive structure that directly correlates with consumer demand. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA)’s Clean Vehicle Credit acts as a powerful demand creation mechanism for powertrain components by making a new EV purchase significantly more affordable (up to $7,500 credit), provided the vehicle’s battery meets escalating domestic content requirements for both critical minerals and components. This provision immediately increases demand for U.S.-sourced battery cells and other integrated powertrain components, forcing manufacturers to expedite the localization of their sourcing and production to unlock consumer eligibility. Furthermore, the sustained growth in EV adoption—with sales volume increasing 10% year-over-year through the first three quarters of 2024—provides the necessary volume assurance for large-scale domestic factory investments.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge constraining market growth is the vulnerability of the raw material supply chain and the persistent issue of charging infrastructure availability. The reliance on globally concentrated sources for critical minerals like lithium, nickel, and cobalt creates pricing volatility and supply risk that directly impacts the final cost of the battery pack, the most expensive powertrain component. This mineral concentration acts as a cost headwind, threatening to counteract the price reduction achieved through economies of scale and slowing the reduction of the overall EV purchase price premium, thus potentially dampening broader consumer demand. The opportunity lies in accelerating the diversification of the battery supply chain by scaling up domestic refining and recycling capabilities, which would create a resilient, price-stable domestic source of material, ensuring consistent, cost-competitive production of powertrain components.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The EV powertrain is a physical product, with the battery pack being the most material-intensive subsystem. The cost dynamics are dictated heavily by the supply chain of critical minerals, primarily lithium, nickel, and cobalt. Following a period of price inflation in 2022, critical mineral prices stabilized and fell in 2023, contributing to a significant drop in the average price of a battery pack. This stabilization is a direct function of increased mining and refining output exceeding battery demand growth in 2023. This price decrease serves as an immediate catalyst, lowering the cost of goods sold (COGS) for manufacturers and making the final EV product more price-competitive against Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) alternatives, thereby bolstering consumer demand.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global EV powertrain supply chain is characterized by a high degree of dependence on Asian, particularly Chinese, midstream processing and manufacturing for refined materials, precursors, and battery cells. U.S. efforts, supported by legislation, are focused on constructing a new, vertically integrated, and regionalized North American supply chain. This requires establishing domestic capabilities for critical stages, from mineral processing and cathode/anode active material production to cell and module assembly. The logistical complexity involves managing a high-volume flow of high-value, heavy components, with dependencies shifting from overseas raw material transport to establishing reliable, just-in-time cross-country logistics between new U.S. "gigafactories" and final vehicle assembly plants.
US Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
U.S. Federal |
Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) – Clean Vehicle Tax Credit (30D) |
Directly stimulates growth of U.S./North American-sourced battery packs, power electronics, and electric motors to meet stringent Critical Mineral and Battery Component requirements for consumer eligibility. Compels a shift in manufacturer sourcing and production geography. |
|
U.S. Federal |
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Emissions Standards |
Establishes stringent tailpipe emissions requirements that effectively mandate an aggressive increase in the market share of zero-emission vehicles, generating structural, long-term demand for all EV powertrain components. |
|
U.S. Federal |
Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL) |
Allocated over $7 billion for domestic battery supply chain and manufacturing, directly reducing the capital expenditure risk for companies establishing domestic cell manufacturing, thus increasing the supply-side capacity of the core powertrain component. |
US Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Segment Analysis:
- By Propulsion Type: Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
BEVs are the market's leading segment, driving the highest demand for the most technologically advanced and energy-dense powertrain configurations. The core growth driver for the BEV segment is the continuous increase in certified vehicle range and the expanding availability of charging infrastructure. As BEV models achieve median ranges of over 230 miles on a single charge and the federal government funds the national charging network buildout, consumer "range anxiety" diminishes. This directly elevates the necessity for large, high-voltage battery packs, sophisticated Battery Management Systems (BMS), and high-efficiency power electronics to manage energy flow effectively, ensuring the advertised range is met. The growing presence of BEVs in the light truck category, which has high-power and high-torque requirements, further elevates the performance and durability specifications demanded from the electric motor and transmission components.
- By Vehicle Type: Commercial Vehicle
The commercial vehicle segment, encompassing medium- and heavy-duty trucks, is emerging as a critical growth vector for powertrain suppliers. Corporate decarbonization commitments and municipal fleet electrification grants drive its demand. Unlike the passenger segment, the need for commercial vehicles is less price-elastic and more reliant on total cost of ownership (TCO) benefits, which is achieved through lower fuel and maintenance costs. This creates a high, specialized demand for extremely robust, high-torque electric drive axles and large-scale battery packs (often exceeding 400 kWh) with thermal management systems optimized for sustained high-load usage cycles. The need for reliable uptime translates directly into demand for highly durable, modular powertrain components that facilitate rapid servicing and component replacement.
US Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Competitive Analysis:
The US EV powertrain market is characterized by a blend of established automotive Tier 1 suppliers and agile, integrated vehicle manufacturers. Competition centers on battery chemistry innovation, component integration (e.g., 3-in-1 e-Axle units), and vertical integration depth.
- General Motors (GM) has strategically positioned itself through its proprietary Ultium platform, which modularizes the battery architecture for high flexibility across various vehicle segments. The company's focus is on increasing profitability per EV through scale and component commonality. A key initiative is the joint venture for battery cell manufacturing, Ultium Cells LLC, which began production in late 2022. This vertical integration secures a stable, North American supply of the core powertrain component, directly supporting its goal of wholesaling approximately 200,000 GM-branded EVs in 2024.
- Tesla, Inc. maintains a formidable competitive advantage through its deep vertical integration, producing its own battery cells (4680 format) and highly efficient integrated drive units across its Gigafactories. Tesla's strategy centers on manufacturing innovation to reduce per-unit cost and maximize component energy density. By maintaining control over the complete powertrain design and manufacturing, Tesla can implement rapid improvements in efficiency and cost, putting competitive pressure on non-integrated OEMs. The company's volume focus resulted in the production of over 1.77 million vehicles in 2024, driving unprecedented demand for its internally sourced powertrain components.
US Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Developments
- July 2025 (General Motors): GM announced that its Ultium Cells LLC plant in Spring Hill, Tennessee, will begin making lower-cost Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries in addition to nickel-based cells. This capacity addition is a direct strategic move to enable the production of more affordable EV models, such as the Chevrolet Equinox EV, by securing a cost-effective alternative battery chemistry for mass-market vehicles.
- January 2024 (U.S. Department of Energy): The Department of Energy allocated $131 million to various projects aimed at advancing research and development in EV batteries and charging systems. This government-supported R&D funding directly targets technology cost reduction and range extension, which are critical for increasing the performance and cost-competitiveness of future U.S.-manufactured powertrain components.
US Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 18.022 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 41.23 billion |
| Growth Rate | 18.00% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Propulsion Type, Vehicle Type |
| Companies |
|
US Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT
- Battery Pack
- Transmission
- Power Electronics
- Battery Management System
- Thermal Management System
- Others
- BY PROPULSION TYPE
- Battery Electric Vehicle
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Passenger Car
- Commercial Vehicle
- Others