Report Overview
Brazil Advanced Battery Market Highlights
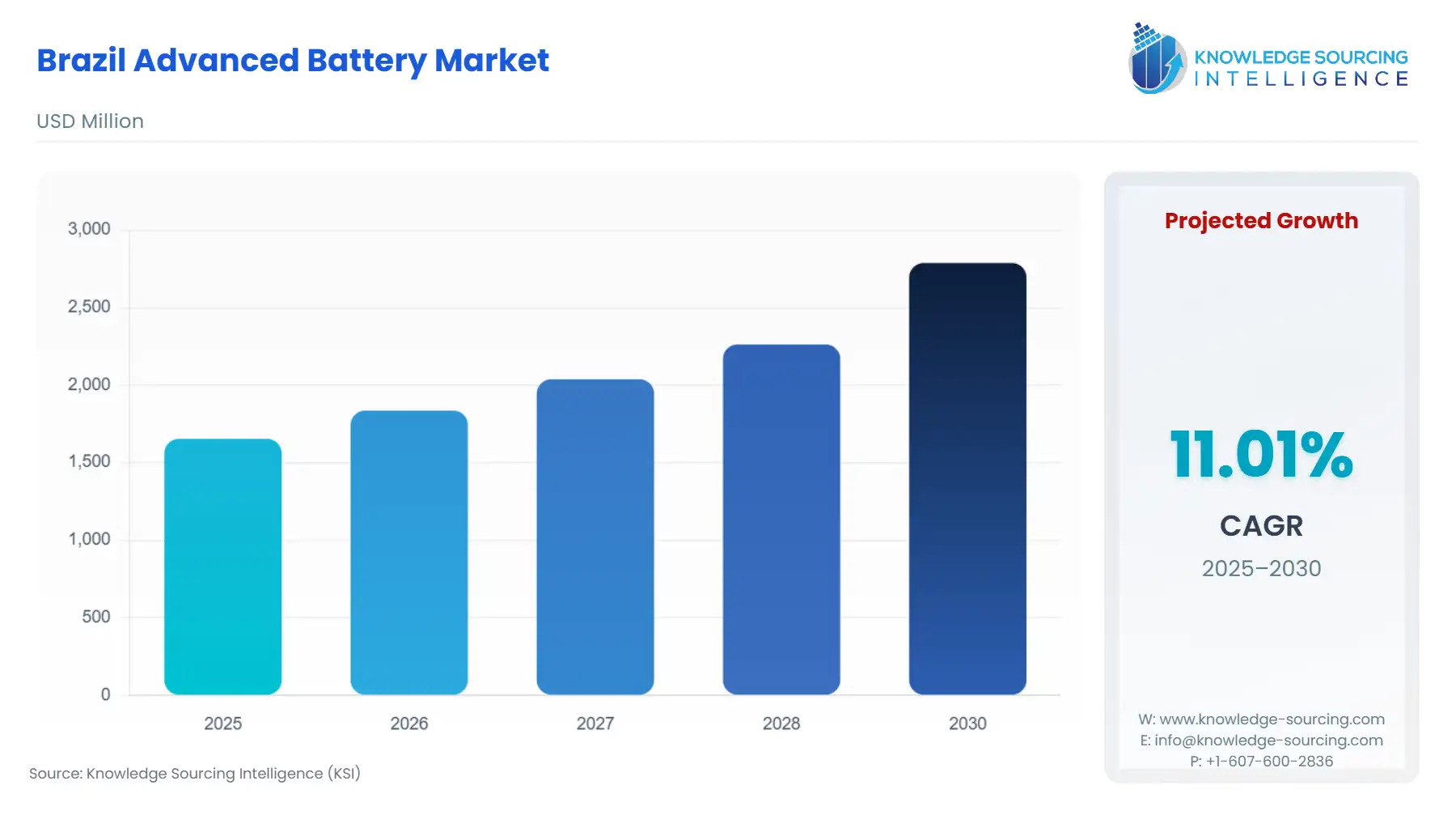
Brazil Advanced Battery Market Size:
The Brazil Advanced Battery Market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 11.01%, reaching USD 2.788 billion in 2030 from USD 1.654 billion in 2025.
The Brazilian advanced battery market is navigating a critical inflection point, fundamentally shaped by the country's imperative to integrate its rapidly expanding variable renewable energy sources, particularly solar and wind, into its hydro-dominated grid. Historically reliant on massive hydropower, the system faces increasing flexibility and reliability challenges due to climatic volatility and the mismatch between peak solar generation (midday) and peak demand (evening). Advanced battery technologies, specifically Lithium-ion batteries, are therefore transitioning from niche applications to essential grid assets, securing system flexibility and enabling the monetization of intermittent power generation. This shift is reinforced by progressive regulatory steps aimed at establishing clear market rules for grid access and remuneration for storage solutions.
Brazil Advanced Battery Market Analysis:
-
Growth Drivers:
The explosive growth in solar PV capacity directly propels demand for advanced batteries. Brazil added 15 GW of solar PV capacity in 2023, rising to the sixth-largest global solar market. This variable generation creates operational challenges for the National System Operator (ONS), particularly the sharp drop in output during evening peak demand (7 PM to 9 PM), often necessitating load shedding. Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) directly address this by absorbing excess solar generation during the day and discharging stored energy during peak hours, creating a robust need for utility-scale and commercial batteries to stabilize supply. Furthermore, high energy tariffs for consumers in the regulated market make behind-the-meter storage economically attractive, as consumers utilize batteries to reduce consumption during high-cost peak periods, further stimulating demand in the residential and commercial segments.
-
Challenges and Opportunities
A primary challenge remains the high upfront capital expenditure for storage technologies, even with falling global battery pack prices. This cost factor creates a barrier to rapid and widespread deployment, particularly for smaller enterprises and residential users. Another constraint is the reliance on imports for critical battery raw materials like lithium and cobalt, creating supply chain vulnerabilities and exposing manufacturers to global price volatility. This dependency can undermine the long-term industry stability required for large-scale domestic manufacturing. Conversely, significant opportunities exist in regulatory finalization, particularly with ANEEL's work on compensation mechanisms that allow for the "stacking" of revenue streams from multiple services like frequency regulation and energy arbitrage. This clear pathway to multi-faceted monetization will de-risk investment and increase the internal rate of return for BESS projects, fundamentally increasing demand for deployment. The government's push for new capacity auctions, including dedicated tenders for BESS, represents a direct mechanism to translate policy into firm demand contracts.
-
Raw Material and Pricing Analysis:
The advanced battery market, a physical product, is intrinsically linked to the supply and cost of critical minerals. Brazil holds a competitive position in the global supply chain, being the world's largest supplier of niobium and possessing reserves of lithium and natural graphite, all strategic minerals for the energy transition. Despite this, the country's manufacturing sector remains heavily dependent on imports for refined lithium and cobalt. This reliance on a concentrated global supply chain exposes the final product pricing to international commodity market volatility, creating uncertainty for long-term project planning and potentially impacting the cost competitiveness of locally assembled batteries against imported solutions. The increasing domestic focus on exploring lithium and graphite reserves signals an opportunity to vertically integrate the supply chain, which could stabilize pricing and reduce demand-side risk from import tariffs and geopolitical friction.
-
Supply Chain Analysis:
The advanced battery supply chain in Brazil exhibits a structure dominated by raw material extraction upstream, but with a critical dependence on midstream and downstream imports. Brazil’s mining sector extracts key minerals like nickel, copper, niobium, and graphite. However, the complex midstream process—which involves refining and processing these materials into specialized battery components like Cathode Active Material (CAM) and Anode Active Material (AAM)—is predominantly situated in Asia. Logistical complexities arise from the necessity of importing highly engineered components and battery cells for final assembly within Brazil. This global dependency introduces lead-time risks and limits local content creation, making the market vulnerable to global supply constraints. Key local companies are focusing on assembly and system integration, while simultaneously exploring avenues to onshore LFP (Lithium-Iron-Phosphate) technology manufacturing to mitigate global dependencies.
Brazil Advanced Battery Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
|
Federal (Brazil) |
Law No. 14,300/2022 (Legal Framework for Distributed Generation) |
Explicitly defined PV systems combined with batteries as dispatchable sources, thereby creating a new, regulated category of energy resource. This mandate directly increases the premium and demand for batteries in distributed generation projects to secure dispatch priority. |
|
ANEEL (Regulator) |
Public Consultation No. 39/2023 (ESS Regulatory Framework) |
Initiated the refinement of regulations for Energy Storage Systems, establishing clear authorization processes and allowing for the stacking of revenue streams. This policy clarity reduces regulatory risk for investors, catalyzing demand for BESS projects in the utility and commercial segments. |
|
MME (Ministry) |
Public Consultation No. 176 of 2024 (Proposed Energy Storage Auction Model) |
Proposed an auction mechanism for 10-year BESS contracts to provide four hours of daily dispatchable power. This translates the government's reliability imperative into firm, long-term contract demand for utility-scale battery deployment starting in 2029. |
Brazil Advanced Battery Market Segment Analysis:
-
By Application – Energy Storage Systems (Utility-scale): The utility-scale ESS segment is characterized by policy-driven requirements, directly linked to the need for grid flexibility following the massive deployment of intermittent renewables. As Brazil's total electricity from hydro declines and the share of centralized wind and solar increases, the system operator (ONS) faces challenges balancing supply, especially during the daily evening demand peak. Utility-scale batteries directly resolve this by providing large-scale ancillary services, such as frequency regulation and capacity reserve. The Ministry of Mines and Energy's proposal for a BESS auction model in 2024, offering 10-year contracts for dispatchable power, is the single most significant factor currently translating grid-level need into high-volume commercial demand for batteries. This focus on reliability and dispatchability creates a specific need for systems with long-duration discharge capabilities, typically greater than four hours.
-
By Technology – Lithium-ion Batteries: The Lithium-ion (Li-ion) segment dominates the advanced battery market, largely due to its high energy density, superior cycle life, and falling cost trajectory. Li-ion technology, including LFP (Lithium-Iron-Phosphate) chemistry, is the de facto standard for both the rapidly expanding electric vehicle sector and grid-scale ESS. The need for Li-ion in Brazil is intrinsically tied to its versatility across applications, from small-scale consumer electronics to multi-megawatt utility projects. For the automotive sector, Li-ion is essential for powering the growing penetration of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), with major international manufacturers exploring local production. For energy storage, the falling average price of battery packs in 2024 enhances the economic viability of new Li-ion BESS installations, reinforcing its position as the primary advanced battery technology in the country.
Brazil Advanced Battery Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The competitive landscape is characterized by the presence of large global original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and increasingly capable local integrators. International companies are seeking to leverage Brazil’s energy transition and raw material potential, while domestic firms focus on specialized manufacturing and distribution.
-
Contemporary Amperex Technology Limited (CATL): As the global leader in battery manufacturing, CATL’s strategic positioning in Brazil focuses on strengthening the partnership for domestic battery production, specifically for electric vehicles and energy storage systems. This positioning leverages their global market share (39% of the global EV battery market and 37% in energy storage) to integrate their technology solutions into Brazil's electrification and grid modernization efforts.
-
ISA CTEEP: The company has demonstrated a commitment to utility-scale deployment with a notable 30MW/60MWh lithium battery module installation launched in 2022. This project acts as a functional demonstration of BESS as a transmission asset to provide backup during peak summer demand, signaling the company's focus on grid reliability and large-scale, system-integrated solutions.
-
UCB Power: A local Brazilian manufacturer that stands out for expanding its production capacity to serve the energy storage market. The company produces over 72,000 lithium batteries annually and is recognized as the country's first domestic manufacturer of LFP technology, strategically targeting localized supply for industrial and energy storage applications.
Brazil Advanced Battery Market Developments:
-
August 2025: Representatives from Contemporary Amperex Technology Limited (CATL) met with the Minister of Mines and Energy in Brasília to reinforce a partnership aimed at boosting domestic battery production for electric vehicles, signaling a high-level corporate commitment to local manufacturing capacity in the immediate future.
-
August 2025: UCB Power, a domestic Brazilian manufacturer, was noted to be producing over 72,000 lithium batteries annually and confirmed its status as the country's first domestic manufacturer of LFP (Lithium-Iron-Phosphate) technology.
Brazil Advanced Battery Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 1.654 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 2.788 billion |
| Growth Rate | 11.01% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Technology, Capacity, Material, Sales Channel |
| Companies |
|
Brazil Advanced Battery Market Segmentation:
-
BY TECHNOLOGY
-
Lithium-ion Batteries
-
Lead-acid Batteries
-
Solid-state Batteries
-
Nickel-metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
-
Flow Batteries
-
Sodium-ion Batteries
-
Others
-
-
BY CAPACITY
-
Low Capacity (<50 Ah)
-
Medium Capacity (50-200 Ah)
-
High Capacity (>200 Ah)
-
-
BY MATERIAL
-
Cathode Material
-
Anode Material
-
Others
-
-
BY APPLICATION
-
Automotive
-
Electric Vehicles
-
Hybrid Electric Vehicles
-
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles
-
-
Energy Storage Systems
-
Residential
-
Commercial & Industrial
-
Utility-scale
-
-
Consumer Electronics
-
Industrial
-
Motive Power
-
Stationary
-
-
Medical
-
Aerospace & Defense
-
Others
-
-
BY SALES CHANNEL
-
OEM
-
Aftermarket
-