Report Overview
Smart Grid Market Size, Highlights
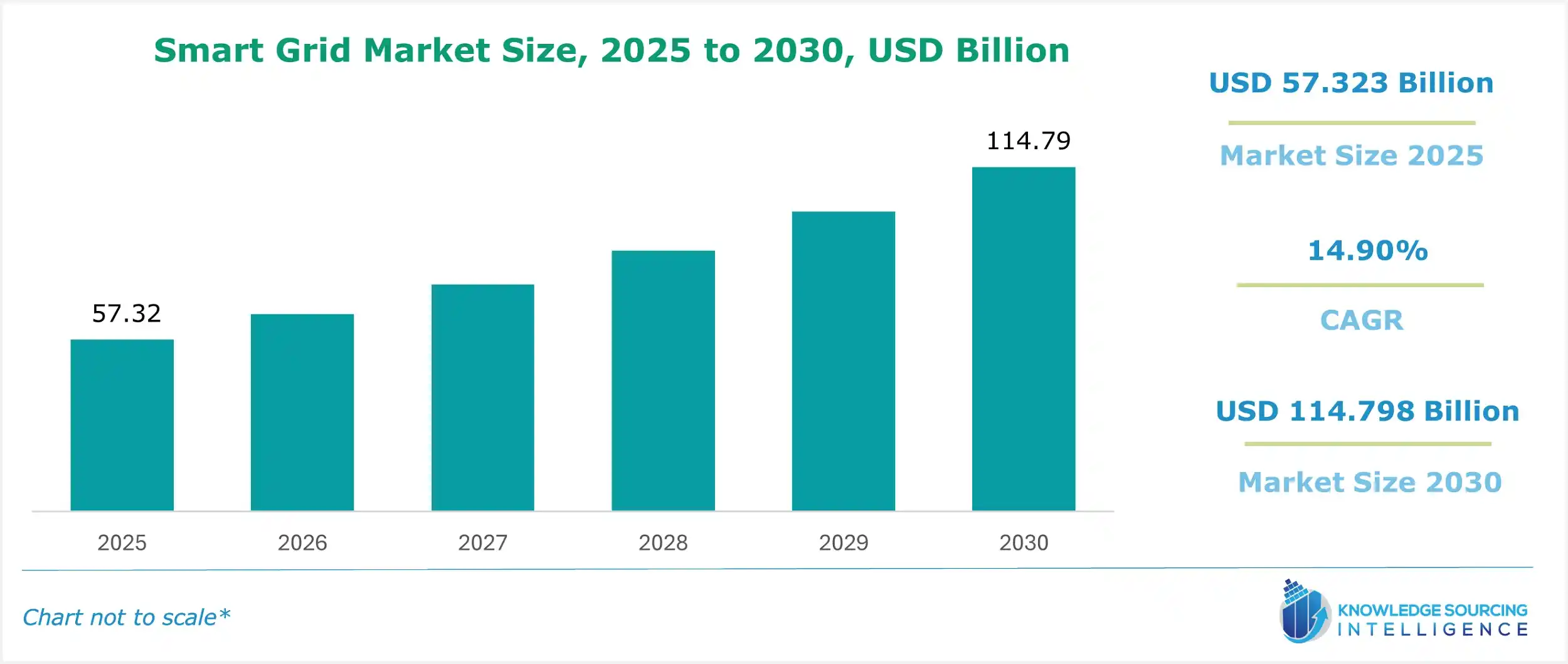
Smart Grid Market Size:
The smart grid market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.45%, reaching a market size of USD 85,999.455 million in 2030 from USD 57,323.493 million in 2025.
Smart Grid Market Overview:
The grid is a well-connected electro-supply network that uses modern digital communication technology to identify and respond in real-time to variations in usage at a locality. This innovative system is part of today's electrical grid network because it is very sophisticated in feedback management, such as demand response management systems (DRMS) and active network management (ANM), among others. This whole energy flow is automatically monitored, automated, and controlled by a highly interconnected network using meters, sensors, digital controls, and analytical tools.
The network makes this electricity reliable and efficient in delivering it to its consumers where and when they want it, from many modern applications and technologies, and makes way for the environment and the economy as well. Emerging economies are considering these technologies to be a strategic advantage in infrastructure development, which would be beneficial in terms of reducing their carbon emission targets as well as becoming integral to future practice in overall economic prosperity.
The smart grid market is revolutionizing energy delivery through smart grid technology and grid modernization. Power grid digitalization enhances efficiency, integrating utility automation and intelligent grid solutions. Energy management systems (EMS) optimize resource allocation, while advanced distribution management systems (ADMS) enable real-time grid monitoring and control. These technologies support reliable, sustainable energy distribution, addressing rising demand and renewable integration challenges. By leveraging IoT, AI, and data analytics, smart grids improve resilience and reduce outages. The market plays a vital role in driving innovative, scalable solutions for modern energy needs, transforming traditional utilities into adaptive, efficient systems.
Smart Grid Market Trends:
The smart grid market is evolving rapidly with the rise of distributed energy resources (DERs), microgrids, and advanced digital technologies. These systems enhance grid reliability, resilience, and energy autonomy, especially as utilities adapt to decentralized and renewable energy models.
Technologies such as virtual power plants (VPPs) and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems are transforming the way electricity is stored and distributed. VPPs aggregate energy from various sources like solar panels, batteries, and wind farms, while V2G allows electric vehicles to supply power back to the grid, supporting load balancing and renewable energy integration.
Demand response (DR) programs are gaining traction as they improve load forecasting, reduce peak demand, and stabilize the grid. Meanwhile, prosumers—consumers who generate their own energy are playing a greater role in energy markets, enabled by advanced prosumer management platforms.
Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) facilitates real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven grid optimization. These innovations support the development of scalable, adaptive, and sustainable energy networks.
With growing global energy needs and climate change targets, smart grid technologies offer a path toward a more efficient, flexible, and low-carbon energy future.
Smart Grid Market Growth Drivers:
-
Growing interest in energy efficiency is contributing to the smart grid market growth
One of the major driving factors for the global smart grid market is increasing energy efficiency demands for electrical supply systems. Because the infrastructure is mostly old and there are no real-time monitoring capabilities, the antiquated power grids usually have increased energy losses during transmission and distribution. Smart grids have cut down these losses by harnessing advanced technologies such as smart meters and grid automation for efficient control and optimization of the electricity flow. Therefore, optimal use of resources results in reduced operating costs and wastage of energy. Smart grids, in addition, support demand response programs for better load management and energy savings.
-
Utilizing renewable energy sources is anticipated to boost the smart grid market.
Smart grids will connect solar and wind energy sources to electrical systems. Unlike traditional sources, these renewables produce energy sporadically and unpredictably. Attempting to manage such variations with the conventional power grid has proven ineffective. Smart grids, being high-tech, present a highly dynamic and responsive infrastructure, which arbitrates the management and distribution of variable amounts of energy from renewable sources. This augmentable capability becomes necessary to increase the proportion of renewable energy added to our electrical networks to transform energy practices into more sustainable ones. But thanks to their cutting-edge technology, smart grids are better able to control and balance these variations.
Moreover, integrated power systems will enable even real-time monitoring and control of energy generation and consumption, assuring a constant and reliable electricity supply. Integration among forms of energy is critical for reducing dependence on fossil fuels and moving to more sustainable energy systems. Smart grids also support distributed generation, where energy is generated closer to its point of consumption, lowering transmission losses and promoting renewable energy resources.
-
Expanding government laws and regulations are anticipated to increase the market demand
Rules and regulations from the Government Affect the Completion and Operation of Smart Grids. It has also been noted as having a high potential for achieving energy efficiency, reducing carbon emissions, and transitioning to renewable energy. Countries around the world have already legislated for all these policies, for instance, laws, rules, and regulations that support and sometimes mandate smart grid technologies.
Some are financial incentives, subsidies, and regulatory frameworks that encourage investments and innovations in that regard. Such laws include the installation of smart meters in homes and businesses, which have catalyzed the growth of smart grids significantly. The complete and safe development of the smart grid is also undertaken by government initiatives aimed at setting up standards and protocols for interoperability and security.
-
Increasing advancements in ICT are anticipated to increase the market demand
Real-time data collection, analysis, and management are made possible by the integration of contemporary ICT into grid infrastructure. Because it allows for predictive maintenance, improved load management, and prompt response to power outages or other problems, this data is essential to the effective operation of smart grids. Smart grid capabilities are further enhanced by technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning, which enable more complex data analysis and decision-making. In addition to increasing the power supply's dependability and efficiency, these developments open the door for cutting-edge energy management services and applications.
Smart Grid Market Restraints:
-
The high investment cost is anticipated to hamper the market growth
The market growth is expected to be restrained by the very high investment costs of these grid systems. The setting up of transmission networks connecting the end users to the advanced grid requires massive upfront investments in these technologies. High post-deployment maintenance and operating costs are another major concern for utility providers.
Some emerging economies like Brazil, Mexico, and India also have adequate infrastructure but need substantial investments to update their system. It is worth stating that poor government regulations regarding the upgrading and expansion of grid infrastructures and low accessibility of electricity, especially in developing nations, also constrain the growth of the market.
Smart Grid Market Geographical Outlook:
-
North America is witnessing exponential growth during the forecast period.
Emerging demands for revitalizing decrepit electrical infrastructures and the ever-increasing trend for the utilization of alternative energy sources, among others, drive the smart grid market within North America. Also supportive of the development of smart grids are incentives and policies advocating the adoption of smart technology installation, all integrated into the solid regulatory framework of the region. Lastly, there would also be increased demands for increased grid efficiency and reliability in the wake of severe weather conditions. Furthermore, the market is encouraged through the popularization of smart metering infrastructure and the promotion of energy independence.
Smart Grid Market Key Developments:
- Nov 2025: IFS and Siemens announced a strategic partnership to develop AI-driven “autonomous grid” solutions, combining IFS’s industrial AI (asset management & scheduling) with Siemens’ grid planning and infrastructure capabilities.
- Mar 2025: Schneider Electric launched its One Digital Grid Platform, a unified, AI-powered software suite for grid planning, operations, asset management, and DER integration.
- Mar 2025: At DISTRIBUTECH 2025, Siemens demonstrated enhancements in its Gridscale X digital grid platform, including real-time analytics, digital twins, predictive maintenance, and AI-driven tools for DER management.
- October 2024: Schneider Electric Introduces New Smart Grid Solutions at Enlit Europe 2024 to Manage Net-Zero Demands and Enhance Grid Flexibility and Resilience. At Enlit 2024, Schneider Electric, a pioneer in the digital revolution of energy automation and management, will unveil its most recent developments.
List of Top Smart Grid Companies:
- Schneider Electric SE
- Duke Energy Corporation
- General Electric Company
- Itron Inc.
- Siemens AG
Smart Grid Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Smart Grid Market Size in 2025 | USD 57.323 billion |
| Smart Grid Market Size in 2030 | USD 114.798 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 14.90% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in Smart Grid Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Smart Grid Market Segmentation:
- By Component
- Software
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure
- Smart Grid Distribution Management
- Smart Grid Network Management
- Grid Asset Management
- Substation Automation
- Smart Grid Security
- Others
- Hardware
- Sensors
- Programmable Logic Controller
- Smart Meter
- Networking Hardware
- Service
- Consulting
- Deployment and Integration
- Support and Maintenance
- Software
- By Geography
- North America
- USA
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Australia
- Others
- North America